❗❗ 必看经验
在博主刷题期间,基本上是碰到一道二叉树就不会碰到一道就不会,有时候一个下午都在搞一道题,看别人解题思路就算能看懂,自己写就呵呵了。一气之下不刷了,改而先去把二叉树的基础算法给搞搞懂,然后又去把剑指offer里所有关于二叉树的题目挑了出来做,越不会就越把自己往奔溃的边缘虐。还别说,这一搞,神清气爽。也怪之前什么基础准备都没有就直接去题库里挑战题目了。
在这里想说的是,在刷题之前一定得先有自己的知识储备,比如说最起初的数据结构总得会吧,或者说基础的数据结构里都有些啥啥时重点之类的。别像我一样什么都不准备的上来就是刷题,越刷越怀疑人生,每题都是打击。拿二叉树的遍历来说,你连个遍历里的递归结果怎么的出来的都不知道,就算这个算法背下来了也还是不懂,而且就三行代码,你好意思只背不理解吗。在我刷题过程中,很多题都是万变不离其宗重点就是遍历的那三行代码。
所以,二叉树起步第一步,先把基础算法在纸上图图画画吧,一件事半功倍的事。是递归的就从结束条件哪里一步一步往回退,不用递归的就去了解二叉树与进栈入栈的关系。传送门 - 二叉树的基础算法
目录
- 题4:重建二叉树
- 题17:树的子结构
- 题18:二叉树的镜像
- 题22:从上往下打印二叉树
- 题23:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
- 题24:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
- 题26:二叉搜索树与双向链表
- 题38:二叉树的深度
- 题39:平衡二叉树
- 题57:二叉树的下一个结点
- 题58:对称的二叉树
- 题59:按之字形顺序打印二叉树
- 题60:把二叉树打印成多行
- 题61:序列化二叉树
- 题62:二叉搜索树的第k小的结点
二叉树结构:
function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
题4:重建二叉树
难度:♡♡
前中序
//pre:[1, 2, 4, 7, 3, 5, 6, 8]
//vin: [4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6]
function reConstructBinaryTree(pre, vin) {
let tree = null
if (pre.length > 1) {
const root = pre.shift() //从前序遍历头中取出一个的父节点
const index = vin.indexOf(root) //父节点位于中序遍历中的位置
tree = new TreeNode(root)
tree.left = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(0, index), vin.slice(0, index)) //递归父节点左边的节点
tree.right = reConstructBinaryTree(pre.slice(index), vin.slice(index + 1)) //递归父节点右边的节点
} else if (pre.length === 1) {
tree = new TreeNode(pre[0])
}
return tree
}
后中序
//post:[7, 4, 2, 5, 8, 6, 3, 1]
//vin: [4, 7, 2, 1, 5, 3, 8, 6]
function reConstructBinaryTree(post, vin) {
let tree = null
if (post.length > 1) {
const root = post.pop() //从后序遍历尾中取出一个的父节点
const index = vin.indexOf(root) //父节点位于中序遍历中的位置
tree = new TreeNode(root)
tree.left = reConstructBinaryTree(post.slice(0, index), vin.slice(0, index)) //递归父节点左边的节点
tree.right = reConstructBinaryTree(post.slice(index), vin.slice(index + 1)) //递归父节点右边的节点
} else if (post.length == 1) {
tree = new TreeNode(post[0])
}
return tree
}
题17:树的子结构
难度:♡♡♡♡
子结构
题目:输入两棵二叉树A,B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(ps:我们约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
思路:DoesTreeHaveTree 函数有点像先序遍历中的递归,得到父节点值比较,如果相等就再分别比较它们的左节点和右节点值是否相等
function HasSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) {
let result = false
if (pRoot1 != null && pRoot2 != null) {
if (pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val) { //判断父节点
result = DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1, pRoot2)
}
if (!result) {//父节点不满足,看看它左节点是否满足
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2)
}
if (!result) {//左节点不满足,从其右节点是否满足
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
}
}
return result
}
function DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1, pRoot2) {
if (pRoot2 == null) { //root2比到底了,则一定是子结构
return true
}
if (pRoot1 == null) { //root2还没比完,root1就到底了,则一定不是子结构
return false
}
if (pRoot1.val != pRoot2.val) { //节点值不相等
return false
}
//节点值相等,继续比较它们的左右节点值是否相等
return DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.left) && DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.right)
}
举一反三 子树
function HasSubtree(pRoot1, pRoot2) {
let result = false
if (pRoot1 != null && pRoot2 != null) {
if (pRoot1.val == pRoot2.val) { //判断父节点
result = DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1, pRoot2)
