第二节 操作系统是如何工作的
By 20135203齐岳
函数调用堆栈
计算机工作三个法宝
存储程序计算机、中断机制、堆栈
深入理解函数调用堆栈
堆栈是C语言程序运行时必须的一个记录调用路径和参数的空间
堆栈的作用
- 函数调用框架
- 传递参数
- 保存返回地址
- 提供局部变量空间
堆栈相关的寄存器
- esp,堆栈指针,指向栈顶
- ebp,基址指针,指向栈底,在C语言中用作记录当前函数调用基址。
其他关键寄存器
cs(代码段寄存器) : eip:总是指向下一条的指令地址
- 顺序执行:总是指向地址连续的下一条指令
- 跳转/分支:执行这样的指令的时候, cs : eip的值会根据程序需要被修改
参数传递与局部变量
-
建立框架(相当于 call 指令)
push %ebp movl %esp,%ebp -
拆除框架(相当于 ret 指令)
movl %ebp,%esp pop %ebp
函数返回时一定会拆除框架,建立和拆除是一一对应的。
- 传递参数
在建立子函数的框架之前,局部变量的值保存在调用者堆栈框架中,所以在子函数框架建立之前可以采用变址寻址的方式将变量值入栈。
函数的返回值通过eax寄存器传递
借助Linux内核部分源代码模拟存储程序计算机工作模型及时钟中断
mykernel实验思想
中断实现了多道程序设计,再各个程序的执行流之间来回切换,CPU将程序的ebp压入栈,并指向一个中断处理程序,从而由CPU和内核代码共同实现了保存现场和恢复现场
C代码中嵌入汇编代码的写法
__asm__(
汇编语句模板:
输入部分:
输出部分:
破坏描述部分:);
实验——在mykernel基础上构造一个简单的操作系统内核
实验过程
本次实验是通过分析一个简单的时间片轮转多道程序内核源代码来理解操作系统的工作原理。
首先运行此内核,可以看到提供可一个代码在内核中运行的上下文环境。

然后cd mykernel 找到mymain.c和myinterrupt.c两个源代码,进入https://github.com/mengning/mykernel/blob/master可以找到本次实验需要的几个重要的源代码。然后将上面两个代码修改成网站中找到的代码,除此之外还要加上mypcb.h。
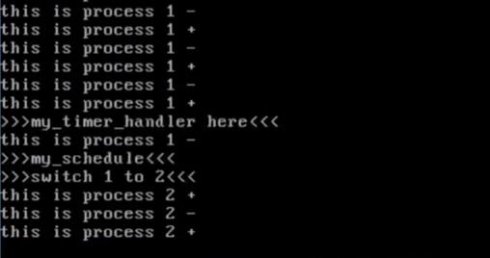
返回之后再次运行,可看到0、1、2、3几个进程相互切换。
源代码分析
mypcb.h
这个代码的目的是定义一个进程控制块(PCB)。
/*
* linux/mykernel/mypcb.h
*
* Kernel internal PCB types
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#define MAX_TASK_NUM 4
#define KERNEL_STACK_SIZE 1024*8
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread {
unsigned long ip;//用于eip的保存
unsigned long sp;//用于esp的保存
};
typedef struct PCB{//用于表示一个进程,定义了进程管理相关的数据结构
int pid;
volatile long state; /* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
char stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE];
/* CPU-specific state of this task */
struct Thread thread;
unsigned long task_entry;
struct PCB *next;
}tPCB;
void my_schedule(void);//调用了my_schedule,表示调度器
mymain.c
/*
* linux/mykernel/mymain.c
*
* Kernel internal my_start_kernel
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
tPCB * my_current_task = NULL;
volatile int my_need_sched = 0;//定义一个标志,用来判断是否需要调度
void my_process(void);
void __init my_start_kernel(void)
{
int pid = 0;//初始化一个进程0
int i;
/* Initialize process 0*/
task[pid].pid = pid;
task[pid].state = 0;/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
task[pid].task_entry = task[pid].thread.ip = (unsigned long)my_process;
//定义进程0的入口为my_process
task[pid].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[pid].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
task[pid].next = &task[pid];
//因为一开始系统里只有进程0,所以这一行代码表示的是pid的next还是指向自己
/*fork more process */
//创建更多其他的进程,在初始化这些进程的时候可以直接拷贝0号进程的代码
for(i=1;i<MAX_TASK_NUM;i++)
{
memcpy(&task[i],&task[0],sizeof(tPCB));
task[i].pid = i;
task[i].state = -1;
task[i].thread.sp = (unsigned long)&task[i].stack[KERNEL_STACK_SIZE-1];
//每个进程都有自己的堆栈,把创建好的新进程放到进程列表的尾部,这样就完成了创建
task[i].next = task[i-1].next;
task[i-1].next = &task[i];
}
/* start process 0 by task[0] */
pid = 0;
my_current_task = &task[pid];
asm volatile(
"movl %1,%%esp
" /* set task[pid].thread.sp to esp */
"pushl %1
" /* push ebp */
"pushl %0
" /* push task[pid].thread.ip */
"ret
