函数式接口
此文章仅仅记录函数式分类的学习
函数式接口(Functional Interface)就是一个有且仅有一个抽象方法(函数式方法),但是可以有多个非抽象方法的接口。
函数式接口主要用于接受,Lambda 表达式 和 方法引用 的赋值,定义其目标元素。
//函数式接口(只有一个方法)
interface Test{void aaa()}
/* 等同于
@FunctionalInterface
interface AAA{
void aaa();
}
*/
class TestImpl{
void aaa(){
System.out.println("方法引用");
}
}
public class TestLambda{
public static void main(String[]
\Lambda表达式
Test t = () -> System.out.println("Lambda");
t.aaa();
\方法引用
Test t2 = new TestImpl()::aaa;
t2.aaa();
}
}
可以看到,使用 Lambda 表达式 和 方法引用 时,需要定义一个接口(Test 接口),用于接受 Lambda 和 方法引用 的赋值。
为了避免每次都创建所需的接口,Java 8 引入了 java.util.function 包。其中包含了 一组接口 ,供不同情形使用。
类库中提供的接口
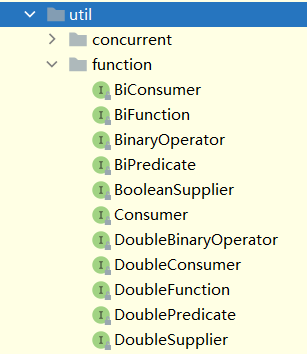
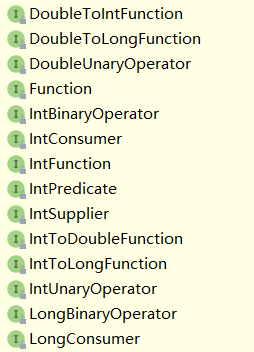
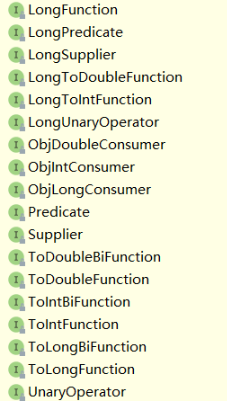
命名原则
- 如果只处理对象,而非基本类型,名称则为:
Function,Consumer,Predicate等。参数类型通过泛型添加 - 如果接收的参数是基本类型,则由名称的第一部分表示。如
LongConsumer,DoubleFunction,IntPredicate等,但返回基本类型的Supplier接口例外。 - 如果返回值是基本类型,则用
To表示,如ToLongFunction<T>和IntToLongFunction - 如果返回值类型与参数类型相同,则是一个
Operator:单个参数使用UnaryOperator, 两个参数使用BinaryOperator。 - 如果接收参数并返回一个布尔值,则是一个 谓词(Predicate)。
- 如果接受的两个参数类型不同,则名称中有一个
Bi
代码实例
Lambda 表达式
class Foo{}
class Bar{
Foo f;
Bar(Foo f){
this.f = f;
}
}
class IBaz{
int i;
IBaz(int i){
this.i = i;
}
}
class LBaz{
long l;
LBaz(long l){
this.l = l;
}
}
class DBaz{
double d;
DBaz(double d){
this.d = d;
}
}
public class FunctionVariants {
static Function<Foo , Bar> f1 = f -> new Bar(f);
static IntFunction<IBaz> f2 = i -> new IBaz(i);
static LongFunction<LBaz> f3 = l -> new LBaz(l);
static DoubleFunction<DBaz> f4 = d -> new DBaz(d);
static ToIntFunction<IBaz> f5 = ib -> ib.i;
static ToLongFunction<LBaz> f6 = lb -> lb.l;
static ToDoubleFunction<DBaz> f7 = db -> db.d;
static IntToLongFunction f8 = i -> i;
static IntToDoubleFunction f9 = i -> i;
static LongToIntFunction f10 = l -> (int)l;
static LongToDoubleFunction f11 = l -> l;
static DoubleToIntFunction f12 = d -> (int)d;
static DoubleToLongFunction f13 = d -> (long)d;
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bar b = f1.apply(new Foo());
IBaz ib = f2.apply(11);
LBaz lb = f3.apply(11);
DBaz db = f4.apply(11);
int i = f5.applyAsInt(ib);
long l = f6.applyAsLong(lb);
double d = f7.applyAsDouble(db);
l = f8.applyAsLong(12);
d = f9.applyAsDouble(12);
i = f10.applyAsInt(12);
d = f11.applyAsDouble(12);
i = f12.applyAsInt(14.0);
l = f13.applyAsLong(14.0);
}
}
方法引用
class AA{}
class BB{}
class CC{}
public class ClassFunctionals {
static AA f1(){
return new AA();
}
static int f2(AA aa1 , AA aa2){
return 1;
}
static void f3(AA aa){
}
static void f4(AA aa , BB bb){
}
static CC f5(AA aa){
return new CC();
}
static CC f6(AA aa , BB bb){
return new CC();
}
static boolean f7(AA aa){
return true;
}
static boolean f8(AA aa , BB bb){
return true;
}
static AA f9(AA aa){
return new AA();
}
static AA f10(AA aa1 , AA aa2){
return new AA();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Supplier<AA> s = ClassFunctionals::f1;
s.get();
//2个参数,返回类型为整形
Comparator<AA> c = ClassFunctionals::f2;
c.compare(new AA() , new AA());
Consumer<AA> cons = ClassFunctionals::f3;
cons.accept(new AA());
BiConsumer<AA , BB> bicons = ClassFunctionals::f4;
bicons.accept(new AA() , new BB());
//AA 代表参数类型,CC 代表返回类型
Function<AA , CC> f = ClassFunctionals::f5;
CC cc = f.apply(new AA());
BiFunction<AA , BB ,CC> bic = ClassFunctionals::f6;
cc = bic.apply(new AA() , new BB());
Predicate<AA> p = ClassFunctionals::f7;
boolean result = p.test(new AA());
BiPredicate<AA , BB> bip = ClassFunctionals::f8;
result = bip.test(new AA() , new BB());
UnaryOperator<AA> uo = ClassFunctionals::f9;
AA aa = uo.apply(new AA());
BinaryOperator<AA> bo = ClassFunctionals::f10;
aa = bo.apply(new AA() , new AA());
}
}