文本预处理
文本是一类序列数据,一篇文章可以看作是字符或单词的序列,下面介绍文本数据的常见预处理步骤,预处理通常包括四个步骤:
- 读入文本
- 分词
- 建立字典,将每个词映射到一个唯一的索引(index)
- 将文本从词的序列转换为索引的序列,方便输入模型
step1:读入文本
import collections
import re
def read_time_machine():
with open('/home/kesci/input/timemachine7163/timemachine.txt', 'r') as f:
lines = [re.sub('[^a-z]+', ' ', line.strip().lower()) for line in f]
return lines
lines = read_time_machine()
print('# sentences %d' % len(lines))
step2:分词
def tokenize(sentences, token='word'):
"""Split sentences into word or char tokens"""
if token == 'word':
return [sentence.split(' ') for sentence in sentences]
elif token == 'char':
return [list(sentence) for sentence in sentences]
else:
print('ERROR: unkown token type '+token)
tokens = tokenize(lines)
tokens[0:2]
step3:建立字典
构建一个字典(vocabulary),将每个词映射到一个唯一的索引编号,以便于方便模型处理。
class Vocab(object):
def __init__(self, tokens, min_freq=0, use_special_tokens=False):
counter = count_corpus(tokens) # :
self.token_freqs = list(counter.items())
self.idx_to_token = []
if use_special_tokens:
# padding, begin of sentence, end of sentence, unknown
self.pad, self.bos, self.eos, self.unk = (0, 1, 2, 3)
self.idx_to_token += ['', '', '', '']
else:
self.unk = 0
self.idx_to_token += ['']
self.idx_to_token += [token for token, freq in self.token_freqs
if freq >= min_freq and token not in self.idx_to_token]
self.token_to_idx = dict()
for idx, token in enumerate(self.idx_to_token):
self.token_to_idx[token] = idx
def __len__(self):
return len(self.idx_to_token)
def __getitem__(self, tokens):
if not isinstance(tokens, (list, tuple)):
return self.token_to_idx.get(tokens, self.unk)
return [self.__getitem__(token) for token in tokens]
def to_tokens(self, indices):
if not isinstance(indices, (list, tuple)):
return self.idx_to_token[indices]
return [self.idx_to_token[index] for index in indices]
def count_corpus(sentences):
tokens = [tk for st in sentences for tk in st]
return collections.Counter(tokens) # 返回一个字典,记录每个词的出现次数
下面尝试用Time Machine作为语料构建字典:
vocab = Vocab(tokens)
print(list(vocab.token_to_idx.items())[0:10])
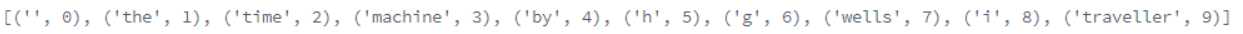
step4:将词转为索引
for i in range(8, 10):
print('words:', tokens[i])
print('indices:', vocab[tokens[i]])

用现有工具进行分词
我们前面介绍的分词方式非常简单,它至少有以下几个缺点:
- 标点符号通常可以提供语义信息,但是我们的方法直接将其丢弃了
- 类似“shouldn't", "doesn't"这样的词会被错误地处理
- 类似"Mr.", "Dr."这样的词会被错误地处理
我们可以通过引入更复杂的规则来解决这些问题,但是事实上,有一些现有的工具可以很好地进行分词,我们在这里简单介绍其中的两个:spaCy和NLTK。
下面是一个简单的例子:
text = "Mr. Chen doesn't agree with my suggestion."
1. 使用spaCy
import spacy
nlp = spacy.load('en_core_web_sm')
doc = nlp(text)
print([token.text for token in doc])

2. 使用MLTK
from nltk.tokenize import word_tokenize
from nltk import data
data.path.append('/home/kesci/input/nltk_data3784/nltk_data')
print(word_tokenize(text))
