判断题
1-1

F:将向量空间想象为一个首尾相接的圆环,并称这种向量为循环向量。存储在其中的队列称为循环队列(Circular Queue)。这种循环队列可以以单链表的方式来在实际编程应用中来实现。因此,循环队列是一个抽象的数据结构,而单向循环链表或循环数组是具体的实现方式,不是数据结构本身。<分析摘录自链接https://blog.csdn.net/Invokar/article/details/80010758>
单选题
2-2

这里注意人家的要求,用头指针和队列个数size代替一般队列的表示方法,这样就不用考虑尾指针了,最多可以直接填满。
2-3

这是一般的循环队列的表示,注意末尾要保留一个。
编程题
7-1
关于这道题目,模拟即可,需要定义两个结构体数组,一个是存窗口的,包括在此窗口排队的人数以及最后结束时间,另一个是存人的,包括其到达时间和处理时间。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Person{
int T, P;
};
struct Window{
int num_person;
int endtime;
};
int N, T, P, K;
Person p[1000+10];
Window w[11];
int main()
{
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &N);
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &T, &P);
if(P > 60)
P = 60;
p[i].T = T;
p[i].P = P;
}
scanf("%d", &K);
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
w[i].num_person = 0;
w[i].endtime = 0;
}
int sum_time = 0, max_time = 0, end_time = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
int minwindow = 1e9, idx = -1;
bool Wait = true;
for(int j = 0; j < K; j++)
{
if(p[i].T >= w[j].endtime)
{
w[j].num_person++;
Wait = false;
w[j].endtime = p[i].T + p[i].P;
break;
}
else //寻找等待时间最小的窗口
{
if(minwindow > w[j].endtime)
{
minwindow = w[j].endtime;
idx = j;
}
}
}
if(Wait)
{
sum_time += minwindow - p[i].T;
max_time = max(max_time, minwindow - p[i].T);
w[idx].endtime += p[i].P;
w[idx].num_person++;
}
}
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
if(w[i].endtime > end_time)
end_time = w[i].endtime;
}
printf("%.1lf %d %d
", (double)sum_time / (double)N, max_time, end_time);
for(int i = 0; i < K; i++)
{
if(i != 0) printf(" ");
printf("%d",w[i].num_person);
}
}
7-2
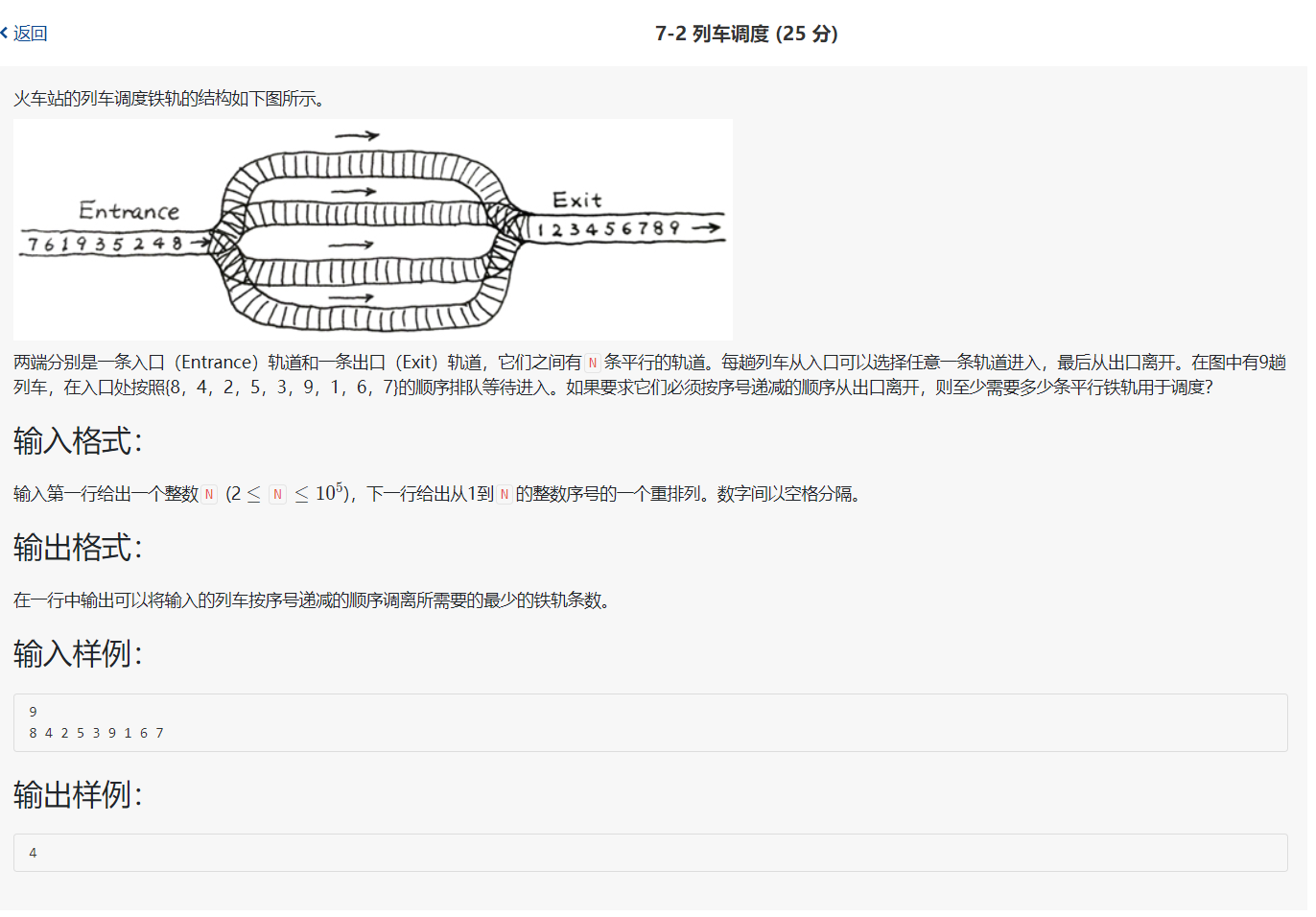
该题目目前不会,
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<set>
using namespace std;
int N, num;
set<int> p;
int main()
{
// freopen("input.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("output.txt", "w", stdout);
scanf("%d", &N);
scanf("%d", &num);
p.insert(num);
--N;
while(N--)
{
scanf("%d", &num);
if(p.upper_bound(num) != p.end())
p.erase(p.upper_bound(num));
p.insert(num);
}
cout << p.size() << endl;
}