一、前言
文件上传是一个比较常见的功能,传统的选择方式的上传比较麻烦,需要先点击上传按钮,然后再找到文件的路径,然后上传。给用户体验带来很大问题。html5开始支持拖拽上传的需要的api。nodejs也是一个最近越来越流行的技术,这也是自己第一次接触nodejs,在nodejs开发中,最常用的开发框架之一是expess,它是一个类似mvc模式的框架。结合html5、nodejs express实现了拖拽上传的功能。
二、基础知识普及
1、NodeJs基础知识
nodejs简单来说就是一个可以让js在服务端也能运行的开发平台,nodejs发展非常很快,很多国内公司也已经开始使用比如淘宝等。传统的web应用程序开发平台依靠多线程来实现高并发请求的响应。而nodejs采用了单线程、异步式IO、事件驱动的设计模型,给nodejs带来了巨大的性能提升。这也是nodejs最大的特点,在nodejs中,所有的IO操作都是通过回调的方式进行,nodejs在执行IO操作时会把IO请求推送一个事件队列,等待程序进行处理,等处理完IO,然后调用回调函数返回结果。
比如在查询数据库操作如下:
mysql.query("SELECT * FROM myTable",function(res){
callback(res);
});
在以上代码中,nodejs在执行以上语句时,不会等待数据库返回结果,而是继续执行后面的语句。在数据库获取到数据后,会发送到事件循环队列中,等到线程进入事件循环队列后,才执行callback的东西。
关于nodejs更多的知识,我也知识看了两天,了解不多。了解更多的知识可以在网络上搜索。
nodejs入门的知识 http://www.nodebeginner.org/index-zh-cn.html http://blog.jobbole.com/17174/
2、express基础知识
nodejs是一个比较活跃的开源社区,它拥有大量的第三方开发库,其中Express是其中最广泛的、最常用的框架之一。也是nodejs官方推荐的框架。它除了对常见http操作的封装,还实现了路由控制、模版解析支持、动态试图、用户回话等等。但它也不是一个万能的框架,绝大多数功能是对http的封装,它只是一个轻量级的框架。很多功能还需要集成第三方库还实现。
exress提供了非常方便的上传功能的支持,在文件上传请求以后,express会接收文件并把文件存在一个临时目录,然后在路由到的方法中,我们只需把文件从临时目录下拷贝到我们要存放用户上传文件夹即可。在文件上传部分,服务器端的实现就是基于express这个功能来实现的。
3、html5拖曳上传api
html5提供很多新的特性,拖拽事件以及文件上传就是新特性之一。由于篇幅有限,后面重点介绍拖曳上传的代码实现。就不一一列出html5提供的拖曳上传的apil了,感兴趣的可以参考:http://w3school.com.cn/html5/html5_ref_eventattributes.asp#Mouse_Events http://wen866595.iteye.com/blog/1898236
三、拖曳上传实现
1、代码实现
先来看下前端js的文件目录:
其中:
uploader.js主要实现对html5支持的上传功能的封装。
uploaderQueue.js主要实现上传文件队列的管理,以及文件上传对象,把文件队列中的文件上传到服务器。
uploaderApp.js主要文件上传的入口,主要实现上传窗口对拖曳事件的监听并把拖曳文件推进上传文件队列,启动文件上传程序。
下面对核心代码(需要)做简单的解释,全都代码可以到这里下载:FileUploader
首先对html5提供的文件上传做简单的封装uploader.js

function uploader(url, data, files) { this._files = files; this._data = data; this._url = url; this._xhr = null; this.onloadstart = {}; this.onload = {}; this.onloadend = {}; this.onprogress = {}; this.onerror = {}; this.ontimeout = {}; this.callback = {};//请求完成后回调 _self = this; } uploader.prototype = { init: function () { if (!isValid()) { throw e; } this._xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); this._bindEvents(); }, send: function () { if (this._xhr == null) { this.init(); } var formData = this._createFormData(); this._xhr.open('post', this._url, true); this._xhr.send(formData); }, _bindEvents: function () { _self = this; this._xhr.upload.loadstart = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.onloadstart, e); } this._xhr.upload.onload = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.onload, e); }; this._xhr.upload.onloadend = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.onloadend, e); } this._xhr.upload.onprogress = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.onprogress, e) }; this._xhr.upload.onerror = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.onerror, e); }; this._xhr.upload.ontimeout = function (e) { evalFunction(_self.ontimeout, e); } this._xhr.onreadystatechange = function () { if (_self._xhr.readyState == 4) { if (typeof _self.callback === 'function') { var status = _self._xhr.status; var data = _self._xhr.responseText; _self.callback(status, data); } } } }, _createFormData: function () { var formData = new FormData(); this._addDataToFormData(formData); this._addFileToFormData(formData); return formData; }, _addDataToFormData: function (formData) { if (this._data) { for (var item in this._data) { formData.append(item, this._data[item]); } } }, _addFileToFormData: function (formData) { if (this._files) { for (var i = 0; i < this._files.length; i++) { var file = this._files[i]; formData.append('file[' + i + ']', this._files[i]); } } } };
var uploaderFactory = { send: function (url, data, files, callback) { var insUploader = new uploader(url, data, files); insUploader.callback = function (status, resData) { if (typeof callback === 'function') { callback(status, resData); } } insUploader.send(); return insUploader; } };
uploader对象主要是对html5提供的原生api进行简单的封装。uploaderFactory提供一个简单的接口,使用它可以像jquery的ajax方法一样完成,文件上传调用。html5中提供的文件上传的支持,是在原来XMLHttpRequest基础之上扩展一些属性和方法,提供了FormData对象,来支持文件上传操作。
文件上传队列(uploaderQueue.js)也是一个比较重要的对象,它包括两个对象一个是Queue,文件队列对象,主要负责管理文件队列的增删改查询等操作,另一个对象是UploadEngine,文件上传引擎,它的功能主要是负责从文件队列中取出文件对象,调用uploader对象上传文件,然后更新文件队列中的文件状态。Queue以及UploadEngine都是单例对象。
首先来看下文件队列对象:

(function (upladerQueue) { var Status = { Ready: 0, Uploading: 1, Complete: 2 } var _self = null; var instance = null; function Queue() { this._datas = []; this._curSize = 0;//当前长度 _self = this; } Queue.prototype = { add: function (data) { var key = new Date().getTime(); this._datas.push({key: key, data: data, status: Status.Ready}); this._curSize = this._datas.length; return key; }, remove: function (key) { var index = this._getIndexByKey(key); this._datas.splice(index, 1); this._curSize = this._datas.length; }, get: function (key) { var index = this._getIndexByKey(key); return index != -1 ? this._datas[index].data : null; }, clear: function () { this._datas = []; this._curSize = this._datas.length; }, size: function () { return this._curSize; }, setItemStatus: function (key, status) { var index = this._getIndexByKey(key); if (index != -1) { this._datas[index].status = status; } }, nextReadyingIndex: function () { for (var i = 0; i < this._datas.length; i++) { if (this._datas[i].status == Status.Ready) { return i; } } return -1; }, getDataByIndex: function (index) { if (index < 0) { return null; } return this._datas[index]; }, _getIndexByKey: function (key) { for (var i = 0; i < this._datas.length; i++) { if (this._datas[i].key == key) { return i; } } return -1; } }; function getInstace() { if (instance === null) { instance = new Queue(); return instance; } else { return instance; } } upladerQueue.Queue = getInstace(); upladerQueue.UploadStatus = Status; })(window.uploaderQueue);
上传文件队列使用一个数组管理每个文件对象信息,每个文件对象有key,data,status三个属性,该对象主要负责文件对象的增加、删除、更新、查找的功能。
上传文件队列中另一个比较重要的对象是上传引擎对象(uploadEngine.js)

(function (upladerQueue) { var instance = null; var _self; function uploadEngine() { this._url = null; this._curUploadingKey = -1;//标志 this.uploadStatusChanged = {}; this.uploadItemProgress={}; _self = this; } uploadEngine.prototype = { setUrl: function (url) { this._url = url; }, run: function () { if (this._curUploadingKey === -1 && this._url) { this._startUpload(); } }, _startUpload: function () { _self = this; var index = upladerQueue.Queue.nextReadyingIndex(); if (index != -1) { this._uploadItem(index); } else { this._curUploadingKey = -1; return null; } }, _uploadItem: function (index) { var data = upladerQueue.Queue.getDataByIndex(index).data; _self = this; this._readyUploadItem(index); var upload = uploaderFactory.send(this._url, null, data.files, function (status, data) { _self._completedUploadItem.call(_self, status, data); }); this._uploadItemProgress(upload); }, _uploadItemProgress: function (upload) { upload.onprogress = function (e) { _self.uploadItemProgress(_self._curUploadingKey,e); } }, _readyUploadItem: function (index) { this._curUploadingKey = upladerQueue.Queue.getDataByIndex(index).key; if (typeof this.uploadStatusChanged === 'function') { this.uploadStatusChanged(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading); } upladerQueue.Queue.setItemStatus(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading); }, _completedUploadItem: function (status, data) { if (typeof this.uploadStatusChanged === 'function') { this.uploadStatusChanged(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Complete); } upladerQueue.Queue.setItemStatus(this._curUploadingKey, upladerQueue.UploadStatus.Complete); this._startUpload(); } }; function getInstace() { if (instance === null) { instance = new uploadEngine(); } return instance; } upladerQueue.Engine = getInstace(); })(window.uploaderQueue);
该对象比较简单主要提供一个run以及setUrl方法,用于启动上传引擎,以及设置上传路径的功能。内部使用递归的方法把文件队列中的方法全部上传到服务端。使用uploadItemProgress通知外部上传的进度,使用uploadStatusChanged通知文件上传状态,以便更新UI.
uploaderApp.js中主要包括三个对象,一个是类似jquery的一个简单的jquery对象(App$)。主要用于绑定事件。一个是uploaderArea对象,是拖曳上传的窗口区域,另一个是入口对象uploaderMain对象。主要用于初始化对象,对外部提供一个init方法,来初始化整个对象。
了解关于App$以及uploaderArea对象的代码请下载源代码,下面仅对uploaderMain对象做简单的说明。
(function (app) { var _self; function uploaderMain(id) { this._id = id; this._area = null; this.uploaders = []; this._URL = 'file/uploader'; } uploaderMain.prototype = { init: function () { _self = this; this._initArea(); this._initQueueEng(); }, _initQueueEng: function () { uploaderQueue.Engine.setUrl(this._URL); uploaderQueue.Engine.uploadStatusChanged = function (key, status) { if (status === uploaderQueue.UploadStatus.Uploading) { _self._area.hideItemCancel(key); } else if (status === uploaderQueue.UploadStatus.Complete) { _self._area.completeItem(key); _self._area.showItemCancel(key); } } uploaderQueue.Engine.uploadItemProgress = function (key, e) { var progress = e.position / e.total; _self._area.changeItemProgress(key, Math.round(progress * 100)); } }, _initArea: function () { this._area = new app.area(this._id); this._area.init(); this._area.drop = function (e) { var key = uploaderQueue.Queue.add({files: e.dataTransfer.files}); uploaderQueue.Engine.run(); return key; } this._area.cancelItem = function (key) { uploaderQueue.Queue.remove(key); } } }; app.main = uploaderMain; })(window.uploaderApp);
在uploaderMain对象,相当于各个对象之间的中介,主要就是做对象的初始化功能、以及对象之间相互调用。使各个对象之间相互协作完成整个模块的功能。对外提供一个init方法来初始化整个程序,在html页面中只需如下代码:
<script type="text/javascript">
var main=new uploaderApp.main('container');
main.init();
</script>
以上代码就是创建一个入口对象,然后使用init方法来启动整个程序。
以上是对前端js的主要方法做的简单解释,如果想详细了解请下载源代码。下面简单看下后端js(nodejs)端实现的主要代码。
在express基础知识时,已经讲过在express已经对文件上传功能做了完整的封装,当路由到action时,文件已经完成上传只是文件上传到了一个临时目录,这个临时目录我们可以在app.js中配置的,配置方式如下:
app.use(express.bodyParser({ uploadDir:__dirname+'/public/temp' }));
这样在文件上传后文件就存放在/public/temp目录下,文件名也是express通过一定的算法随机获取的。在我们写的action中只需要把存在临时目录中的文件移动到服务端存放文件的目录下,然后删除临时目录下的文件即可。具体代码如下:
function uploader(req, res) { if (req.files != 'undifined') { console.dir(req.files); utils.mkDir().then(function (path) { uploadFile(req, res, path, 0); }); } } function uploadFile(req, res, path, index) { var tempPath = req.files.file[index].path; var name = req.files.file[index].name; if (tempPath) { var rename = promise.denodeify(fs.rename); rename(tempPath, path + name).then(function () { var unlink = promise.denodeify(fs.unlink); unlink(tempPath); }).then(function () { if (index == req.files.file.length - 1) { var res = { code: 1, des: '上传成功' }; res.send(res); } else { uploadFile(req, res, path, index + 1); } }); } }
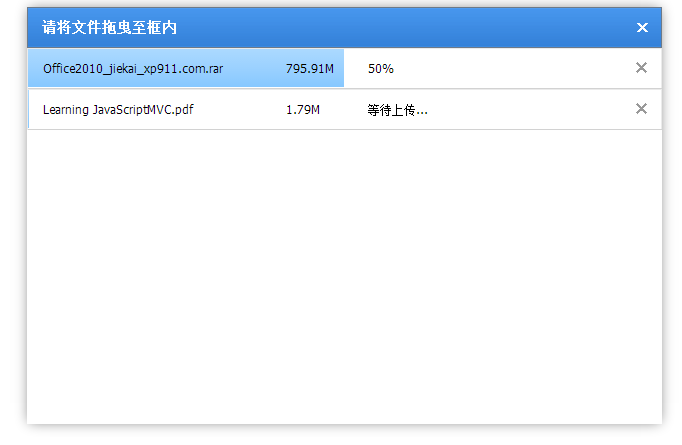
2、实现效果
四、获取代码
