Spring容器是生成Bean的工厂,我们在做项目的时候,会用到监听器去获取spring的配置文件,然后从中拿出我们需要的bean出来,比如做网站首页,假设商品的后台业务逻辑都做好了,我们需要创建一个监听器,在项目启动时将首页的数据查询出来放到application里,即在监听器里调用后台商品业务逻辑的方法,也就是说我们需要在监听器里获取Spring中配置的相应的bean。先把监听器创建出来:
1. 创建InitDataListener
创建一个监听器InitDataListener继承ServletContextListener:
1 //@Component //监听器是web层的组件,它是tomcat实例化的,不是Spring实例化的。不能放到Spring中 2 public class InitDataListener implements ServletContextListener { 3 4 private ProductService productService = null;//productService中定义了跟商品相关的业务逻辑 5 6 @Override 7 public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) { 8 9 } 10 11 @Override 12 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { 13 14 } 15 16 }
并在web.xml中配置该监听器:
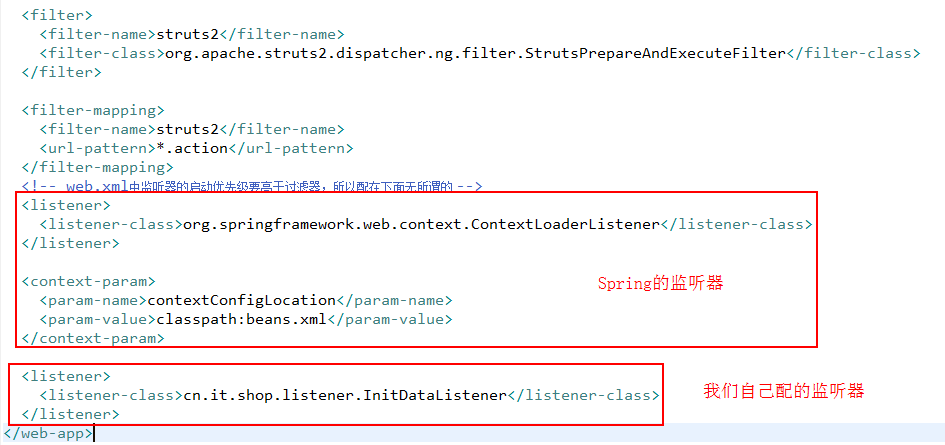
如上,productService中定义了商品的一些业务逻辑,并且这个productService是交给Spring管理的,那么我们如何得到这个对象呢?首先肯定的一点是:我们不能自己new出来,因为new出来的话就跟Spring的IoC没有关系了……主要有三种方式可以实现,我们先一个个分析,最后比较优劣。
2. 直接加载beans.xml文件
这种方式比较简单粗暴,不是要加载配置文件么?那好,我加载就是了,如下:
1 //@Component //监听器是web层的组件,它是tomcat实例化的,不是Spring实例化的。不能放到Spring中 2 public class InitDataListener implements ServletContextListener { 3 4 5 private ProductService productService = null; //productService中定义了跟商品相关的业务逻辑 6 7 @Override 8 public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) { 9 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { 14 // 获取业务逻辑类productService查询商品信息 15 