1. 本周学习总结
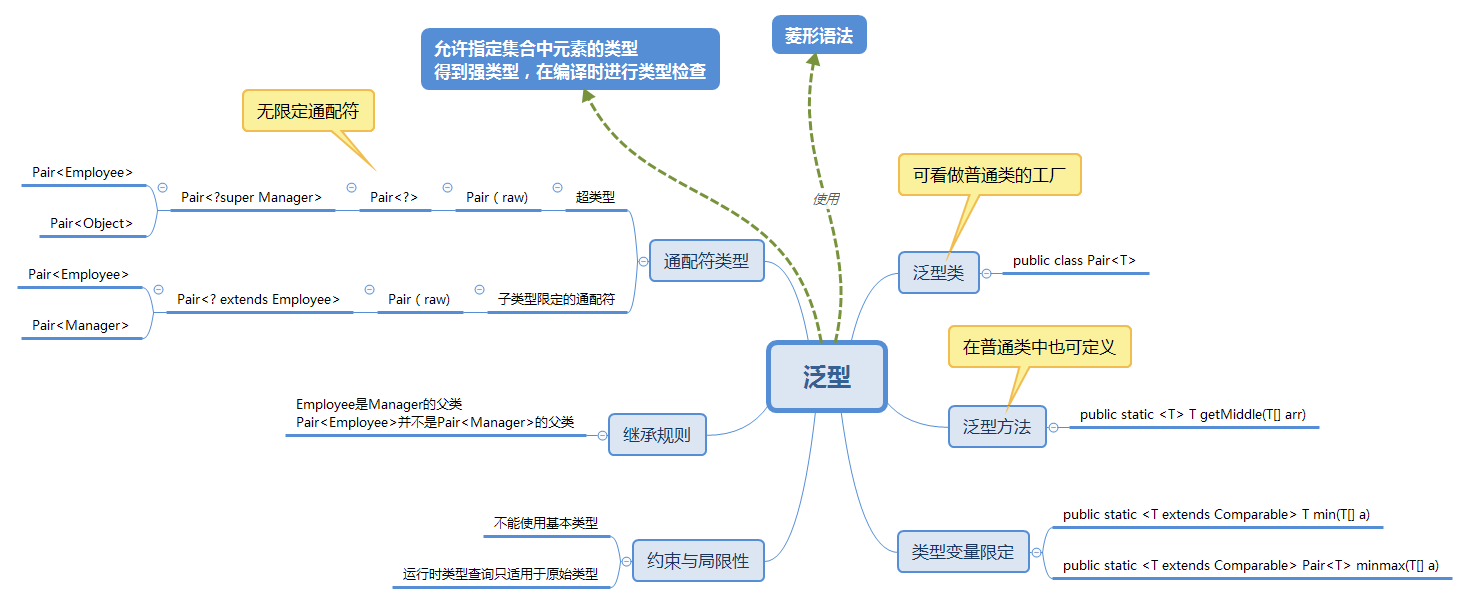
**1.1 以你喜欢的方式(思维导图或其他)归纳总结集合与泛型相关内容。 **
**1.2 选做:收集你认为有用的代码片段 **
class ArrayAlg
{
public static <T extends Comparable> Pair<T> minmax(T[] a)
{
if (a == null || a.length == 0) return null;
T min = a[0];
T max = a[0];
for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
{
if (min.compareTo(a[i]) > 0) min = a[i];
if (max.compareTo(a[i]) < 0) max = a[i];
}
return new Pair<T>(min, max);
}
}
public class Pair<T>
{
public Pair() { first = null; second = null; }
public Pair(T first, T second) { this.first = first; this.second = second; }
public T getFirst() { return first; }
public T getSecond() { return second; }
public void setFirst(T newValue) { first = newValue; }
public void setSecond(T newValue) { second = newValue; }
private T first;
private T second;
}
2. 书面作业
**1.本次作业题集集合 **
**1.List中指定元素的删除(题目4-1) **
**1.1 实验总结 **
public static List<String> convertStringToList(String line)编写这个函数时需要使用sc.next()来添加字符串,使得其能够用空格分开。public static void remove(List<String> list, String str)编写这个函数时需要使用iterator迭代器,这样能够使用迭代器的remove()函数来移除元素,能够从最后一个元素来移除,可以避免从第一个开始移除元素导致元素下标改变,有些元素不能够移除。
**2.统计文字中的单词数量并按出现次数排序(题目5-3) **
**2.1 伪代码(简单写出大体步骤) **
while(有输入){
输入;
num=1;
if(输入为"!!!!!")
break;
if(重复出现)
键值加1;
加入strMap;
}
建立List;
排序;
if(小于10){
遍历输出;
}
else{
遍历输出前十个;
}
}
**2.2 实验总结 **
使用Map中的TreeMap,TreeMap本身能够对Key进行排序,这时我们只要在只用嵌套,将Map转为List,对value进行排序。然后进行遍历输出排序后前十个。
**3.倒排索引(题目5-4) **
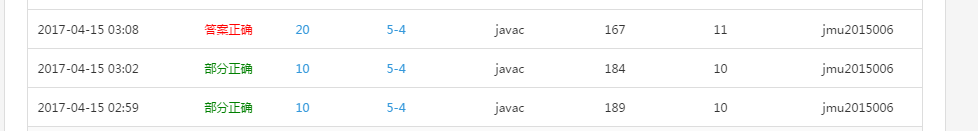
**3.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号) **
**3.2 伪代码(简单写出大体步骤) **
建立Map类型两个;
num=1;
while(有行输入){
赋值;
if(输入为"!!!!!")
break;
else{
放入数组中;
放入map中;
for(遍历){
建立Set类型;
if(包含)
赋值;
添加;
放入strMap;
}
num++;
}
}
while(有输入){
赋值;
if(无输入)
输出;
放入数组;
建立Set;
for(遍历行){
for(遍历索引){
if(不存在或无交集){
break;
}
else{
获键值;
}
}
}
}
**3.3 实验总结 **
- 使用Map(TreeMap)来存放输入的字符串,但是由于是要通过TreeMap中的Value来找出对应的Key,所以我们需要将Integer使用Set类型(每个单词有可能有好几行)。同时还需要另外建立一个Map类型,它的String和Integer是和前一个相反的,这样就能实现题目中的查找了。然后就是输入字符串,建立联系。
- 使用for循环实现遍历,因为输入的查找的单词有可能在字符串中都有,但是有可能组合起来的没有,这时候就需要进行每一行和输入的每一个单词的比较,并且set1中的数据需要是几个单词都存在的行,所以我们需要取Set的集合,可以使用
retainAll()函数。
**4.Stream与Lambda **
编写一个Student类,属性为:
private Long id;
private String name;
private int age;
private Gender gender;//枚举类型
private boolean joinsACM; //是否参加过ACM比赛
创建一集合对象,如List,内有若干Student对象用于后面的测试。
**4.1 使用传统方法编写一个方法,将id>10,name为zhang, age>20, gender为女,参加过ACM比赛的学生筛选出来,放入新的集合。在main中调用,然后输出结果。 **
public Student1 findstudent(){
if(id>10&&name.equals("zhang")&& age>20&& gender.equals(Gender.female)&&joinsACM){
Student1 s=new Student1(id,name,age,gender,joinsACM);
return s;
}
else
return null;
}

**4.2 使用java8中的stream(), filter(), collect()编写功能同4.1的函数,并测试。 **
ArrayList<Student1> List1 = (ArrayList<Student1>) List.stream()
.filter(Student1 -> (Student1.getId() > 10&& Student1.getName().equals("zhang")
&& Student1.getAge() > 20 &&
Student1.getGender().equals(Gender.female)
&& Student1.isJoinsACM()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());

**4.3 构建测试集合的时候,除了正常的Student对象,再往集合中添加一些null,然后重新改写4.2,使其不出现异常。 **
ArrayList<Student1> List1 = (ArrayList<Student1>) List.stream()
.filter(Student1 -> Student1!=null&&(Student1.getId() > 10&& Student1.getName().equals("zhang")
&& Student1.getAge() > 20 &&
Student1.getGender().equals(Gender.female)
&& Student1.isJoinsACM()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());

**5.泛型类:GeneralStack(题目5-5) **
**5.1 截图你的提交结果(出现学号) **

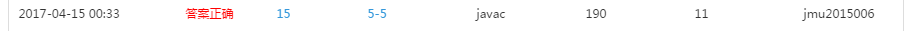
**5.2 GeneralStack接口的代码 **
interface GeneralStack<T>{
public T push(T item);
public T pop();
public T peek();
public boolean empty();
public int size();
}
**5.3 结合本题,说明泛型有什么好处 **
泛型的好处在于:我们不需要使用强制转换,像这题中我们使用Double型,Integer型及Car型都只要用泛型定义后就可以直接使用,不需要强制转换成需要的类型,够不容易出错,并且当我们使用了和定义的泛型不同时,在编译阶段就会直接报错,不需要等到执行时才报错。
**6.泛型方法 **
基础参考文件GenericMain,在此文件上进行修改。
**6.1 编写方法max,该方法可以返回List中所有元素的最大值。List中的元素必须实现Comparable接口。编写的max方法需使得String max = max(strList)可以运行成功,其中strList为List<String>类型。也能使得Integer maxInt = max(intList);运行成功,其中intList为List<Integer>类型。 **
public class GenericMain {
public static <T extends Comparable<T>> T max(List<T> list) {
T Max=list.get(0);
for(T e:list){
if(e.compareTo(Max)>0)
Max=e;
}
return Max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String>strList=new ArrayList<String>();
List<Integer>intList=new ArrayList<Integer>();
strList.add("Ad");
strList.add("Cv");
strList.add("EE");
strList.add("aww");
intList.add(42);
intList.add(231);
intList.add(1);
intList.add(112);
System.out.println(max(strList));
System.out.println(max(intList));
}
}
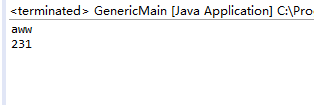
**6.2 选做:现有User类,其子类为StuUser,且均实现了Comparable接口。编写方法max1,基本功能同6.1,并使得max1(stuList);可以运行成功,其中stuList为List<StuUser>类型。 **
public class GenericMain {
public static <StuUserComparator extends Comparable<StuUser>> StuUser max1(List<StuUser> list) {//Comparable<StuUser>改用Comparable<User>也行
StuUser Max=list.get(0);
for(StuUser e:list){
if(e.compareTo(Max)>0)
Max=e;
}
return Max;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<StuUser>stuList=new ArrayList<StuUser>();
stuList.add(new StuUser(12,"Amy"));
stuList.add(new StuUser(23,"keke"));
stuList.add(new StuUser(84,"Kimheechul"));
stuList.add(new StuUser(78,"Kangkang"));
System.out.println(max1(stuList));
}
}
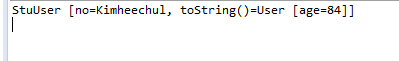
**6.3 选做:编写int myCompare(T o1, T o2, Comparator c)方法,该方法可以比较User对象及其子对象,传入的比较器c既可以是Comparator<User>,也可以是Comparator<StuUser>。注意:该方法声明未写全,请自行补全。 **
**7.选做:逆向最大匹配分词算法 **
集合实验文件中的第07次实验(集合).doc文件,里面的题目6.
**7.1 写出伪代码 **
**7.2 实验总结 **
**8.选做:JavaFX入门 **
**完成其中的作业1、作业2。内有代码,可在其上进行适当的改造。建议按照里面的教程,从头到尾自己搭建。 **
3. 码云上代码提交记录及PTA实验总结
题目集:jmu-Java-05-集合
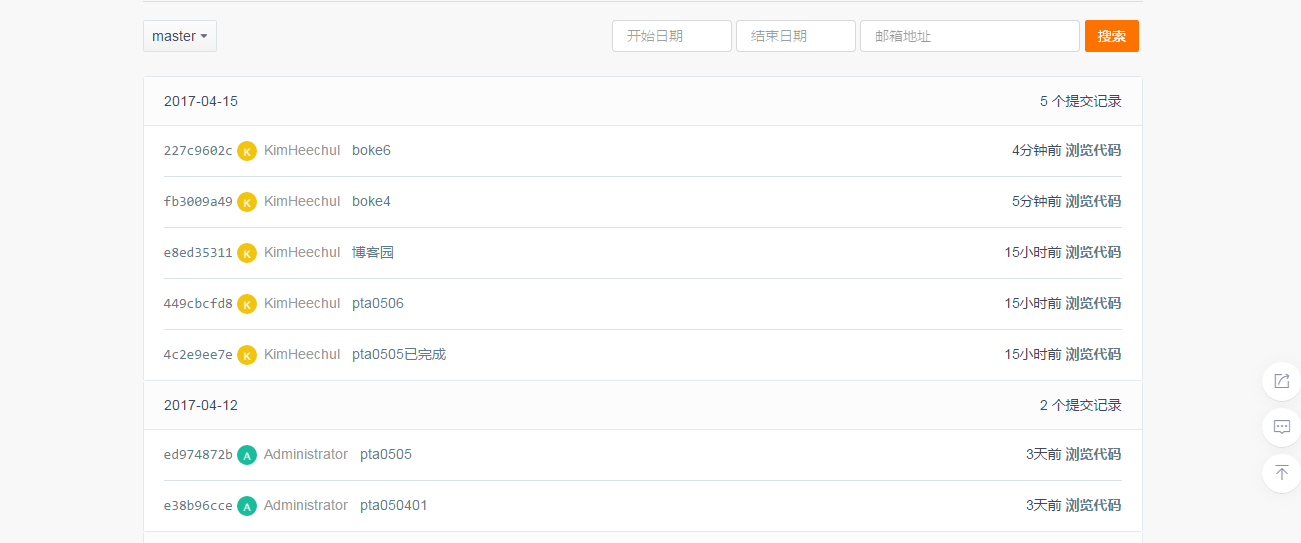
**3.1. 码云代码提交记录 **
在码云的项目中,依次选择“统计-Commits历史-设置时间段”, 然后搜索并截图
**3.2. PTA实验 **
- 函数(4-1),编程(5-3,5-4,5-5)

- 实验总结已经在作业中体现,不用写。