在使用EF的过程中,导航属性的lazy load机制,能够减少对数据库的不必要的访问。只有当你使用到导航属性的时候,才会访问数据库。但是这个只是对于单个实体而言,而不适用于显示列表数据的情况。
这篇文章介绍的是,使用Lazy<T>来提高显示列表页面的效率。
这里是相关的源代码 PerformanceTest.zip
阅读目录:
一、问题的描述
二、数据表和EF实体介绍
三、lazy load的性能
四、使用StudentExtensionRepository来提高效率
五、进一步改进,使用StudentExtensionRepository1来实现按需访问数据库
六、总结
一,问题的描述
在使用EF的过程中,导航属性的lazy load机制,能够减少对数据库的不必要的访问。只有当你使用到导航属性的时候,才会访问数据库。
比如有个学生Student实体,只有当我访问Student的StudentScore(成绩实体)导航属性的时候,才会去访问StudentScore表。
问题是导航属性只是解决了单个实体访问导航属性时候的性能问题,而在实际开发过程中,常常遇到的问题是,我要显示一个列表的Student的信息,并且每个Student都要获取StudentScore信息,怎么办?
也许有人会说,可以使用EF的eager loading, 在读出Student信息的时候,把StudentScore一起读取出来就可以了。
是的,就像下面这样就能解决当前的问题,但是会面临不够通用,无法应对变化的情况。
var students = context.Students .Include(b => b.StudentScore) .ToList();
如果遇到需求,不需要StudentScore信息的时候,我们就又要改回lazy load的方式.
如果遇到需求,需要显示Student另外一个关联属性StudentHealthy信息的时候,又必须让StudentScore用Lazy load方式,而StudentHealthy采用eager loading
下面就介绍如何使用Lazy<T>来解决这个兼顾代码设计和性能的问题.
二, 数据表和EF实体介绍
如下图所示,一共用到3张表:
Student: 学生信息表