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); 16 productService = (ProductService) context.getBean("productService"); 17 System.out.println(productService); //输出看看拿到了没有 18 19 //下面是具体productService相关操作…… 20 } 21 22 }
这种方法完全没问题,思路很清晰,先加载配置文件beans.xml,然后获取bean,但是启动tomcat后,我们看看控制台输出的信息:
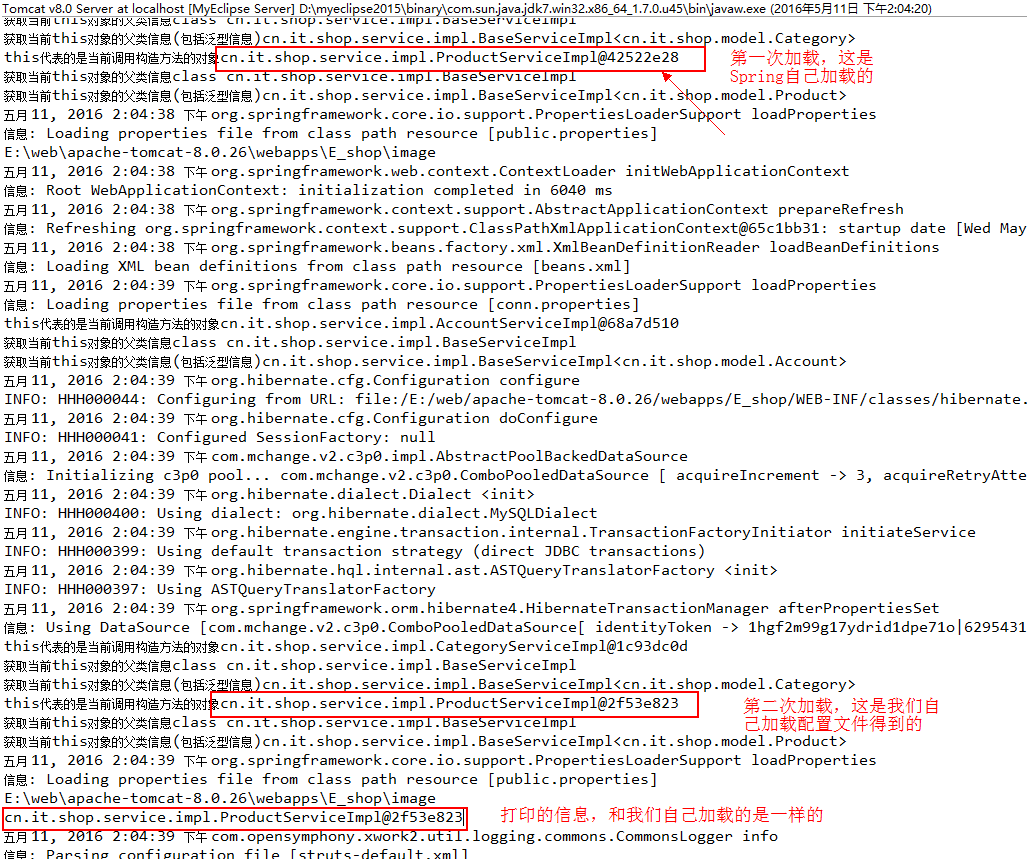
到这里应该发现这种方式的弊端了,加载了两次配置文件,也就是说那些bean被实例化了两次,从打印的信息来看,是拿到我们自己加载配置文件是实例化的bean。这种方式明显不可取。
3. 从ServletContext中获取
从上面的方法中,我们最起码可以知道,Spring通过自己的监听器已经加载过一次配置文件了,我们没必要再加载一次,那么很容易想到,如果知道Spring加载后放到哪里了,那我们就可以从那地方获取该配置文件,下面我们看下Spring加载配置文件的过程:
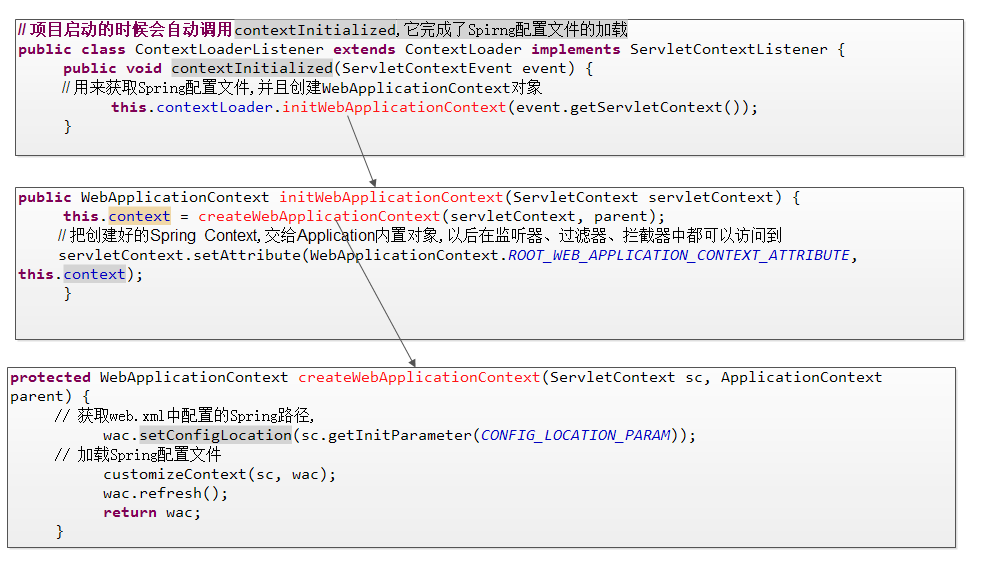
上图中(省略了无关的代码),ContextLoaderListener就是web.xml中我们配置的Spring监听器,它也实现了ServletContextListener并继承了ContextLoader。在监听器中主要通过initWebApplicationContext方法来获取配置文件,并创建WebApplicationContext对象,在initWebApplicationContext方法里主要做两件事:一是拿到Spring的上下文,二是把Spring上下文放到ServletContext中,并且键为:WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE。那么如何拿到Spring的上下文呢?是通过获取web.xml中配置的Spring的路径,CONFIG_LOCATION_PARM其实是个字符串常量,就是上面web.xml中配置Spring监听器下面的:
<context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <!--CONFIG_LOCATION_PARM就是contextConfigLocation--> <param-value>classpath:beans.xml</param-value> </context-param>
所以就很明显了,通过web.xml中配置的路径拿到beans.xml,然后加载这个配置文件,实例化bean。
现在我们既然知道了Spring在加载配置文件后,把它放在了ServletContext中,那么我们就可以去这里面直接拿!
