技术在于交流、沟通,本文为博主原创文章转载请注明出处并保持作品的完整性
unordered_set与与unordered_map相似,这次主要介绍unordered_set
unordered_set它的实现基于hashtable,它的结构图仍然可以用下图表示,这时的空白格不在是单个value,而是set中的key与value的数据包
有unordered_set就一定有unordered_multiset.跟set和multiset一样,一个key可以重复一个不可以
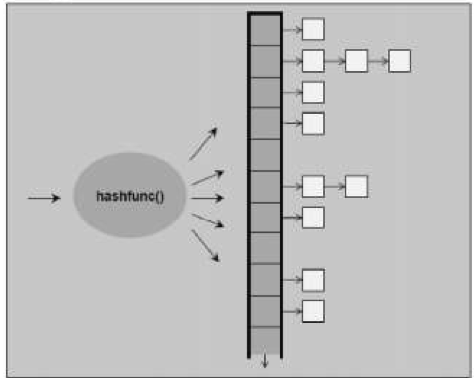
unordered_set是一种无序集合,既然跟底层实现基于hashtable那么它一定拥有快速的查找和删除,添加的优点.基于hashtable当然就失去了基于rb_tree的自动排序功能
unordered_set无序,所以在迭代器的使用上,set的效率会高于unordered_set
template<class _Value, class _Hash = hash<_Value>, class _Pred = std::equal_to<_Value>, class _Alloc = std::allocator<_Value> > class unordered_set : public __unordered_set<_Value, _Hash, _Pred, _Alloc> { typedef __unordered_set<_Value, _Hash, _Pred, _Alloc> _Base; ... }
参数1 _Value key和value的数据包
参数2 _Hash hashfunc获取hashcode的函数
参数3 _Pred 判断key是否相等
参数4 分配器
下面介绍一下unordered_set的基本使用,最后我会分享一下我的测试代码
一 定义
//定义 unordered_set<int> c1; //operator= unordered_set<int> c2; c2 = c1;
二 容量操作
//判断是否为空 c1.empty(); //获取元素个数 size() c1.size(); //获取最大存储量 max_size() c1.max_size();
三 迭代器操作
//返回头迭代器 begin() unordered_set<int>::iterator ite_begin = c1.begin(); //返回尾迭代器 end() unordered_set<int>::iterator ite_end = c1.end(); //返回const头迭代器 cbegin() unordered_set<int>::const_iterator const_ite_begin = c1.cbegin(); //返回const尾迭代器 cend() unordered_set<int>::const_iterator const_ite_end = c1.cend(); //槽迭代器 unordered_set<int>::local_iterator local_iter_begin = c1.begin(1); unordered_set<int>::local_iterator local_iter_end = c1.end(1);
四 基本操作
//查找函数 find() 通过给定主键查找元素 unordered_set<int>::iterator find_iter = c1.find(1); //value出现的次数 count() 返回匹配给定主键的元素的个数 c1.count(1); //返回元素在哪个区域equal_range() 返回值匹配给定搜索值的元素组成的范围 pair<unordered_set<int>::iterator, unordered_set<int>::iterator> pair_equal_range = c1.equal_range(1); //插入函数 emplace() c1.emplace(1); //插入函数 emplace_hint() 使用迭代器 c1.emplace_hint(ite_begin, 1); //插入函数 insert() c1.insert(1); //删除 erase() c1.erase(1);//1.迭代器 value 区域 //清空 clear() c1.clear(); //交换 swap() c1.swap(c2);
五 篮子操作
//篮子操作 篮子个数 bucket_count() 返回槽(Bucket)数 c1.bucket_count(); //篮子最大数量 max_bucket_count() 返回最大槽数 c1.max_bucket_count(); //篮子个数 bucket_size() 返回槽大小 c1.bucket_size(3); //返回篮子 bucket() 返回元素所在槽的序号 c1.bucket(1); // load_factor 返回载入因子,即一个元素槽(Bucket)的最大元素数 c1.load_factor(); // max_load_factor 返回或设置最大载入因子 c1.max_load_factor();
六 内存操作
// rehash 设置槽数 c1.rehash(1); // reserve 请求改变容器容量 c1.reserve(1000);
七 hash func
//hash_function() 返回与hash_func相同功能的函数指针 auto hash_func_test = c1.hash_function(); //key_eq() 返回比较key值得函数指针 auto key_eq_test = c1.key_eq();
八 测试代码
#include <iostream> #include <unordered_set> using namespace std; namespace wzj001{ void coutUnorderedSet(std::unordered_set<int>& m, string funcName) { std::unordered_set<int>::iterator it; std::cout << funcName << ": "; for ( it = m.begin(); it != m.end(); it++ ) std::cout << *it << " "; std::cout << std::endl; } void initUnorderSet(unordered_set<int>& tmp) { for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++) tmp.insert(i); } string turnBoolToString(bool tmp) { return tmp ? "true" : "false"; } void basicOperationUnorderedSet() { //定义 std::unordered_set<int> c; // 