StudentScores:学生成绩表
StudentHealthies: 学生健康状况表
3张表设计的是1对1关系,现实开发中当然会比这个复杂的多,但是这个对于描述我们的问题已经足够了。
EF中对应于着3张表的Model代码:
[Table("Student")] public class Student { [Key] public int Id { get; set; } public string Name { get; set; } public int Age { get; set; } public virtual StudentScore Score { get; set; } public virtual StudentHealthy Healthy { get; set; } } public class StudentScore { public int Score { get; set; } public int StudentId { get; set; } [ForeignKey("StudentId")] public virtual Student Student { get; set; } } public class StudentHealthy { public int Score{ get; set; } public int StudentId { get; set; } [ForeignKey("StudentId")] public virtual Student Student { get; set; } }
三, lazy load的性能
下图中的页面,读取Student的列表,同时访问Student的导航属性Score来获取成绩信息。
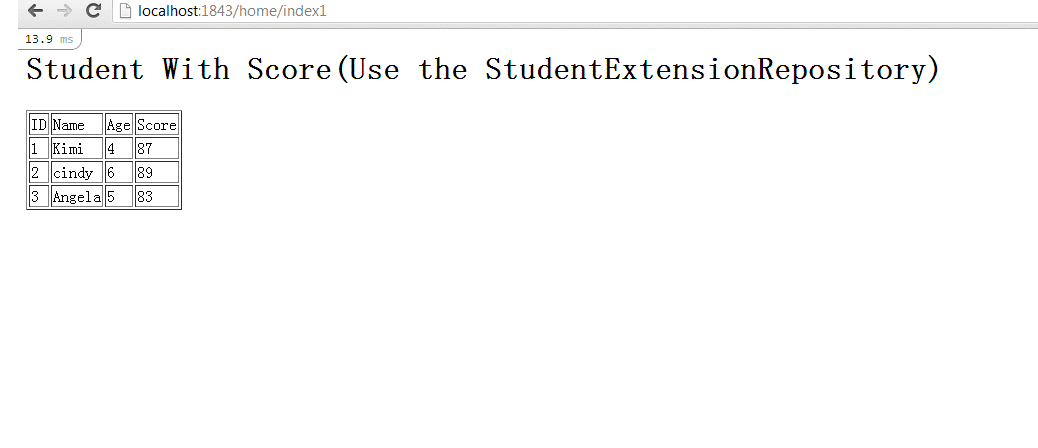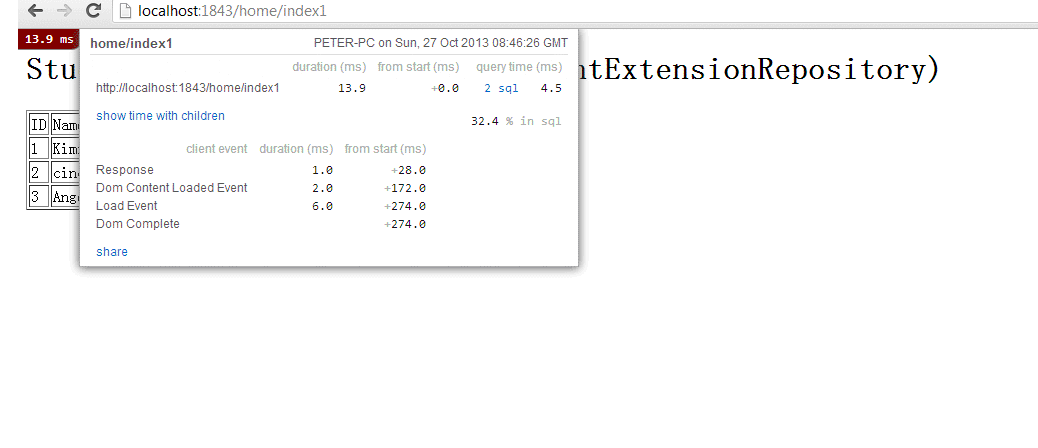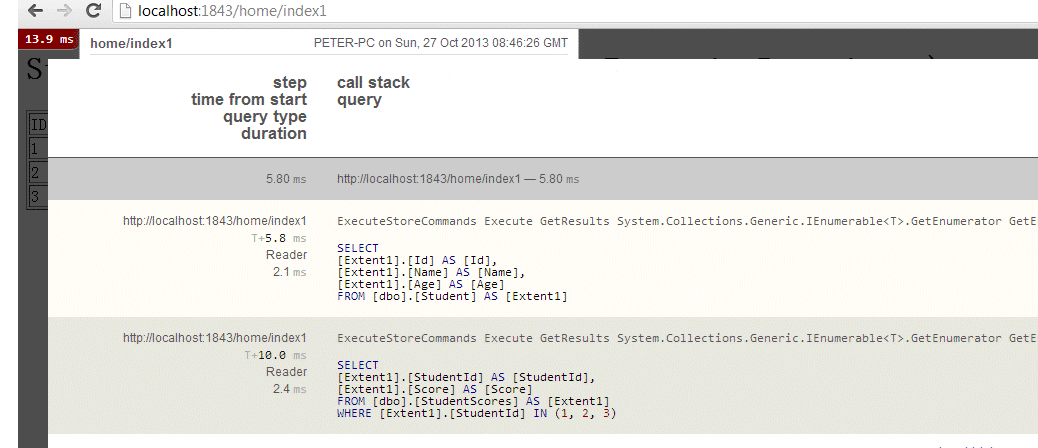
从MiniProfiler能看到,页面一共执行了4个Sql, 其中第一个Sql是从Student表中取出了3条数据,
其余的3个sql是每个Student访问导航属性而导致的数据库访问.