}
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2)
}
if (!result) {
result = HasSubtree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2)
}
}
return result
}
function DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1, pRoot2) {
//同时到达底部null,才是子树
if (!pRoot2 && !pRoot1) {
return true
}
//此时已经排除了两者都为null的情况,只要有一个为null则不是
if (!pRoot2 || !pRoot1) {
return false
}
//没到达底部的时候,没有一个为null
if (pRoot1.val != pRoot2.val) {
return false
}
//节点值相等,继续比较它们的左右节点值是否相等
return DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.left) && DoesTreeHaveTree(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.right)
}
题18:二叉树的镜像
难度:♡♡
思路:中序遍历,每次都交换下本轮节点的左右节点
function Mirror(root) {
if (root === null) {
return
}
const temp = root.left
root.left = root.right
root.right = temp
Mirror(root.left)
Mirror(root.right)
}
题22:从上往下打印二叉树
难度:♡♡♡♡♡
思路:即二叉树的层次遍历(广度优先遍历,利用队列即可)

function PrintFromTopToBottom(root) {
// write code here
let tempTree = []
let rs = []
if (root) tempTree.push(root)
while (tempTree.length) {
root = tempTree.shift()
rs.push(root.val)
if (root.left) tempTree.push(root.left)
if (root.right) tempTree.push(root.right)
}
return rs
}
题23:二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
难度:♡♡♡♡
题目:输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则输出Yes,否则输出No。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
思路:找规律。后序遍历最后一个是根节点,数组中可以分为比根节点值小的部分,与比根节点大的部分。然后递归。例:(3 6 5) (9) 7
重要的是递归的结束条件sequence.length <= 1,一开始以为只要等于1就可以了,忽略了数组左边或者右边部分为空的情况,比如[6, 5, 9, 7]递归到[6,5]时,左边为[],右边为[6]
//sequence:[3, 6, 5, 9, 7]
//sequence:[6, 5, 9, 7]
//sequence:[3, 6, 4, 5, 9, 7]
function VerifySquenceOfBST(sequence) {
if (sequence.length) {
return helpVerify(sequence)
}
return false
}
function helpVerify(sequence) {
if (sequence.length <= 1) {//此条件下,递归结束。
return true
}
let index = 0
const key = sequence[sequence.length - 1] //后序遍历最后一个是根节点
while (sequence[index] < key) { //在数组中查找比根节点小和比根节点大的分界点
index++
}
const pos = index //记录分界点,此时分界点左边全是小于根节点值的
while (sequence[index] > key) { //判断根节点右边是否全部大于根节点值
index++
}
if (index != (sequence.length - 1)) { //接while
return false
}
//现在有左右两个部分,递归执行
return helpVerify(sequence.slice(0, pos)) && helpVerify(sequence.slice(pos, sequence.length - 1))
}
题24:二叉树中和为某一值的路径
难度:♡♡♡♡
题目:输入一颗二叉树的根节点和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。路径定义为从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。(注意: 在返回值的list中,数组长度大的数组靠前)
思路:万变不离其宗——中序遍历
function FindPath(root, expectNumber) {
// write code here
let result = [] //存放所有满足条件的路径
if (root) {
let path = [] //记录当前路径,当当前路劲满足条件的时候,push进result,
let currentSum = 0 //记录当前路径的和
isPath(root, expectNumber, path, result, currentSum)
}
return result
}
function isPath(root, expectNumber, path, result, currentSum) {
currentSum += root.val
path.push(root.val)
if (currentSum == expectNumber && !root.left && !root.right) { //根结点开始往下一直到叶结点,当前sum等于目标数
result.push(path.slice(0)) //注意:这里不能直接push(path),数组是引用类型。也可ES6用法:push([...path])
}
if (root.left) { //当前root有左节点
isPath(root.left, expectNumber, path, result, currentSum)
}
if (root.right) { //当前root有右节点
isPath(root.right, expectNumber, path, result, currentSum)
}
// 走到底(叶子)了,无论当前路径满不满足条件,都要回退到父节点继续搜索
path.pop()
}
举一反三
如果不是从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点,而是任意路径呢?
