技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性。
向量容器vector是一个动态数组,内存连续,它是动态分配内存,且每次扩张的原来的二倍.
他的结构如下

一 定义
vector< 类型 > 标识符(最大容量,初始所有值)
vector是一种类模板,那么他有很多行为与类相似
头文件 #include <vector>
//a.定义 vector<typeName> v; vector<int> v; //b.拷贝构造 vector<typeName> v1(v); 例:vector<int> v1(v); vector<int> v1(v); //c.赋值拷贝 v1 = v; //如果v的size比v1的size大,则自动扩充v1的空间,反之亦然 //d.按指定元素个数定义 vector<int> v2(5); //v2含有5个值为0的元素 //e.指定元素个数及类型 vector<int> v3(5,10);//v3包含5个值为10的int类型元素 //f.与array间的转换 int a[3]={0,1,2}; vector<int> v4(a,a+3);
二 基本使用
vector<int> v; //在vector尾端插入元素 //但是没有在前面插入元素,上面的vector结构图中,我们可以看出来vector是一种向后扩充的容器, //如果在前面插入,那后面所有的元素将后移,造成巨大的消耗,所以没有push_front() //同理没有pop_front() v.push_back(1); //删除最后一个元素 v.pop_back(); //返回元素个数 int count = v.size(); //重新设定vector的size v.resize(2*(v.size())); //判断容器是否为空 bool isEmpty = v.empty(); //[index]操作,返回下表为index的元素 int tmp = v[1]; //定义迭代器 vector<int> ::iterator iter = v.begin(); for(int i = 0; i<3; i++ ) { v.push_back(1); // 1 1 1 } //在 v的前面插入两个 5 v.insert(iter, 2, 5); // 5 5 1 1 1 //在头部插入3 v.insert(v.begin(), 3);//3 5 5 1 1 1 //在尾部插入3 v.insert(v.end(), 3);//3 5 5 1 1 1 3 //下表5的前面插入3 v.insert(v.begin()+5, 3);//3 5 5 1 1 3 1 3 //删除指定下标元素 v.erase(v.begin()+1); //3 5 1 1 3 1 3 //清空 v.clear(); //起始地址 v.data(); //最后一个元素后面的地址 v.end(); //实际内存大小 v.capacity(); //at(下标) v.at(1); //返回最后一个元素 v.back(); //返回第一个元素 v.front(); //将指定区间内的元素赋值给v v.assign(v.begin()+1, v.begin()+2); //赋值 将三个 1 赋值给v 那么vecotr将变为 1 1 1 v.assign(3, 1); //最大内存 v.max_size(); //输出 for(auto iii : v) { cout << iii <<endl; }
三 vector支持的算法
增加头文件#include<algorithm> //算法
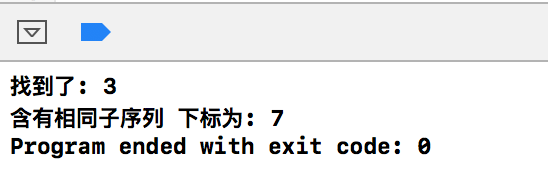
#include <algorithm> int main() { //可以使用的全局算法有 //搜索算法:find() 、search() 、count() 、find_if() 、search_if() 、count_if() //分类排序:sort() 、merge() //删除算法:unique() 、remove() //生成和变异:generate() 、fill() 、transformation() 、copy() //关系算法:equal() 、min() 、max() vector<int> c; for(int i = 0; i<10; i++ ) { c.push_back(i); // } //查找函数 find(begin,end, searchItem) auto pItem = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), 3); if(pItem != c.end()) cout << "找到了: " << *pItem << endl; else cout << "没找到" << endl; vector<int> c1; for(int i = 0; i<10; i++ ) { c1.push_back(i+10); // } //查找函数search 是否包含子序列容器向量 如果包含 返回包含位置 auto pItem1 = ::search(c.begin(), c.end(), c1.begin()+2, c1.begin()+5); if(pItem1 != c.end()) cout << "找到了: " << *pItem1 << endl; else cout << "没找到" << endl; //算法就不一一举例了 return 0; }
