一、概述
Spring的三大核心思想:IoC(控制反转),DI(依赖注入),AOP(面向切面编程)。本问讲着重介绍一下控制反转。
何谓控制反转:Spring 通过一种称作控制反转(IoC)的技术促进了松耦合。当应用了IoC,一个对象依赖的其它对象会通过被动的方式传递进来,而不是这个对象自己创建或者查找依赖对象。你可以认为IoC与JNDI相反——不是对象从容器中查找依赖,而是容器在对象初始化时不等对象请求就主动将依赖传递给它。
通俗的讲,控制权由代码中转到了外部容器,控制权的转移,就是所谓反转。也就是说,正常我们都是 new 一个新对象,才可以调用对象。有了控制反转就不需要了,交给容器来管理,我们只需要通过一些配置来完成把实体类交给容器这么个过程。这样可以减少代码量,简化开发的复杂度和耦合度。
二、面向接口编程
在一个面向对象的系统中,系统的各种功能是由许许多多的不同对象协作完成的。在这种情况下,各个对象内部是如何实现自己的,对系统设计人员来讲就不那么重要了;而各个对象之间的协作关系则成为系统设计的关键。小到不同类之间的通信,大到各模块之间的交互,在系统设计之初都是要着重考虑的,这也是系统设计的主要工作内容。面向接口编程就是指按照这种思想来编程。
面向接口编程,具体到某一个接口,对于调用者来说,我们不关心该接口是由哪个实现类来实现的,也不关心具体是怎么实现的,你只需把该接口提供给调用者就可以了。
三、编码实现IoC
下面,我们使用IoC思想来实现一个简单的面向接口编程。
首先定义两个接口 IAccountService 和 IOrderService,如下:

public interface IAccountService { int insertAccount(String msg); }

public interface IOrderService { void insert(String msg); }
然后,定义这两个接口的实现类

public class AccountBigServiceImpl implements IAccountService { @Override public int insertAccount(String msg) { System.out.println("===== AccountBigServiceImpl ====" + msg); return 0; } }

public class AccountSamllServiceImpl implements IAccountService { @Override public int insertAccount(String msg) { System.out.println("smallService"); return 0; } }

public class OrderServiceImpl implements IOrderService { @Override public void insert(String msg) { System.out.println("===== OrderServiceImpl ====" + msg); } }
正常我们使用下面这段代码来调用这两个接口
public class Controller { public static void main(String[] args) { IAccountService accountService = new AccountBigServiceImpl(); accountService.insertAccount("Hello!!"); IOrderService orderService = new OrderServiceImpl(); orderService.insert("World!!"); } }
我们在 Controller 这个类中直接 new 了 IAccountService 和 IOrderService 这两个接口的子类:AccountBigServiceImpl 和 OrderServiceImpl。这样就违背上面提到的面向接口编程的思想,我既要处理 Controller 这个类中的业务逻辑,还要关心 IAccountService 和 IOrderService 这两个接口具体的实现类是谁,上面是使用 AccountBigServiceImpl 这个类来实现接口 IAccountService,如果我要使用 AccountSamllServiceImpl这个实现类来实现这个接口,那我还得修改 Controller 中的代码,显然这样做的维护成本就太高了,而且也很容易出错,那么,我们可以想其他的办法。
首先,我们使用一个配置文件来定义这两个接口指向的实现类

IAccountService=com.jack.course.spring.factory.impl.AccountBigServiceImpl
IOrderService=com.jack.course.spring.factory.impl.OrderServiceImpl
然后,我们再定义一个工厂类
public class ServiceFactory { private static final String CONF_FILE_NAME = "factory/conf.properties"; private static Properties prop; private static Map<String, Object> beanContainer; /** * 静态代码块,程序执行时只会被加载一次 */ static { try { beanContainer = Maps.newHashMap(); //1.从配置文件中找出关系 prop = new Properties(); prop.load(ServiceFactory.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(CONF_FILE_NAME)); } catch (IOException e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } } public static <T> T getService(Class<T> clazz){ if (beanContainer.containsKey(clazz.getSimpleName())){ return (T) beanContainer.get(clazz.getSimpleName()); } try { //2.根据关系,将具体的实现类返回 Object obj = instanceObj(clazz); beanContainer.put(clazz.getSimpleName(),obj); return (T) obj; } catch (Exception e) { throw new IllegalArgumentException(e); } } private static <T> Object instanceObj(Class<T> clazz) throws Exception { String className = prop.getProperty(clazz.getSimpleName()); Class<?> instance = Class.forName(className); return instance.newInstance(); } }
注意:以上代码做了两处优化。第一,把读取配置文件的操作单独抽出来放入静态代码块,只会执行一次不会重复读取。第二,定义了一个 Map 作为 bean容器存放实例化后的对象,如果容器中已经存在实例化后的对象就可以直接返回,不用在重现通过 instanceObj() 方法来实例化对象了,通过这两处优化,能够大大提高性能。
这个工厂类实现的功能是:通过读取配置文件 conf.properties 得到接口的具体实现类,然后通过反射来生成一个对象传给 Controller,这样 Controller 类当中就可以不关心接口的实现类是谁,怎么实现也不用关心。
那我们 Controller 中就可以这么实现
public class Controller { public static void main(String[] args) { IAccountService accountService = ServiceFactory.getService(IAccountService.class); accountService.insertAccount("Hello!"); IOrderService orderService1 = ServiceFactory.getService(IOrderService.class); IOrderService orderService2 = ServiceFactory.getService(IOrderService.class); orderService1.insert("One"); orderService2.insert("Two"); } }
这样,我们如果想修改实现类的话,只需要修改配置文件就行了,不用修改代码。
运行结果如下:

以上,我们就通过 IoC 的思想实现了面向接口编程。但是,我们这样的实现就完全没有问题吗?
我们稍微修改一下 AccountBigServiceImpl 实现类,增加一个有参数的构造方法来覆盖默认的构造方法
public class AccountBigServiceImpl implements IAccountService { private AccountBigServiceImpl(String msg) { System.out.println(msg); } @Override public int insertAccount(String msg) { System.out.println("===== AccountBigServiceImpl ====" + msg); return 0; } }
然后再执行 Controller,就会报错了。原因是因为我们使用 newInstance 实例化对象时使用的是默认的无参构造方法。
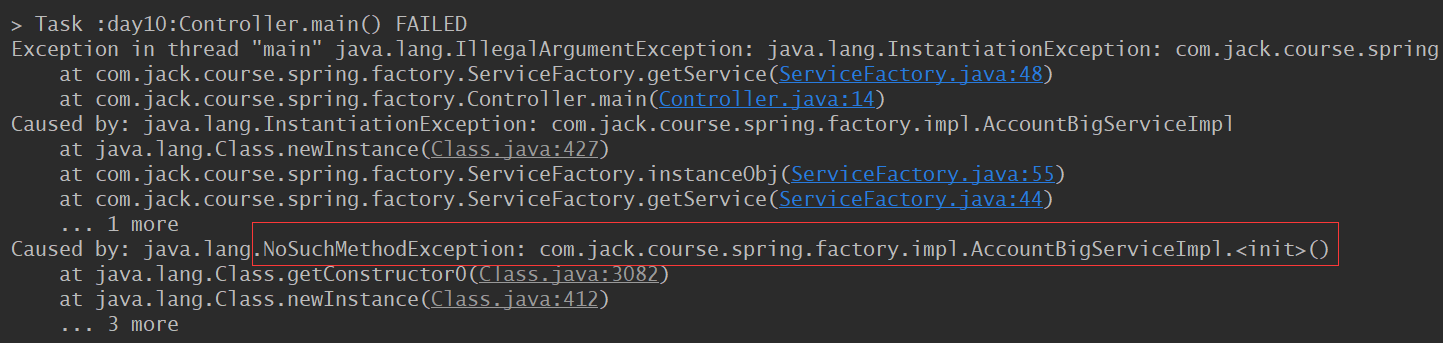 那么,我们通过修改工厂类,也可以实现该功能。但是,可能慢慢还会发现有其他问题,那么我们是不是要全部自己来实现呢,我们可以直接来使用 Spring 框架即可。Spring 框架把我们能想到的和想不到的功能都给实现了,我们只需直接使用就可以了。
那么,我们通过修改工厂类,也可以实现该功能。但是,可能慢慢还会发现有其他问题,那么我们是不是要全部自己来实现呢,我们可以直接来使用 Spring 框架即可。Spring 框架把我们能想到的和想不到的功能都给实现了,我们只需直接使用就可以了。
四、使用XML文件配置IoC
我们基于 MVC 三层架构来做一个简单的实现,分为:表现层(Controller)、业务逻辑层(Service)和持久层(Dao)。
定义两个接口

public interface IocxService { String foo(String msg); }

public interface IocxDao { String iocxFoo(String msg); }
再定义三个类,IocxController、IocxServiceImpl 和 IocxDaoImpl

public class IocxController { private IocxService iocxService; public IocxController() { System.out.println("***** IocxController init ******"); } public String iocxFoo(String msg){ return iocxService.foo(msg); } public void setIocxService(IocxService iocxService){ this.iocxService = iocxService; } }

public class IocxServiceImpl implements IocxService { private IocxDao iocxDao; private Set<String> infos; private List<IocxAccount> accounts; private Map<String, String> mapData; @Override public String foo(String msg) { System.out.println("IocxServiceImpl = " + msg); System.out.println("infos = " + infos); return iocxDao.iocxFoo("account"); } public void setIocxDao(IocxDao iocxDao) { this.iocxDao = iocxDao; } public void setInfos(Set<String> infos) { this.infos = infos; } public void setAccounts(List<IocxAccount> accounts) { this.accounts = accounts; } public void setMapData(Map<String, String> mapData) { this.mapData = mapData; } }

public class IocxDaoImpl implements IocxDao { private String info; private Integer rows; public IocxDaoImpl(String info) { this.info = info; System.out.println("单参数构造方法"); } public IocxDaoImpl(String info, Integer rows) { this.info = info; this.rows = rows; System.out.println("俩参数构造方法"); } @Override public String iocxFoo(String msg) { return "IocxDaoImpl response"; } }
IocxController 为 Controller 层,定义一个类型为 IocxService(Service层) 的依赖属性,同时也定义了这个依赖属性的 set 方法。
IocxServiceImpl 为 Service 层,定义了一个类型为 IocxDao(Dao层) 的依赖属性,同时定义了另外三个 Set、List 和 Map 属性,并为这四个属性定义 set 方法
IocxDaoImpl 为 Dao 层,定义了两个不同参数的构造方法以及实现了 IocxDao 接口的 iocxFoo 方法。
就这样,Controller 层依赖于 Service 层,Service 层依赖于 Dao 层。
再来看一下 XML 配置文件 beans.xml 当中的配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <!-- 默认实现单例: scope="singleton" --> <!-- 要实现多例: scope="prototype" --> <bean id="controller" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.controller.IocxController" scope="prototype"> <!-- DI,依赖注入,基于属性往对应的对象中注入数据 --> <property name="iocxService" ref="service"/> </bean> <bean id="service" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.service.impl.IocxServiceImpl"> <property name="iocxDao" ref="dao"/> <!-- Set注入 --> <property name="infos"> <set> <value>aaa</value> <value>bbb</value> <value>ccc</value> </set> </property> <!-- List注入 --> <property name="accounts"> <list> <ref bean="abc1"/> <ref bean="abc2"/> <ref bean="abc3"/> </list> </property> <!-- Map注入 --> <property name="mapData"> <map> <entry key="k1" value="v1"/> <entry key="k1" value="v1"/> </map> </property> </bean> <bean id="abc1" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.pojo.IocxAccount"> <property name="name" value="hahah-haha"/> </bean> <bean id="abc2" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.pojo.IocxAccount"> <property name="name" value="hahah-haha"/> </bean> <bean id="abc3" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.pojo.IocxAccount"> <property name="name" value="hahah-haha"/> </bean> <bean id="dao" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.dao.impl.IocxDaoImpl"> <constructor-arg value="test" index="0"/> <constructor-arg value="1024" index="1"/> </bean> <!-- 懒加载:用到时才加载,不用时不加载 --> <bean id="orderTestLazy" class="com.jack.course.spring.iocx.pojo.OrderTestLazy" lazy-init="true"/> </beans>
从 XML 配置文件中可以看到,我们将每一个类都通过 id 和 class 对应的关系放入到了每个 bean 标签当中,id需要是唯一的,这就有点像上面我们自己实现 IoC 的时候定义的properties配置文件,Spring 一样是通过反射机制去加载类和生成对象。同时,我们看到配置文件中是通过 property 标签,基于属性的名字往对应的对象中去注入数据,这就是所谓的 DI(依赖注入),不过这里有个前提,这个属性必须在对应的类中定义且实现了它的 set 方法。另外,像非自定义的属性类型 Set、List、Map 的属性,XML文件中同样描述了如何注入。下面是测试程序:

public class App { @Test public void testNormal() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocx/beans.xml"); IocxController controller = context.getBean("controller", IocxController.class); String response = controller.iocxFoo("hello"); System.out.println("response:::" + response); } /** * 测试单例/多例模式 * 默认: scope="singleton" * 要实现多例: scope="prototype" */ @Test public void testScope() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocx/beans.xml"); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { IocxController controller = context.getBean("controller", IocxController.class); System.out.println("controller = " + controller); } } @Test public void testFactory() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocx/beans.xml"); Object obj = context.getBean("beanFactory"); // com.jack.course.spring.iocx.service.impl.IocxServiceImpl@6b53e23f System.out.println("obj = " + obj); } /** * 测试懒加载 * * 默认是非懒加载 * * 需要配置懒加载时,设置属性 lazy-init="true" */ @Test public void testLazyInit() { ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocx/beans.xml"); // Object controller = context.getBean("controller"); Object orderTestLazy = context.getBean("orderTestLazy"); // System.out.println("controller = " + controller); System.out.println("orderTestLazy = " + orderTestLazy); } }
步骤是先读取配置文件,再生成实例化对象,最后再调用方法。使用配置文件的方法看上去比较麻烦,现在已经很少有人使用这种方式。
五、使用注解+XML文件配置IoC
同样,还说先定义两个接口

public interface IocaService { String foo(String msg); }

public interface IocaDao { String foo(String msg); }
接着是三个类,IocaController、IocaServiceImpl 和 IocaDaoImpl

@Controller // 相当于是<bean id=xxx class=xxx> public class IocaController { @Autowired // 相当于是 <propertity name=iocaService ref=""> private IocaService iocaService; public String foo(String msg) { return iocaService.foo(msg); } @Autowired private Gson gson; public String format(Object object) { return gson.toJson(object); } }

@Service public class IocaServiceImpl implements IocaService { @Autowired private IocaDao iocaDao; @Override public String foo(String msg) { return iocaDao.foo(msg); } }

@Repository public class IocaDaoImpl implements IocaDao { @Override public String foo(String msg) { System.out.println("msg = " + msg); return "dao response!!!"; } }
我们注意到:Controller、Service、Dao层分别使用 @Controller、@Service 和 @Repository 注解,关联属性使用 @Autowired 注解注入数据。
再来看一下 XML配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 创建容器时指定扫描包的路径 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.jack.course.spring.ioca"/> <!-- 因为不能给非自定义类加注解,所以需要在配置文件中注明 --> <bean id="gson" class="com.google.gson.Gson"/> </beans>
配置文件中主要有两个内容,一个是指明注解扫描的包的路径,二是 IocaController 类中定义了 Gson 类型的属性,该类属于第三方 Jar包,没有办法添加注解,所以需要在配置文件中注明。下面是测试程序:

public class App { @Test public void testNormal() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioca/beans.xml"); IocaController controller = applicationContext.getBean(IocaController.class); String resp = controller.foo("hello"); System.out.println("resp = " + resp); } @Test public void testFormat() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("ioca/beans.xml"); IocaController controller = applicationContext.getBean(IocaController.class); Map<String, String> mapData = Maps.newHashMap(); mapData.put("abc", "xyz"); mapData.put("name", "jim"); String resp = controller.format(mapData); System.out.println("resp = " + resp); } }
步骤同样是先读取配置文件,再生成实例化对象,最后再调用方法。注解加配置文件的方式看上去比较简介,但是如果引入的第三方 Jar包比较多,在配置文件中就需要添加很多内容,所以这种方式也不建议使用。
六、使用全注解配置IoC
使用全注解的方式我们就不需要 XML 配置文件了,只需要新增一个配置类。同时,如果有一些数据库的配置文件需要加载的话,也可以在配置文件中进行配置
/** * 注解配置文件 * @author Luolei */ // 相当于 beans.xml,标注这是一个配置类 @Configuration // <context:component-scan base-package="com.jack.course.spring.ioca"/> @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.jack.course.spring.ioca") // 相当于我们自己实例化了一个Properties对象, 并将相关数据读进来 @PropertySource("ioca/db.properties") public class IocaConfiguration { // 相当于 <bean id="gson" class="com.google.gson.Gson"/> @Bean public Gson createGson(){ return new Gson(); } @Value("${driver}") private String driver; @Value("${url}") private String url; @Value("${usname}") private String username; @Value("${passwd}") private String passwd; @Bean public DataSource createDataSource(){ DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(passwd); System.out.println("config datasources: " + driver + "*" + url + "*" + username + "*" + passwd); return dataSource; } }
测试程序如下:

/** * 读取配置类IocaConfiguration */ public class App { @Test public void testFormat() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocaConfiguration.class); IocaController controller = applicationContext.getBean(IocaController.class); Map<String, String> mapData = Maps.newHashMap(); mapData.put("abc", "123"); mapData.put("name", "456"); String resp = controller.format(mapData); System.out.println("resp = " + resp); } @Test public void testDataSource() { ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocaConfiguration.class); IocaController controller = applicationContext.getBean(IocaController.class); controller.callDataSource(); } }
这里读取的就不是 XML 配置文件,而是上面那个配置类。
常用注解说明:
- @Component
- 用于把当前类对象存入spring容器中;
- 属性 value:用于指定bean的id。当我们不写时,它的默认值是当前类名首字母改小写;
- @Controller
- 一般用于表现层;
- @Service
- 一般用于业务层;
- @Repository
- 一般用于持久层;
以上三个注解他们的作用和Conmponant一样。
它们三个是spring框架为我们提供明确的三层使用的注解,使我们的三层对象更加清晰用于注入数据的。
它们的作用就和在 xml 配置文件中的 bean 标签中写一个<property>标签的作用是一样的。
- @Autowired
- 自动按照类型注入,只要容器中有唯一的一个 bean 对象类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,就可以注入成功;
- 如果 IoC 容器中没有任何 bean 的类型和要注入的变量类型匹配,则报错;
- 如果 IoC 容器中有多个类型匹配时,先按照数据类型在 IoC中 查找,再以变量名称为 IoC 中 id 查找 bean 对象注入;
- 书写位置可以是变量上,也可以是方法上;
- 和使用 XML 配置文件不一样的是:在使用注解注入时,set方法就不是必须的了;
- @Qualifier
- 在按照类中注入的基础之上再按照名称注入。它在给类成员注入时不能单独使用。但是在给方法参数注入时可以;
- 属性value:用于指定注入bean的 id;
- @Resource
- 直接按照bean的id注入,可以独立使用;
- 属性name:用于指定bean的 id;
以上三种注解只能注入其他bean类型的数据,而基本类型和String类型无法使用上述注解实现。另外,集合类型的注入只能用 XML 文件来实现。
- @Value
- 用于注入基本类型和String类型的数据;
- 属性value:用于指定数据的值,它可以使用 spring 中 SpEL表达式;
- SpEL 表达式的写法:${表达式};
- @Scope
- bean的作用范围;
- 属性value:两个值 singleton 和 prototype;
- singleton单例模式:全局有且仅有一个实例;
- prototype原型模式:每次获取Bean的时候会有一个新的实例;
新增注解:
- @Configuration
- 指定当前类是一个配置类,它的作用和bean.xml一样;
- 当配置类作为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象创建的参数时,该注解可以不写;
- 配置类中可以不写,因为获取容器时通过ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfiguration.class);扫描主配置类。其余配置类需要写。并在主配置类中@ComponentScan({"com.test"})添加扫描的类,建议最好还是写,免得麻烦;
- @ComponentScan
- 用于通过注解指定spring在创建容器时要扫描的包;
- 属性value:它和basePackages的作用一样,都适用于指定创建容器时要扫描的包;
- 我们使用此注解就等同于在xml中配置了:<context:component-scan base-package="com.jack.course.spring.ioca"/>;
- 默认就会装配标识了@Controller,@Service,@Repository,@Component注解的类到spring容器中。当然,这个的前提就是你需要在所扫描包下的类上引入注解。
- @Bean
- 把当前方法的返回值作为bean对象存入spring的ioc容器中;
- 属性name:用于指定bean的id。默认值是当前方法的名称;
- 当我们使用注解配置方法时,如果方法有参数,spring框架会去容器中查找有没有可用的bean对象;
- 查找的方式和Autowired注解的作用是一样的。先根据数据类型查找,再根据id查找,均在ioc容器中查找;
- @PropertySource
- 用于指定properties文件的位置;
- 属性value:指定文件的名称和路径;
- @Import
- 导入其他的配置类.指定配置类的.class;
- 属性value:用于指定配置类的字节码;
- 当我们使用Import的注解之后,有Import注解的类就是父配置类即主配置类,而导入的都是子配置类;
七、Spring 整合 Junit

@Controller // 相当于是<bean id=xxx class=xxx> public class IocaController { @Autowired // 相当于是 <propertity name=iocaService ref=""> private IocaService iocaService; public String foo(String msg) { return iocaService.foo(msg); } @Autowired private Gson gson; public String format(Object object) { return gson.toJson(object); } @Autowired private DataSource dataSource; public void callDataSource(){ System.out.println(dataSource); } }

// 相当于 beans.xml,标注这是一个配置类 @Configuration // <context:component-scan base-package="com.jack.course.spring.ioca"/> @ComponentScan(basePackages = "com.jack.course.spring.ioca") // @ComponentScan(value = "com.jack.course.spring.ioca") // 相当于我们自己实例化了一个Properties对象, 并将相关数据读进来 @PropertySource("ioca/db.properties") public class IocaConfiguration { // 相当于 <bean id="gson" class="com.google.gson.Gson"/> @Bean(name = "gson") public Gson createGson(){ return new Gson(); } @Value("${driver}") private String driver; @Value("${url}") private String url; @Value("${usname}") private String username; @Value("${passwd}") private String passwd; /** * 创建数据源对象 * @return DataSource */ @Scope("prototype") @Bean(name = "dataSource") public DataSource createDataSource(){ DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setUsername(username); dataSource.setPassword(passwd); System.out.println("config datasources: " + driver + "*" + url + "*" + username + "*" + passwd); return dataSource; } }
使用Spring 做单测
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) /** * 加载配置类IocaConfiguration * 相当于: ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(IocaConfiguration.class) * * 也可以使用xml配置文件的形式 * 相当于:ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("iocx/beans.xml"); */ // @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:iocx/beans.xml"}) @ContextConfiguration(classes = IocaConfiguration.class) public class App2 { @Autowired private IocaController controller; @Test public void testNormal() { String resp = controller.foo("hello"); System.out.println("resp = " + resp); } @Test public void testFormat() { Map<String, String> mapData = Maps.newHashMap(); mapData.put("abc", "xyz"); mapData.put("name", "jim"); String resp = controller.format(mapData); System.out.println("resp = " + resp); } }
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
- 就是一个运行器,测试时使用,里面的参数需要传入 .class类对象;
- @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) 表示让测试运行于 Spring 环境;
@ContextConfiguration(classes = IocaConfiguration.class)
- 用于Spring整合JUnit4测试时,使用注解引入配置类或xml配置文件;
- 属性 locations:引入xml 配置文件;
- 属性classes:引入配置类;
八、Spring 整合 JDBC
XML 配置文件版
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="datasource"/> </bean> <bean id="datasource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource"> <property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"/> <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.182.128:3306/cakes"/> <property name="username" value="root"/> <property name="password" value="123456"/> </bean> </beans>
首先将 jdbcTemplate 和 datasource 加入bean 容器
测试程序
/** * 读取jdbc/beans.xml文件中的配置 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:jdbc/beans.xml") public class App { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate template; @Test public void testSpringJdbcTemplate(){ template.execute("insert into user(name,passwd) values('jack','123455')"); } }
注解版
数据库连接配置

driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.182.128:3306/cakes usname=root passwd=123456
配置类

@Configuration @ComponentScan(basePackages="com.jack.course.spring.jdbc") @PropertySource("jdbc/db.properties") public class JdbcConfiguration { @Value("${driver}") private String driver; @Value("${url}") private String url; @Value("${usname}") private String userName; @Value("${passwd}") private String passwd; /** * 用于创建一个JdbcTemplate对象 */ @Bean public JdbcTemplate createTemplate(DataSource dataSource) { return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource); } /** * 创建数据源对象 */ @Bean public DataSource createDataSource() { DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource(); dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver); dataSource.setUrl(url); dataSource.setUsername(userName); dataSource.setPassword(passwd); return dataSource; } }
测试程序
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = JdbcConfiguration.class) public class App2 { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void testSpringJdbcTemplate(){ jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into user(name,passwd) values('木木','123459')"); } }