" /* pop task[pid].thread.ip to eip */
"popl %%ebp
"
:
: "c" (task[pid].thread.ip),"d" (task[pid].thread.sp)
/* input c or d mean %ecx/%edx*/
);
}
/* %0表示参数thread.ip,%1表示参数thread.sp。
movl %1,%%esp表示把参数thread.sp放到esp中;
接下来push %1,又因为当前栈为空,esp=ebp,所以等价于push ebp;
然后push thread.ip;ret等价于pop thread.ip;最后pop ebp */
void my_process(void)//定义所有进程的工作,if语句表示循环1000万次才有机会判断是否需要调度。
{
int i = 0;
while(1)
{
i++;
if(i%10000000 == 0)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d -
",my_current_task->pid);
if(my_need_sched == 1)
{
my_need_sched = 0;
my_schedule();
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE "this is process %d +
",my_current_task->pid);
}
}
}
myinterrupt.c
/*
* linux/mykernel/myinterrupt.c
*
* Kernel internal my_timer_handler
*
* Copyright (C) 2013 Mengning
*
*/
#include <linux/types.h>
#include <linux/string.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/tty.h>
#include <linux/vmalloc.h>
#include "mypcb.h"
extern tPCB task[MAX_TASK_NUM];
extern tPCB * my_current_task;
extern volatile int my_need_sched;
volatile int time_count = 0;
/*
* Called by timer interrupt.
* it runs in the name of current running process,
* so it use kernel stack of current running process
*/
void my_timer_handler(void)
/* 用于设置时间片的大小,时间片用完时设置调度标志。
当时钟中断发生1000次,并且my_need_sched!=1时,把my_need_sched赋为1。
当进程发现my_need_sched=1时,就会执行my_schedule。 */
{
#if 1
if(time_count%1000 == 0 && my_need_sched != 1)
{
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_timer_handler here<<<
");
my_need_sched = 1;
}
time_count ++ ;
#endif
return;
}
void my_schedule(void)
{
tPCB * next;
tPCB * prev;
if(my_current_task == NULL //task为空,即发生错误时返回
|| my_current_task->next == NULL)
{
return;
}
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>my_schedule<<<
");
/* schedule */
next = my_current_task->next;//把当前进程的下一个进程赋给next
prev = my_current_task;//当前进程为prev
if(next->state == 0)/* -1 unrunnable, 0 runnable, >0 stopped */
{
/* switch to next process */
/*如果下一个进程的状态是正在执行的话,就运用if语句中的代码表示的方法来切换进程*/
asm volatile(
"pushl %%ebp
" /* save ebp 保存当前进程的ebp*/
"movl %%esp,%0
" /* save esp 保存当前进程的esp*/
"movl %2,%%esp
" /* restore esp 把下一个进程的sp放到esp中*/
"movl $1f,%1
" /* save eip 保存eip*/
"pushl %3
"
"ret
" /* restore eip */
"1: " /* next process start here */
"popl %%ebp
"
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<
",prev->pid,next->pid);
}
else
/* 与上一段代码不同的是如果下一个进程为新进程时,就运用else中的这一段代码。
首先将这个进程置为运行时状态,将这个进程作为当前正在执行的进程。 */
{
next->state = 0;
my_current_task = next;
printk(KERN_NOTICE ">>>switch %d to %d<<<
",prev->pid,next->pid);
/* switch to new process */
asm volatile(
"pushl %%ebp
" /* save ebp */
"movl %%esp,%0
" /* save esp */
"movl %2,%%esp
" /* restore esp */
"movl %2,%%ebp
" /* restore ebp */
"movl $1f,%1
" /* save eip */
"pushl %3
"
"ret
" /* restore eip */
: "=m" (prev->thread.sp),"=m" (prev->thread.ip)
: "m" (next->thread.sp),"m" (next->thread.ip)
);
}
return;
}
参考资料
【原创作品转载请注明出处】 《Linux内核分析》MOOC课程http://mooc.study.163.com/course/USTC-1000029000