参考子树与子结构
题26:二叉搜索树与双向链表
难度:♡♡♡
思路:重点就是用指针p记录上一个的节点。画个图就很好理解了。还是以中序遍历为顺序
function Convert(pRootOfTree) {
if (!pRootOfTree) return null
let p = null //指针,记录前一个结点
p = ConvertSub(pRootOfTree, p)
let re = p
while (re.left) {
re = re.left
}
return re
}
function ConvertSub(pNode, p) {
if (pNode.left) p = ConvertSub(pNode.left, p);
if (p == null) {
p = pNode //找到最左端
} else {
p.right = pNode
pNode.left = p
p = pNode
}
if (pNode.right) p = ConvertSub(pNode.right, p);
return p
}
题38:二叉树的深度
难度:♡♡
树的深度是从根节点开始(其深度为1)自顶向下逐层累加。高度是从叶节点开始(其高度为1)自底向上逐层百累加的。虽然树的深度和高度一样,但是具体到树的某个节点,其深度和高度是不一样的。
方法一:
function TreeDepth(pRoot) {
if (!pRoot) return 0;
var left = 1 + TreeDepth(pRoot.left);
var right = 1 + TreeDepth(pRoot.right);
return Math.max(left, right)
}
方法二:
该方法从根路径开始,是题24的学以致用,都是找个数组记录路径,每走到一个叶子节点就计算当前路径长,和上一次的长度做比较。然后pop退回父节点计算别的路径的长度。
function TreeDepth(pRoot) {
// write code here
let longest = 0
if (pRoot) {
let path = []
longest = getTreeDepth(pRoot, path, longest)
}
return longest
}
function getTreeDepth(pRoot, path, longest) {
path.push(pRoot.val)
if (!pRoot.left && !pRoot.right && path.length > longest) {
longest = path.length
}
if (pRoot.left) {
longest = getTreeDepth(pRoot.left, path, longest)
}
if (pRoot.right) {
longest = getTreeDepth(pRoot.right, path, longest)
}
path.pop()
return longest
}
题39:平衡二叉树
难度:♡♡♡
是一空树或它的左右两个子树的高度差(称为平衡因子)不大于1的二叉排序树。并且左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。
思路:牢牢抓住平衡二叉树定义的重点,左右两个子树都是一棵平衡二叉树。二叉树深度稍微改动下就好了,加一个判断左右子树高度差是否不大于1:Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ?
var isBalanced = function(root) {
return judge(root) !== -1
};
const judge = (root) => {
if(root == null){
return 0
}
let left = judge(root.left);
if(left === -1){
return -1
}
let right = judge(root.right);
if(right === -1){
return -1
}
return Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ? -1 : Math.max(left, right) + 1
}
题57:二叉树的下一个结点
难度:♡♡♡

function GetNext(pNode) {
// write code here
if (!pNode) {
return null
}
//有右子树的
if (pNode.right) {
pNode = pNode.right;
while (pNode.left) { //下个结点就是其右子树最左边的点
pNode = pNode.left
}
return pNode
}
// 没有右子树
while (pNode.next) { //有父节点
let p = pNode.next //p指向当前节点的父节点
if (p.left == pNode) { //直到当前结点是其父节点的左孩子为止
return p
}
pNode = pNode.next
}
return null //尾节点
}
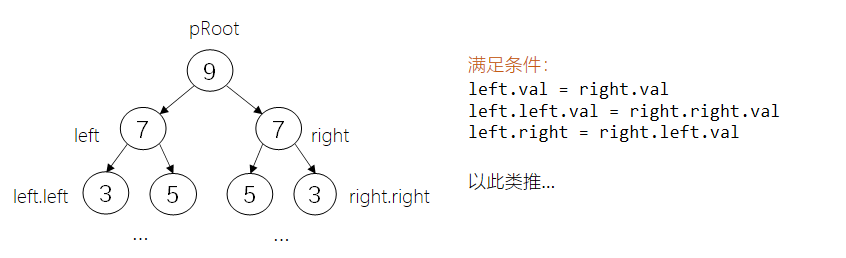
题58:对称的二叉树
难度:♡♡♡♡♡
思路:之前做过的递归都是一棵树的递归,现在分别将这棵树的左右子树递归
function isSymmetrical(pRoot) {
// write code here
if (pRoot == null) {
return true
}