输出结果
四 内存管理
上面提到过vector的扩充是以2倍的形式扩充,它的扩充过程可以理解成 if (v.size()元素个数 > v.capacity()实际内存) v.resize(2*v.capacity())
当vector发现元素个数大于实际内存时, vector将重新申请一块内存为原来的内存2倍的空间 然后将原来的元素一一copy过去,我们都知识申请内存是非常耗时的,所以我们一定要把握好vector的内存尺度
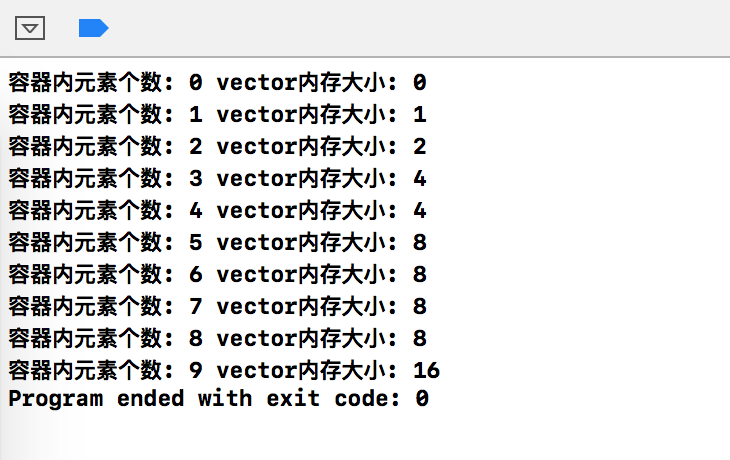
下面来测试一下
void vector_test_capactity() { //创建vector std::vector<int> v; for(int i = 0; i<10 ; i++) { cout<<"容器内元素个数: " << v.size() << " "<<"vector内存大小: " << v.capacity()<<endl; v.push_back(i); } }
输出结果
Source Code
下图是vector类图,类图中的函数为vector一些常用函数,现在来分析一下这些函数

下面是我在Qt中找出的vector的源代码
_Vector_base<_Tp>与_Vector_impl<_Tp>
1 template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc> 2 struct _Vector_base 3 { 4 typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Alloc>::template 5 rebind<_Tp>::other _Tp_alloc_type; 6 typedef typename __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type>::pointer 7 pointer; 8 9 struct _Vector_impl 10 : public _Tp_alloc_type 11 { 12 pointer _M_start; 13 pointer _M_finish; 14 pointer _M_end_of_storage; 15 ... 16 } 17 18 pointer 19 _M_allocate(size_t __n)//申请内存 20 { 21 typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type> _Tr; 22 return __n != 0 ? _Tr::allocate(_M_impl, __n) : 0; 23 } 24 25 void 26 _M_deallocate(pointer __p, size_t __n)//释放内存 27 { 28 typedef __gnu_cxx::__alloc_traits<_Tp_alloc_type> _Tr; 29 if (__p) 30 _Tr::deallocate(_M_impl, __p, __n); 31 } 32 }
你会发现_Vector_base中has a(组合)一个_Vector_impl类,这个类里面包含三个指针分别是_M_start,_M_finish,_M_end_of_storage,结合一下下图你就会明白这三个指针的含义
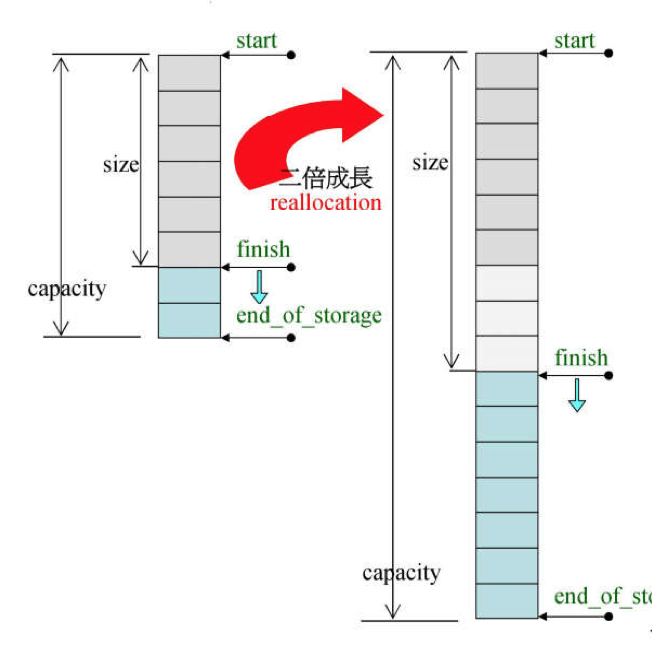
图中的start和finish,end_of_storage分别是上面的三个指针
这个时候我们看下面的源代码begin(),end(),capacity()是不是很容易理解了,_GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT是不抛出任何异常
iterator begin() _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { return iterator(this->_M_impl._M_start); }//返回它的start指针 ... const_iterator end() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { return const_iterator(this->_M_impl._M_finish); }//返回finish指针 ... size_type capacity() const _GLIBCXX_NOEXCEPT { return size_type(this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage//返回start-finish - this->_M_impl._M_start); }
下面我们来看一看vector<_Tp>类,几个相对常用的函数push_back(), operator=和insert()
template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc = std::allocator<_Tp> >
class vector : protected _Vector_base<_Tp, _Alloc>