普通插入,返回pair<迭代器,插入是否成功> pair<unordered_set<int>::iterator, bool> c_insert = c.insert(1); cout << "指向key的迭代器: " << *c_insert.first << " 插入是否成功 "<< turnBoolToString(c_insert.second)<<endl; pair<unordered_set<int>::iterator, bool> c_insert2 = c.insert(2); cout << "指向key的迭代器: " << *c_insert2.first << " 插入是否成功 "<< turnBoolToString(c_insert2.second)<<endl; pair<unordered_set<int>::iterator, bool> c_insert3 = c.insert(1); cout << "指向key的迭代器: " << *c_insert3.first << " 插入是否成功 "<< turnBoolToString(c_insert3.second)<<endl; //按指定区域插入 std::unordered_set<int> c_insert_region; c_insert_region.insert(c.begin(), c.end()); coutUnorderedSet(c_insert_region, "按指定区域插入"); //构造插入 std::unordered_set<int> c_emplace; c_emplace.emplace(1); c_emplace.emplace(2); c_emplace.emplace(3); coutUnorderedSet(c_emplace, "构造插入"); //迭代器插入 std::unordered_set<int> c_emplace_hint; c_emplace_hint.emplace_hint(c_emplace_hint.begin(), 1); c_emplace_hint.emplace_hint(c_emplace_hint.begin(), 2); c_emplace_hint.emplace_hint(c_emplace_hint.begin(), 3); coutUnorderedSet(c_emplace_hint, "迭代器插入"); //删除 std::unordered_set<int> c_erase; initUnorderSet(c_erase); coutUnorderedSet(c_erase, "初始化c_erase"); //指定位置删除 c_erase.erase(c_erase.begin()); coutUnorderedSet(c_erase, "指定位置删除"); //指定key删除 c_erase.erase(8); coutUnorderedSet(c_erase, "指定key删除"); //指定区域删除 c_erase.erase(c_erase.begin(), c_erase.end()); coutUnorderedSet(c_erase, "指定区域删除"); //交换 c.swap(c_emplace); coutUnorderedSet(c, "交换"); } void unorderSetElementLookup() { //查找 std::unordered_set<int> c_find; initUnorderSet(c_find); std::unordered_set<int>::iterator find_iter = c_find.find(10); if(find_iter != c_find.end()) { cout<< "找到元素 : "<< *find_iter << endl; } else cout<< "没找到 !"<< endl; cout << "value出现次数 :" <<c_find.count(1)<< endl; //set key不可重复 pair<std::unordered_set<int>::iterator, std::unordered_set<int>::iterator> tmp = c_find.equal_range(5); if(tmp.first != c_find.end()&& tmp.second != c_find.end()) { cout << "该值所在区间为[" << *tmp.first << "," << *tmp.second << "]" << endl; } } void unorderSetBuckets() { //篮子操作 std::unordered_set<int> c_buckets; initUnorderSet(c_buckets); cout << "篮子个数: " << c_buckets.bucket_count()<< endl; cout << "篮子大小: " << c_buckets.bucket_size(1) << endl; cout << "最大篮子个数: " << c_buckets.max_bucket_count() << endl; cout << "该值所在篮子序号: " << c_buckets.bucket(3) << endl; } void unorderSetHashPolicy() { std::unordered_set<int> c_; cout << "负载: "<< c_.load_factor()<< endl; initUnorderSet(c_); cout << "负载: "<< c_.load_factor()<< endl;//使用的篮子数/篮子总数 默认的篮子数为11 cout << "最大负载: "<< c_.max_load_factor() << endl; c_.reserve(100);//预设篮子数 ,但是还没有设定 c_.rehash(3);//设定篮子数 } void unorderSetObservers() { std::unordered_set<int> c_; initUnorderSet(c_); std::unordered_set<int>::hasher xxx = c_.hash_function(); std::unordered_set<int>::key_equal zzz = c_.key_eq(); cout << "hash_func: " << xxx(11111) << endl; cout << "key_eq: " << turnBoolToString(zzz(11111,11111)) << endl; } } int main() { wzj001::basicOperationUnorderedSet(); wzj001::unorderSetElementLookup(); wzj001::unorderSetBuckets(); wzj001::unorderSetHashPolicy(); wzj001::unorderSetObservers(); }