return judge(pRoot.left, pRoot.right)
}
function judge(left, right) {
// 以下判断是否都走到底
if (left == null) {
return right == null
}
if (right == null) {
return false
}
// 都未走到底
if (left.val != right.val)
return false
return judge(left.left, right.right) && judge(left.right, right.left)
}
题59:按之字形顺序打印二叉树
难度:♡♡♡♡
这道题的解题方法妙就妙在还是按层数从左到右保存节点值,有些人(对,就是我)在层次遍历的代码上加工,对push这一步分类讨论,想着这里是push左边的还是右边的,最后把自己绕晕了。
层次遍历是shift出一个,push进它的左右节点值。这里在while里面加了个for循环,妙的是对同一层的节点进行处理,就算是偶数层要求倒着输出,我们只要有了该层的顺序数组,只要对该数组进行reverse就行了。谁还想去倒着额遍历偶数层的节点,疯了吗吗吗

function TreeNode(x) {
this.val = x;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
function Print(pRoot) {
if (!pRoot) return []
let queue = []
let result = []
let flag = true //true奇数
queue.push(pRoot)
while (queue.length) {
let tempArr = [] //用来存放当前层所有节点的值
const len = queue.length //存放当前队列的长度
for (let i = 0; i < len; i++) {
let temp = queue.shift();
tempArr.push(temp.val);
if (temp.left) {
queue.push(temp.left);
}
if (temp.right) {
queue.push(temp.right);
}
}
if (!flag) {
tempArr.reverse();
}
flag = !flag;
result.push(tempArr);
}
return result
}
题60:把二叉树打印成多行
难度:♡♡♡
题目:从上到下按层打印二叉树,同一层结点从左至右输出。每一层输出一行。
把上面那一题关于倒序某一层所有值的代码去掉就行了。
题61:序列化二叉树
难度:♡♡♡♡
此题想吐槽,重点还是看第4题的重建二叉树吧
function Serialize(pRoot) {
if (!pRoot) {
res.push('#');
} else {
res.push(pRoot.val);
Serialize(pRoot.left);
Serialize(pRoot.right);
}
}
function Deserialize(s) {
if (res.length < 1) return null;
let node = null;
let cur = res.shift();
if (typeof cur == 'number') {
node = new TreeNode(cur);
node.left = Deserialize(s);
node.right = Deserialize(s);
}
return node;
}
题62:二叉搜索树的第k小的结点
难度:♡♡♡♡
思路:第k小即是中序遍历的第K个节点。
占个坑:用非递归写一下
占个坑:第K大呢?
function KthNode(pRoot, k) {
// write code here
if (!pRoot || k <= 0)
return null
let target = null
KthNodeCore(pRoot)
function KthNodeCore(pRoot) {
if (pRoot.left)
KthNodeCore(pRoot.left)
if (!target) {
if (k == 1) {
target = pRoot
return
}
k--
}
if (pRoot.right)
KthNodeCore(pRoot.right)
}
return target
}
扩展 二叉搜索树的第k大节点
二叉搜索树的中序遍历为 递增序列 。
根据以上性质,易得二叉搜索树的 中序遍历倒序 为 递减序列 。
因此,求 “二叉搜索树第 kk 大的节点” 可转化为求 “此树的中序遍历倒序的第 k 个节点”。
我下面的代码在找到第k个后就直接结束递归了,也可以用中序的逆序遍历将逆序存入数组arr,然后取arr[k-1]
function kthLargest(pRoot, k) {
// write code here
if (!pRoot || k <= 0)
return null
let target = null
KthNodeCore(pRoot)
function KthNodeCore(pRoot) {
if (pRoot.right)
KthNodeCore(pRoot.right)
if (!target) {
if (k == 1) {
target = pRoot
return
}
k--
}
if (pRoot.left)
KthNodeCore(pRoot.left)
}
return target.val
}