1 //@Component //监听器是web层的组件,它是tomcat实例化的,不是Spring实例化的。不能放到Spring中 2 public class InitDataListener implements ServletContextListener { 3 4 5 private ProductService productService = null; 6 7 @Override 8 public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) { 9 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 10 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { 15 // 获取业务逻辑类查询商品信息 16 17 // 解决方案二,项目在启动时,把Spring配置文件通过Spring的监听器加载,存储到ServletContext中,我们只要在ServletContext中获取即可。 18 ApplicationContext context = (ApplicationContext) event.getServletContext() 19 .getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE); 20 productService = (ProductService) context.getBean("productService"); 21 System.out.println(productService); 22 } 23 24 }
这样我们就可以拿到produceService的实例化对象了,这种方法好是好,就是getAttribute中的参数太长,也不知道当时程序员的脑门子被夹了还是咋地,估计是想不到其他更合适的名字了吧~
4. 通过Spring提供的工具类加载
也许开发Spring的大牛们也意识到了这个参数名字太长了,于是他们提供了一个方法类,可以加载配置文件:
1 public class InitDataListener implements ServletContextListener { 2 3 4 private ProductService productService = null; 5 6 @Override 7 public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent event) { 8 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 9 10 } 11 12 @Override 13 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { 14 // 获取业务逻辑类查询商品信息 15 16 WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); 17 productService = (ProductService) context.getBean("productService"); 18 System.out.println(productService); 19 } 20 21 }
其实,这里的getWebApplicationContext方法就是把上面的那个方法封装了一下而已,我们看看这个方法的源码就知道了:
public static WebApplicationContext getWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc) {
return getWebApplicationContext(sc, WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
这样更加方便程序员调用,仅此而已……所以一般我们使用第三种方法来获取Spring的配置文件,从而获取相应的实例化bean。
参考文章:http://blog.csdn.net/eson_15/article/details/51373937
----更多文章请看:http://blog.csdn.net/eson_15
代码实践:
Spring整合web项目时的问题:
启动服务器之后:
访问action时,每次访问都会重新加载spring配置文件,效率低下
解决方法:在服务器启动的时候,利用监听器只加载一次spring配置文件即可。
在spring里边不需要自己写代码实现,框架已经做好了封装
只需要配置即可:但是配置监听器时,需要导入一个spring整合web项目的jar包
创建一个web项目,要求每次访问action都无需加载新的xml文件,利用框架的监听器实现只在服务器启动时加载一次xml配置,用于提高性能
开发准备,导入struts相关jar和spring框架IOC相关jar以及spring整合web项目的jar包
第一种自己完成监听器的代码(不推荐,纯属娱乐)
1 package org.lister; 2 3 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 4 import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; 5 import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; 6 7 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 8 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 9 10 public class Lis implements ServletContextListener { 11 12 public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent arg0) { 13 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 14 15 } 16 public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent arg0) { 17 // TODO Auto-generated method stub 18 //服务器启动的时候创建ApplicationContext对象 19 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 20 21 //得到ServletContext对象 22 ServletContext sc=arg0.getServletContext(); 23 24 //保存创建的ApplicationContext对象,在action中调用 25 sc.setAttribute("applicationcontext",ac); 26 } 27 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app version="2.5" 3 xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee 6 http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> 7 <welcome-file-list> 8 <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> 9 </welcome-file-list> 10 11 <!-- struts过滤器配置 --> 12 <filter> 13 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 14 <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> 15 <init-param> 16 <param-name>actionPackages</param-name> 17 <param-value>com.mycompany.myapp.actions</param-value> 18 </init-param> 19 </filter> 20 21 <filter-mapping> 22 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 23 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 24 </filter-mapping> 25 26 <!-- 自己的监听器配置 --> 27 <listener> 28 <listener-class>org.lister.Lis</listener-class> 29 </listener> 30 31 </web-app>
1 package org.model; 2 3 public class User { 4 public void add(){ 5 System.out.println("add。。。。。。。。。。。。"); 6 } 7 }
1 package org.action; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 5 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 6 import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; 7 import org.model.User; 8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 9 10 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext; 11 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 12 13 public class UserAction extends ActionSupport { 14 15 @Override 16 public String execute() throws Exception { 17 System.out.println("进入action"); 18 // ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 19 // User user=(User)ac.getBean("user"); 20 // user.add(); 21 22 //得到ServletContext(上下文对象,即application对象)对象 并且得到里边保存的applicationContext对象; 23 ServletContext servletContext = ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); 24 ApplicationContext ac=(ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("applicationcontext"); 25 if(ac!