题意:
对于给定字符串,我们可将其相邻的两个字符做以下操作:
num[i],num[i+1] -> num[i]-num[i+1],num[i]+num[i+1]
由此可得,变换两次得:-2num[i+1],2num[i]
因为所有数均可转换为偶数,所以结果不可能为“NO”。
当相邻两数均为奇数时,只进行一次变换就可将它们全部变换为偶数;
当相邻数一奇一偶时,只要进行两次就可转换为偶数。
AC代码:
1 #include<bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 4 long long num[100010]; 5 int n; 6 7 int gcd(long long a,long long b){ 8 if(b==0){ 9 return abs(a); 10 } 11 return gcd(b,a%b); 12 } 13 14 int main(){ 15 cin>>n; 16 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 17 cin>>num[i]; 18 } 19 long long ans=0; 20 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 21 ans=gcd(ans,num[i]); 22 } 23 if(ans>1){ 24 cout<<"YES"<<endl<<0<<endl; 25 return 0; 26 } 27 ans=0; 28 for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++){ 29 if(num[i]&1&&num[i+1]&1){ 30 ans++; 31 num[i]=2; 32 num[i+1]=2; 33 } 34 } 35 for(int i=0;i<n;i++){ 36 if(num[i]&1){ 37 ans+=2; 38 } 39 } 40 cout<<"YES"<<endl<<ans<<endl; 41 42 return 0; 43 }
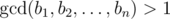 .
.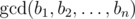 is the biggest non-negative number
is the biggest non-negative number 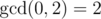 .
.