排序是一项非常常用的操作,你的应用程序在运行时,可能无时无刻不在进行排序操作。排序的算法有很多,但是对于大部分的算法都是串行执行的。当排序的元素很多时,若使用并行算法代替串行,显然可以更加有效的利用CPU,提高排序效率。但将串行算法修改为并行算法并非易事,甚至会极大的增加原有算法的复杂度。下面介绍几种相对简单的算法。
奇偶交换排序:分离数据相关性
在介绍奇偶交换排序前,首先来看一下冒泡排序。在这里,我们将数组从小到大排序:
1 public static int[] bubbleSort(int[] arr){ 2 for (int i = 0;i < arr.length - 1;i++){ 3 for (int j = 0;j < arr.length - 1 - i;j++){ 4 if (j+1 == arr.length-i){ 5 break; 6 } 7 if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]){ 8 int temp = arr[j]; 9 arr[j] = arr[j+1]; 10 arr[j+1] = temp; 11 } 12 } 13 } 14 return arr; 15 }
在冒泡排序的交换过程中,由于每次交换的两个元素存在数据冲突,也就是对于每个元素,它既可能与前面的元素交换,也可能与后面的元素交换,因此很难直接改造成并行算法。如果能够解开这种数据的相关性,就可以比较容易的使用并行算法来实现类似的排序。奇偶交换排序就是基于这种思想的对于奇偶交换来说,它将排序过程分为两个阶段,奇交换和偶交换。对于奇交换来说,它总是比较奇数索引以及相邻的后续元素;偶交换总是比较偶数索引和其相邻的后续元素,并且奇交换和偶交换会成对出现,这样才能保证比较和交换涉及到数组中的每一个元素。
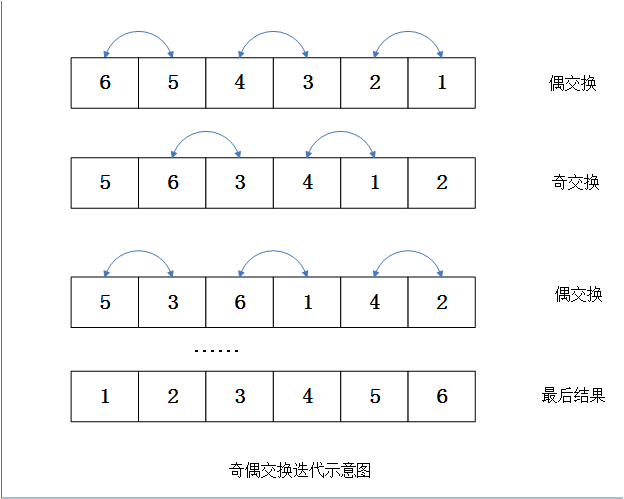
从上图可以看出,由于将整个比较交换独立分割为奇阶段和偶阶段。这就使得在每一个阶段内,所有的比较和交换都是没有数据相关性的。因此,每一次比较和交换都可以独立执行,也就可以并行化了。
下面是奇偶交换的串行实现:
1 public static int[] oddEvevSort(int[] arr){ 2 int exchFlag = 1,start = 0; 3 while (exchFlag == 1 || start == 1){ 4 exchFlag = 0; 5 for (int i = start;i < arr.length - 1;i += 2){ 6 if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]){ 7 int temp = arr[i]; 8 arr[i] = arr[i+1]; 9 arr[i+1] = temp; 10 exchFlag = 1; 11 } 12 } 13 if (start == 0){ 14 start = 1; 15 }else { 16 start = 0; 17 } 18 } 19 return arr; 20 }
上述代码中,exchFlag用来记录当前迭代是否发生了数据交换,而start变量用来表示是奇交换还是偶交换。初始时,start为0,表示进行偶交换,每次迭代结束后,切换start状态。如果上一次发生了数据交换,或者当前进行的是奇交换,循环就不会停止,直到程序不再发生交换,并且当前进行的是偶交换为止(表示奇偶交换已经成对出现)。
下面是奇偶交换的并行排序:
1 public class CurrentOddEven { 2 static int[] arr = {23,3,23,4,5,5,6,6,6453,678,68,9,9,79878,97,897897,98,78}; 3 static int exchFlag = 1; 4 static synchronized void setExchFlag(int v){ 5 exchFlag = v; 6 } 7 8 static synchronized int getExchFlag(){ 9 return exchFlag; 10 } 11 public static class OddEvenSortTask implements Runnable{ 12 int i; 13 CountDownLatch latch; 14 15 public OddEvenSortTask(int i,CountDownLatch latch){ 16 this.i = i; 17 this.latch = latch; 18 } 19 20 @Override 21 public void run() { 