dijkstra算法的运用条件是求某一点到其他点的最短路径问题
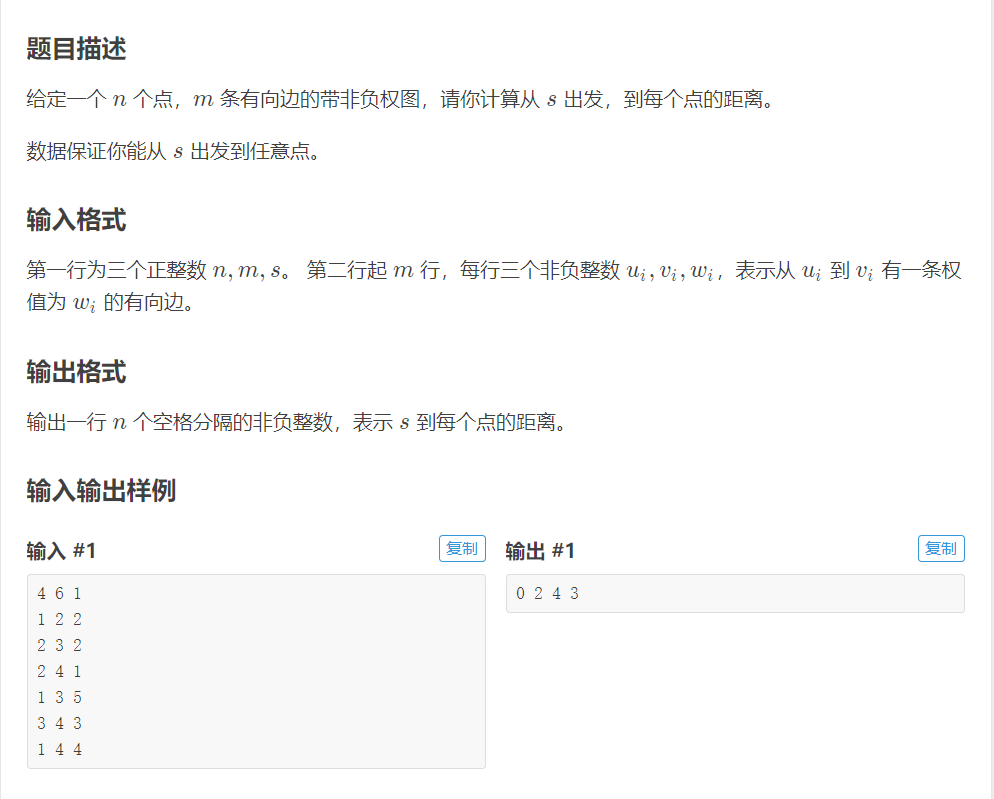
题目链接:https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4779
实现思路:
类似多米诺骨牌问题,推下第一个,后面的骨牌会按时间顺序倒下,那么最先倒下的那条路便是最短路
每次找目前已知的最短路径(到所需的原点),这条路径不可能再被优化,因为如果从其他路绕的话,光是绕路就超过了这个路程(已知的最短路径)
两个数组来做记录,一个是dis数组,记录点到原点的距离(要根据需要更新的),一个vis数组,判断该点到原点的最小值是否确定
vis数组的判断就是每次从dis中选出最小的那个,如果这个点还没有确定最短路径,那么当前的dis值就是最短路径了
(绕路的话,光是绕路的路程就比他目前的路径大了,看不懂的话等下看代码)
然后更新dis
假设目前点是v,原点是s,v有一条边连到f
那么dis[f]=min(dis[f],dis[v]+(v,f));靠这个来判断更新
下面是代码分析
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <cstring> 5 using namespace std; 6 const int inf = 1e6; 7 struct node 8 { 9 int point, value;//point是点的值,value是距离(看node在谁的cun里,就是谁到point的距离) 10 }; //Point是点的值,value是到原点的距离(有两个功能,看这个struct在哪里用) 11 vector<node>cun[100100];//记录邻居 12 struct cmp 13 { 14 bool operator()(node a, node b) 15 { 16 return a.value > b.value; 17 } 18 }; 19 20 priority_queue<node, vector<node>, cmp>q;//优先队列,每次蹦出到原点距离最小的 21 int dis[100100], vis[100100]; 22 void dijkstra(int s) 23 { 24 memset(dis, inf, sizeof(dis));//先把距离设为最大 25 memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis)); 26 dis[s] = 0;//原点到自己距离为0 27 node start; 28 start.point = s; 29 start.value = 0; 30 q.push(start); 31 while (!q.empty()) 32 { 33 node start = q.top(); 34 q.pop(); 35 if (vis[start.point]) continue;//如果取出的这个已经确定vis了,就没必要再算,但是要pop掉,所以这个放在pop下面 36 vis[start.point] = 1;//说明这个点确定了,之后就不需要改他的vis 37 for (int i = 0; i < cun[start.point].size(); i++)//遍历邻居 38 { 39 if (vis[cun[start.point][i].point]) continue;//这个邻居已经确定 40 if (dis[cun[start.point][i].point] > dis[start.point] + cun[start.point][i].value)//从这里走比之前的路更快,更新dis 41 { 42 dis[cun[start.point][i].point] = dis[start.point] + cun[start.point][i].value; 43 node next; 44 next.point = cun[start.point][i].point; 45 next.value = dis[cun[start.point][i].point]; 46 q.push(next); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 51 } 52 int main() 53 { 54 int n, m, s; 55 cin >> n >> m >> s; 56 for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) 57 { 58 int u, v, w; 59 cin >> u >> v >> w; 60 node start; 61 start.point = v; 62 start.value = w; 63 cun[u].push_back(start);//记录邻居 64 } 65 dijkstra(s); 66 for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) 67 { 68 if (i != 1) cout << " "; 69 cout << dis[i]; 70 } 71 }
感谢大犇 @AE酱 的讲课