这里由于Student表中只有3条数据,如果有100条的话,就会导致1+100*3次数据访问,所以这种使用导航属性来获取数据的方式是不适合这种列表数据显示的
这里是页面View的代码:
@model IEnumerable<Student> <h1>Student With Score(Lazy Load)</h1> <table border="1"> <tr><td>ID</td><td>Name</td><td>Age</td><td>Score</td></tr> @foreach(var student in Model) { <tr> <td>@student.Id</td> <td>@student.Name</td> <td>@student.Age</td> <td>@student.Score.Score</td> </tr> } </table>
四, 使用StudentExtensionRepository来提高效率
StudentExtensionRepository解决效率问题的思路是,如果你取出3个student信息的话,它会同时把StudentScore信息取出来。
先来看看StudentExtension的定义
public class StudentExtension { public Student Student { get; set; } public StudentScore StudentScore { get; set; } }
上面的StudentExtension用来保存Student信息,以及和该Student相关的StudentScore数据。
下面是StudentExtensionRepository.cs的具体内容,GetStudents方法中,先取得Student信息,然后获取相关的Score信息。
public class StudentExtensionRepository : IStudentExtensionRepository { private readonly IStudentRepository _studentRepository; private readonly IRepository<StudentScore> _studentScoreRepository; public StudentExtensionRepository(IRepositoryCenter repositoryCenter) { _studentRepository = repositoryCenter.GetRepository<IStudentRepository>(); _studentScoreRepository = repositoryCenter.GetRepository<IRepository<StudentScore>>(); } public IEnumerable<StudentExtension> GetStudents() { var result = new List<StudentExtension>(); var students = _studentRepository.GetStudents().ToList(); //取得score信息 var studentsIds = students.Select(s => s.Id); var scores = _studentScoreRepository.Filter(s => studentsIds.Contains(s.StudentId)).ToList(); foreach (var student in students) { var temp = new StudentExtension { Student = student, StudentScore = scores.FirstOrDefault(s => s.StudentId == student.Id) }; result.Add(temp); } return result; } }
最后,使用新的StudentExtensionRepository,能够发现,显示同样的页面,只用了2个sql访问,减少来数据库的访问,提交了效率。
五, 进一步改进,使用StudentExtensionRepository1来实现按需访问数据库
上面的StudentExtensionRepository的实现,还是无法解决我们开始提出的问题:
如果遇到需求,不需要StudentScore信息的时候,我们就又要改回lazy load的方式.
如果遇到需求,需要显示Student另外一个关联属性StudentHealthy信息的时候,又必须让StudentScore用Lazy load方式,而StudentHealthy采用eager loading
如
果我们要显示Student的另外一个关联表StudentHealthy的数据,还是使用StudentExtensionRepository,会导
致对StudentScore表的访问,但是这是我们不需要的数据,如何改进StudentExtensionRepository的实现,来达到按需访
问数据库呢?
这个时候,就可以用到Lazy<T>来实现Lazy属性,只有真正用到属性的时候,才会真正的访问数据库。
看看我们改造后的StudentExtension1类, 该类同时包含了Score和Healthy信息,但是都是Lazy加载的。
public class StudentExtension1 { public Student Student { get; set; } //Lazy属性 public Lazy<StudentScore> StudentScoreLazy { get; set; } //非Lazy属性,从Lazy属性中取值。当真正用到该属性的时候,会触发数据库访问 public StudentScore StudentScore { get { return StudentScoreLazy.Value; } } public Lazy<StudentHealthy> StudentHealthyLazy { get; set; } public StudentHealthy StudentHealthy { get { return StudentHealthyLazy.Value; } } }
改造后的StudentExtensionRepository1
public IEnumerable<StudentExtension1> GetStudents() { var result = new List<StudentExtension1>(); var students = _studentRepository.GetStudents().ToList(); var studentsIds = students.Select(s => s.Id); //存储Score查询的结果,避免多次访问数据库来获取Score信息 List<StudentScore> scoreListTemp = null; Func<int, StudentScore> getScoreFunc = id => { //第一个Student来获取Score信息的时候,scoreListTemp会是null, 这个时候,会去访问数据库获取Score信息 //第二个以及以后的Student获取Score信息的时候,scoreListTemp已经有值了, 这样就不会再次访问数据库 if (scoreListTemp == null) { scoreListTemp = _studentScoreRepository.Filter( s => studentsIds.Contains(s.StudentId)).ToList(); } return scoreListTemp.FirstOrDefault(s => s.StudentId == id); }; //存储Healthy查询的结果,避免多次访问数据库来获取Healthy信息 List<StudentHealthy> healthyListTemp = null; Func<int, StudentHealthy> getHealthyFunc = id => { if (healthyListTemp == null) { healthyListTemp = _studentHealthyRepository.Filter( s => studentsIds.Contains(s.StudentId)). ToList(); } return healthyListTemp.FirstOrDefault(s => s.StudentId == id); }; foreach (var student in students) { var id = student.Id; var temp = new StudentExtension1 { Student = student, StudentScoreLazy = new Lazy<StudentScore>(() => getScoreFunc(id)), StudentHealthyLazy = new Lazy<StudentHealthy>(() => getHealthyFunc(id)) }; result.Add(temp); } return result; } }
接下来,创建2个不同的页面index2和index3, 他们的代码完全相同,只是View页面中访问的属性不同。
public ActionResult Index2() { var studentExtensionRepository1 = _repositoryCenter.GetRepository<IStudentExtensionRepository1>(); var students = studentExtensionRepository1.GetStudents().ToList(); return View(students); } public ActionResult Index3() { var studentExtensionRepository1 = _repositoryCenter.GetRepository<IStudentExtensionRepository1>(); var students = studentExtensionRepository1.GetStudents().ToList(); return View(students); }
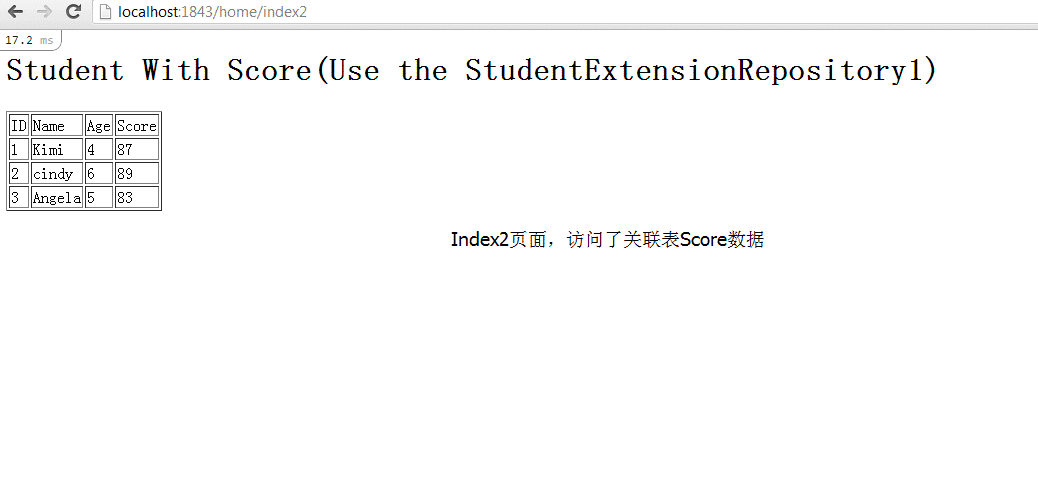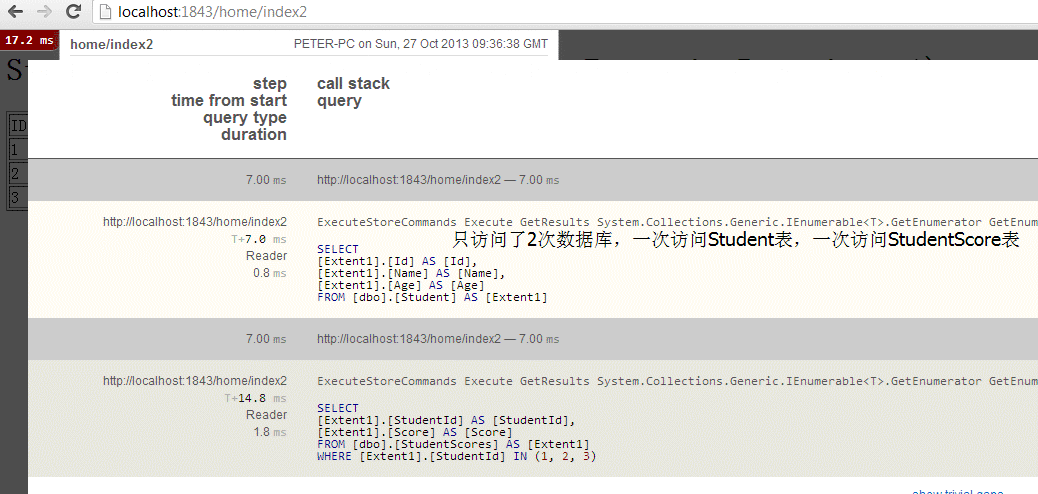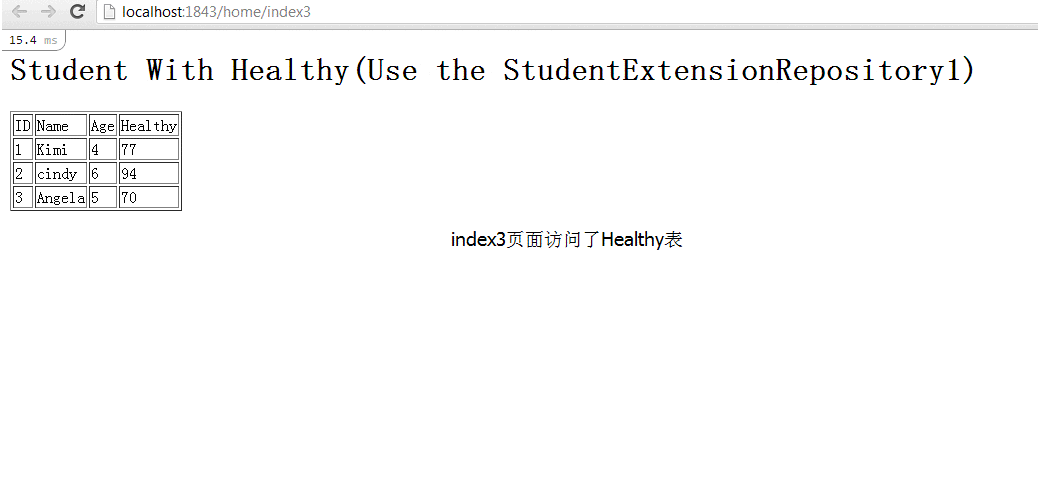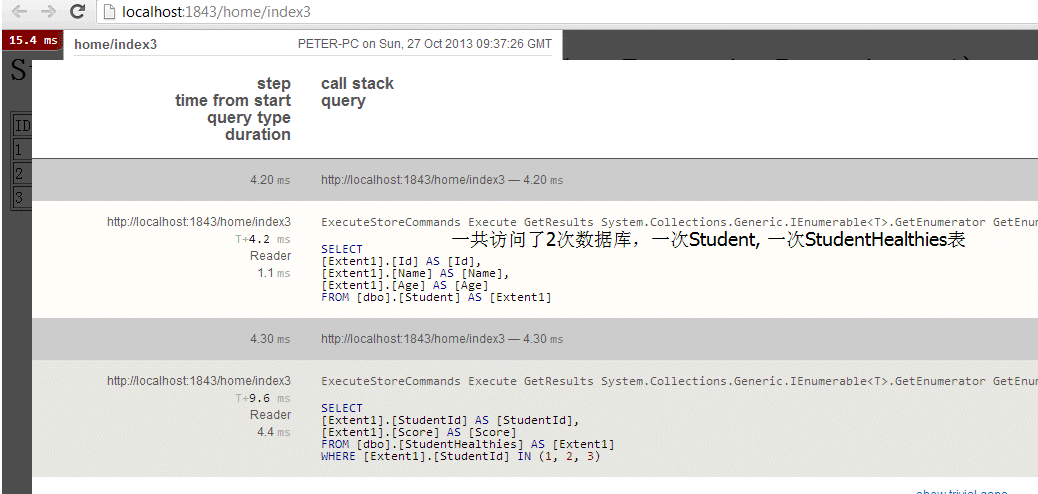
index2.cshtml中,访问了StudentScore属性
<h1>Student With Score(Use the StudentExtensionRepository1)</h1> <table border="1"> <tr><td>ID</td><td>Name</td><td>Age</td><td>Score</td></tr> @foreach(var student in Model) { <tr> <td>@student.Student.Id</td> <td>@student.Student.Name</td> <td>@student.Student.Age</td> <td>@student.StudentScore.Score</td> </tr> } </table>
index3.cshtml,访问了StudentHealthy属性
<h1>Student With Healthy(Use the StudentExtensionRepository1)</h1> <table border="1"> <tr><td>ID</td><td>Name</td><td>Age</td><td>Healthy</td></tr> @foreach(var student in Model) { <tr> <td>@student.Student.Id</td> <td>@student.Student.Name</td> <td>@student.Student.Age</td> <td>@student.StudentHealthy.Score</td> </tr> } </table>
如下图,尽管Index2和Index3的代码中,获取数据的代码完全相同,但是实际的访问数据库的sql却是不同的。这是由于它们View中的显示数据的需求不同引起的。改造后的StudentExtensionRepository1能够根据所需来访问数据库, 来减少对于数据库的不必要的访问。同时它也能够适应更多的情况,无论是只显示Student表数据,还是要同时显示Student, StudentScore和StudentHealthy数据,StudentExtensionRepository1都能提供恰到好处的数据库访问。
六, 总结
以上是使用Lazy<T>结合EF的一次性能优化的闭门造车的尝试,欢迎各位多提意见。如果有更好的方式来,欢迎指教。