22 if (arr[i] > arr[i+1]){ 23 int temp = arr[i]; 24 arr[i] = arr[i+1]; 25 arr[i+1] = temp; 26 setExchFlag(1); 27 } 28 latch.countDown(); 29 } 30 } 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 33 int start = 0; 34 ExecutorService es = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 35 while (getExchFlag() == 1 || start == 1){ 36 setExchFlag(0); 37 //偶数的数组长度,当start=1时,只有length/2-1 个线程 38 CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(arr.length/2-(arr.length%2 == 0?start:0)); 39 for (int i = start;i < arr.length - 1;i += 2){ 40 es.submit(new OddEvenSortTask(i,latch)); 41 } 42 //等待所有线程结束 43 latch.await(); 44 if (start == 0){ 45 start = 1; 46 }else { 47 start = 0; 48 } 49 } 50 for (int temp:arr){ 51 System.out.println(temp); 52 } 53 es.shutdown(); 54 } 55 }
上述代码第11行,定义了奇偶排序的任务类。该任务的主要工作是进行数据的比较和交换(第22~26行)。并行排序的主体在main方法中,使用了countDownLatch来记录线程数量,对于每一次的迭代,使用单独的线程对每一次元素比较和交换操作,在下一次的迭代开始之前,必须等上一次的迭代必须完成。
希尔排序:改进的插入排序
插入排序也是一种很常见的排序算法。它的基本思想:一个未排序的数组(当然也可以是链表)可以分为两个部分,前半部分是已经排序的,后半部分是未排序的。在进行排序时,只需要在未排序的部分中选择一个元素,将其插入前面有序的数组中即可。最终,未排序的部分会越来越少,直到为0,那么排序就完成了。初始时,可以假设已排序部分就是第一个元素。
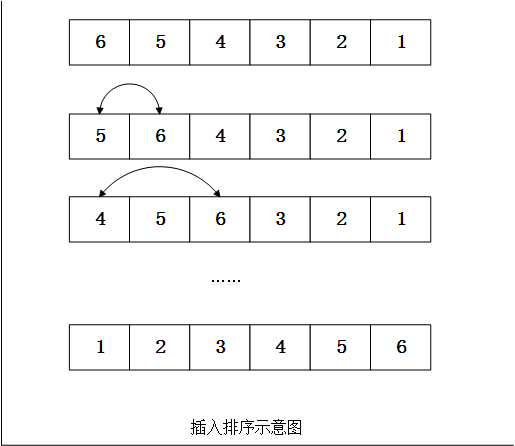
插入排序串行排序如下:
1 public static int[] insertSort(int[] arr){ 2 int length = arr.length; 3 int i,j,key; 4 for (i = 1;i < length;i++){ 5 //key为要准备插入的元素 6 key = arr[i]; 7 j = i - 1; 8 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key){ 9 arr[j+1] = arr[j]; 10 j--; 11 } 12 //找到合适的位置插入key 13 arr[j+1] = key; 14 } 15 return arr; 16 }
上述代码第6行,提取准备插入的元素(也就是未排序序列中的第一个元素)。接着,在已排序的序列中找到这个元素的插入位置(第8~10行),并进行插入(第13行)即可。
简单的插入排序是很难进行并行化的。因为这一次的数据插入依赖于上一次得到的有序序列,因此多个步骤之间无法并行。为此,我们可以对插入排序进行扩展,就是希尔排序。
希尔排序将整个数组根据间隔h分割为若干个数组。子数组相互穿插在一起,每一次排序时,分别对每一个子数组进行排序。如下图所示(借大神的图侵删):
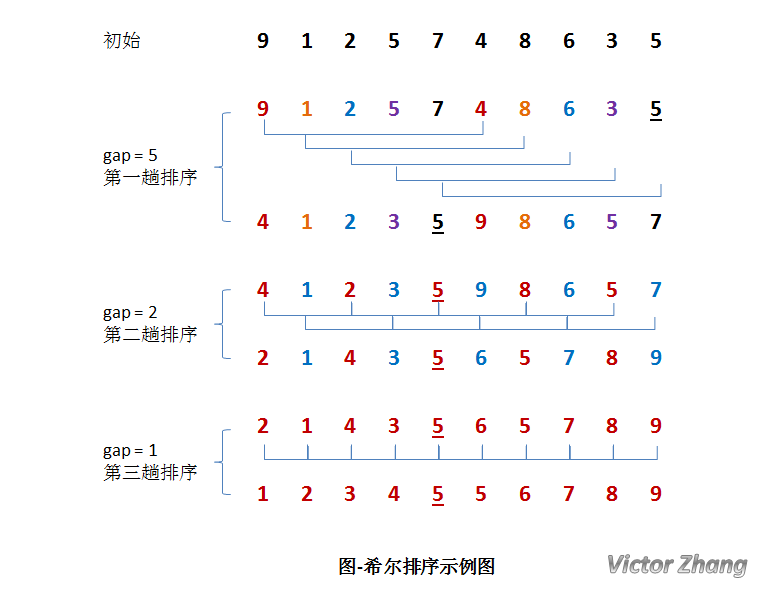
从上图可以看出,每一组排序完成后,可以递减h的值,进行下轮更精细的排序,知道h=1,此时,等价于一次插入排序。
希尔排序的一个主要优点是,即使最小的一个元素在数组的末尾,由于每次元素的移动都以h为间隔进行,因此数组末尾的小元素可以在很少的交换次数下,就被置换到最接近元素最终位置的地方。
下面是希尔排序的串行实现:
1 public static int[] shellSort(int[] arr){ 2 //计算出最大的h值 3 int h = 1; 4 while (h <= arr.length/3){ 5 h = h*3 + 1; 6 } 7 while (h > 0){ 8 for (int i = h;i < arr.length;i++){ 9 if (arr[i] < arr[i - h]){ 10 int temp = arr[i]; 11 int j = i - h; 12 while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > temp){ 13 arr[j + h] = arr[j]; 14 j -= h; 15 } 16 arr[j + h] = temp; 17 } 18 } 19 //计算出下一个h值 20 h = (h - 1)/3; 21 } 22 return arr; 23 }
上述代码的4~6行,计算出一个合适的h值,接着进行正式的希尔排序。第8行代码的for循环进行间隔为h的插入排序,每次排序结束后,递减h的值(第20行),直到h=1,退化为插入排序。
由于希尔排序每次都针对不同的子数组进行排序,各个子数组之间是完全独立的,因此,是可以改写为并行程序的:
1 public class CurrentShellSort { 2 static int[] a = {2,3,1,45,53,3,55,4,65,765,7,7,89687,6,89,69,4354,89,99}; 3 static ExecutorService pool = Executors.newCachedThreadPool(); 4 5 public static class ShellSortTask implements Runnable { 6 7 int x = 0; 8 int h = 0; 9 CountDownLatch l; 10 11 public ShellSortTask(int x, int h, CountDownLatch latch) { 12 this.x = x; 13 this.h = h; 14 this.l = latch; 15 } 16 17 public void run() { 18 int i, j, key; 19 for (i = x + h; i < a.length; i = i + h) { 20 if (a[i] < a[i - h]) { 21 j = i - h; 22 key = a[i]; 23 while (j >= 0 && a[j] > key) { 24 a[j + h] = a[j]; 25 j -= h; 26 } 27 a[j + h] = key; 28 } 29 } 30 l.countDown(); 31 } 32 } 33 34 public static void pShellSort(int[] arr) throws InterruptedException { 35 // 计算出最大的n值 36 int h = 1; 37 CountDownLatch lathc = null; 38 while (h <= arr.length / 3) { 39 h = h * 3 + 1; 40 } 41 while (h > 0) { 42 System.out.println("h=" + h); 43 lathc = new CountDownLatch(h); 44 for (int x = 0; x < h; x++) { 45 pool.submit(new ShellSortTask(x, h, lathc)); 46 } 47 lathc.await(); 48 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); 49 // 计算下一个h值 50 h = (h - 1) / 3; 51 } 52 pool.shutdown(); 53 } 54 //测试 55 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 56 pShellSort(a); 57 } 58 }
输出结果:
h=13 [2, 3, 1, 45, 53, 3, 55, 4, 65, 765, 7, 7, 89687, 6, 89, 69, 4354, 89, 99] h=4 [2, 3, 1, 4, 53, 3, 7, 7, 65, 6, 55, 45, 4354, 89, 89, 69, 89687, 765, 99] h=1 [1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 6, 7, 7, 45, 53, 55, 65, 69, 89, 89, 99, 765, 4354, 89687]
参考:《Java高并发程序设计》 葛一鸣 郭超 编著: