1.1 @Results
@Results注解来映射查询结果集到实体类属性
(1)@Results的基本用法。当数据库字段名与实体类对应的属性名不一致时,可以使用@Results映射来将其对应起来。
column为数据库字段名,porperty为实体类属性名,jdbcType为数据库字段数据类型,id为是否为主键。
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "userId",jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER),
@Result(column = "username", property = "userName",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR),
@Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday",jdbcType = JdbcType.DATE),
@Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR),
@Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
})
List<User> findAll();
如上所示的数据库字段名id与实体类属性名userId,就通过这种方式建立了映射关系。名字相同的可以省略。
1.2 @ResultMap
(2)@ResultMap的用法。当这段@Results代码需要在多个方法用到时,为了提高代码复用性,我们可以为这个@Results注解设置id,然后使用@ResultMap注解来复用这段代码。
@Select("select * from user")
@Results(id = "userMap",value = {
@Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "userId",jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER),
@Result(column = "username", property = "userName",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR),
@Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday",jdbcType = JdbcType.DATE),
@Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR),
@Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress",jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)
})
List<User> findAll();
用@ResultMap()注解来引用
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
@ResultMap(value = {"userMap"})
User findById(Integer id);
1.3 @One
(3)@One的用法。当我们需要通过查询到的一个字段值作为参数,去执行另外一个方法来查询关联的内容,而且两者是一对一关系时,可以使用@One注解来便捷的实现。
一对一:一般都用立即加载
一对多:一般都用懒加载/延迟加载
fetchType = FetchType.EAGER //设置为立即加载
package com.jh.dao; import com.jh.entity.Account; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.One; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.FetchType; import java.util.List; public interface AccountDao { /** * 查询所有账户,并且获取每个账户所属的用户信息 * * @return */ @Select("select * from account") @Results(id = "accountMap", value = { @Result(id = true, property = "id", column = "id"), @Result(property = "uid", column = "uid"), @Result(property = "money", column = "money"), @Result(property = "user", column = "uid", one = @One(select = "com.jh.dao.UserDao.findById", fetchType = FetchType.EAGER)) }) List<Account> findAll(); }
package com.jh.dao; import com.jh.entity.User; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*; import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType; import java.util.List; public interface UserDao { @Select("select * from user") @Results(id = "userMap", value = { @Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "userId", jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER), @Result(column = "username", property = "userName", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday", jdbcType = JdbcType.DATE), @Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR) }) List<User> findAll(); @Select("select * from user where id=#{id}") @ResultMap(value = {"userMap"}) User findById(Integer id); } }
1.4 @Many
(4)@Many的用法。与@One类似,只不过如果使用@One查询到的结果是多行,会抛出TooManyResultException异常,这种时候应该使用的是@Many注解,实现一对多的查询
package com.jh.dao; import com.jh.entity.User; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.FetchType; import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType; import java.util.List; public interface UserDao { @Select("select * from user") @Results(id = "userMap", value = { @Result(id = true, column = "id", property = "userId", jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER), @Result(column = "username", property = "userName", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column = "birthday", property = "userBirthday", jdbcType = JdbcType.DATE), @Result(column = "sex", property = "userSex", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column = "address", property = "userAddress", jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR), @Result(column = "id", property = "accounts",many = @Many(select = "com.jh.dao.AccountDao.findById",fetchType = FetchType.LAZY)) }) List<User> findAll(); } }
package com.jh.dao; import com.jh.entity.Account; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.One; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Result; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Results; import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Select; import org.apache.ibatis.mapping.FetchType; import java.util.List; public interface AccountDao {/** * 根据用户id查询账户信息 * @param id * @return */ @Select("select * from account where uid=#{uid}") List<Account> findById(Integer id); }
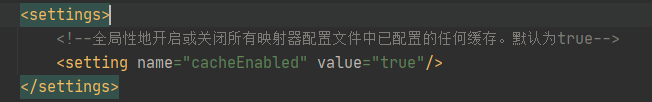
1.5 @CacheNamespace
@CacheNamespace(blocking = true):写在接口名上面,注解方式开启二级缓存

参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/cherlshall/article/details/80950150