{
...
void
push_back(const value_type& __x)()
...
vector&
operator=(const vector& __x);
...
iterator
insert(const_iterator __position, size_type __n, const value_type& __x)
}
1.push_back()
void push_back(const value_type& __x) { if (this->_M_impl._M_finish != this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage)//如果不需要申请内存 { _Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl, this->_M_impl._M_finish,__x);//将x赋给finish ++this->_M_impl._M_finish; // => ++finish } else #if __cplusplus >= 201103L _M_emplace_back_aux(__x); #else _M_insert_aux(end(), __x); #endif }
_M_emplace_back_aux
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L template<typename _Tp, typename _Alloc> template<typename... _Args> void vector<_Tp, _Alloc>:: _M_emplace_back_aux(_Args&&... __args) { const size_type __len = _M_check_len(size_type(1), "vector::_M_emplace_back_aux"); pointer __new_start(this->_M_allocate(__len));//申请一段新的内存,将新的start指针指向新内存的起始位置 pointer __new_finish(__new_start);//初始化finish指针 __try { _Alloc_traits::construct(this->_M_impl, __new_start + size(), std::forward<_Args>(__args)...); __new_finish = 0; __new_finish = std::__uninitialized_move_if_noexcept_a (this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_finish, __new_start, _M_get_Tp_allocator());//将finish指针指向新内存的尾端 ++__new_finish; } __catch(...) { if (!__new_finish)//申请不成功销毁 _Alloc_traits::destroy(this->_M_impl, __new_start + size()); else std::_Destroy(__new_start, __new_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator()); _M_deallocate(__new_start, __len); __throw_exception_again; } std::_Destroy(this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_finish, _M_get_Tp_allocator());//销毁旧内存 _M_deallocate(this->_M_impl._M_start, this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage - this->_M_impl._M_start); this->_M_impl._M_start = __new_start; this->_M_impl._M_finish = __new_finish; this->_M_impl._M_end_of_storage = __new_start + __len; }
2.operator=,运用assign函数重新赋值vector
vector&
operator=(initializer_list<value_type> __l)
{
this->assign(__l.begin(), __l.end());
return *this;
}
3.insert(),参数,插入坐标,内存大小,插入变量
iterator insert(const_iterator __position, size_type __n, const value_type& __x) { difference_type __offset = __position - cbegin();//获取间隔 _M_fill_insert(begin() + __offset, __n, __x);//插入变量 return begin() + __offset;//返回插入位置 }
参考<<侯捷STL标准库>>