=null){ 26 User u=(User) ac.getBean("user"); 27 u.add(); 28 } 29 30 /* 31 //以下代码也能实现 32 ActionContext actioncontext=ActionContext.getContext(); 33 Map application=actioncontext.getApplication(); 34 ApplicationContext ac2=(ApplicationContext) application.get("applicationcontext"); 35 if(ac2!=null){ 36 User u2=(User) ac2.getBean("user"); 37 u2.add(); 38 } 39 */ 40 return NONE; 41 } 42 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 4 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 5 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation=" 6 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> 7 <bean id="user" class="org.model.User"></bean> 8 </beans>
在上边的程序中没有配置spring框架的监听器,只配置了自己定义的,所以也实现了题目要求的功能:

服务器启动的时候加载了配置文件:
然后访问action截图如下:

即使反复请求,只会输出以上两句,控制台并没有打印其他内容,说明xml文件只加载了一次。
第二种:使用框架提供的监听机制,我们只需要配置即可,不多说 直接上代码
1 package org.dao; 2 3 public class UserDao { 4 public void add(){ 5 System.out.println("UserDao........."); 6 } 7 }
1 package org.service; 2 3 import org.dao.UserDao; 4 5 public class Service { 6 private UserDao userdao; 7 8 public void setUserdao(UserDao userdao) {//使用set注入 9 this.userdao = userdao; 10 } 11 12 public void add(){ 13 System.out.println("Service........."); 14 userdao.add(); 15 } 16 }
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <web-app version="2.5" 3 xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee 6 http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd"> 7 <welcome-file-list> 8 <welcome-file>index.jsp</welcome-file> 9 </welcome-file-list> 10 <filter> 11 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 12 <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> 13 <init-param> 14 <param-name>actionPackages</param-name> 15 <param-value>com.mycompany.myapp.actions</param-value> 16 </init-param> 17 </filter> 18 <filter-mapping> 19 <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> 20 <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> 21 </filter-mapping> 22 23 24 <!-- 使用框架提供的监听机制 需要配置下面代码 --> 25 <listener> 26 <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> 27 </listener> 28 29 <context-param> 30 <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> 31 <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> 32 </context-param> 33 </web-app>
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> 2 <beans 3 xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" 4 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" 5 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" 6 xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" 7 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans 8 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd 9 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop 10 http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd"> 11 <bean id="ud" class="org.dao.UserDao"></bean> 12 13 <bean id="us" class="org.service.Service"> 14 <property name="userdao" ref="ud"></property> 15 </bean> 16 17 </beans> 18
1 package org.action; 2 3 import java.util.Map; 4 5 import javax.servlet.ServletContext; 6 7 import org.apache.struts2.ServletActionContext; 8 import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; 9 import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; 10 import org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext; 11 import org.springframework.web.context.support.WebApplicationContextUtils; 12 13 import com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionSupport; 14 15 import org.service.*; 16 public class UserAction extends ActionSupport { 17 18 @Override 19 public String execute() throws Exception { 20 //ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); 21 22 //得到servletContext对象(上下文application对象) 23 ServletContext sc=ServletActionContext.getServletContext(); 24 25 //从上下文对象中取得在服务器启动时创建的ApplicationContext对象 26 //因为在服务器启动的时候就创建了一个applicationContext对象 并且保存在了ServletContext中(上下文application中), 27 //并且键为:WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE 28 ApplicationContext ac=(ApplicationContext)sc.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE); 29 if(ac!=null){ 30 Service s=(Service)ac.getBean("us"); 31 s.add(); 32 }else{ 33 System.out.println("没有取得ApplicationContext对象"); 34 } 35 /* 36 WebApplicationContext context = WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(ServletActionContext.getServletContext()); 37 if(ac!=null){ 38 Service s=(Service)context.getBean("us"); 39 s.add(); 40 }else{ 41 System.out.println("没有取得ApplicationContext对象"); 42 } 43 */ 44 return NONE;//不做任何的返回 45 } 46 }
启动服务器:

反复访问action:

效果和上面的一样,没有反复加载xml生成Spring容器
-------------------------------
欢迎大家转载,但请注明原创链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joke-Jay/p/6507171.html