一、卷积神经网络的简述
卷积神经网络将一个图像变窄变长。原本【长和宽较大,高较小】变成【长和宽较小,高增加】
卷积过程需要用到卷积核【二维的滑动窗口】【过滤器】,每个卷积核由n*m(长*宽)个小格组成,每个小格都有自己的权重值,
长宽变窄:过滤器的长宽决定的
高度变高:过滤器的个数决定的
输入:55000 × 784 = 28*28
输出:55000 × 10
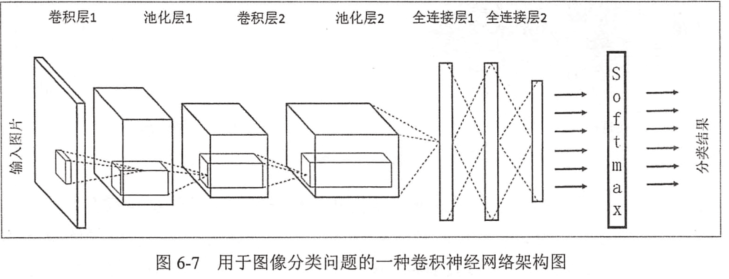
lenet:两层卷积层(卷积层 + 池化层)、两层全连接层
二、代码:
1、数据集:
下载好Mnist数据集加压到文件夹'MNIST_data’中。加载数据
import tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist.input_data as input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot = True) #打印数据集大小 print('训练集大小:',mnist.train.num_examples) print('验证集大小:',mnist.validation.num_examples) print('测试集大小:',mnist.test.num_examples) #打印样本 print(mnist.train.images[0]) print(mnist.train.labels[0])
训练集大小: 55000
验证集大小: 5000
测试集大小: 10000
x:[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0.……0.9960785,……0]
y:[0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 1. 0. 0.]
2、卷积层:tf.nn.conv2d
(1)过滤器:【维度大小、权重w、偏正b、padding、stride】
设置过滤器的参数:
tf.nn.conv2d(输入矩阵,权重,strides,padding),其中strides的第一个1和最后一个1必须有,中间为输入矩阵尺寸的x和y的大小。padding有两种值,SAME和VALLD。
- input tensor shape:[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]
- filter tensor shape:[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]

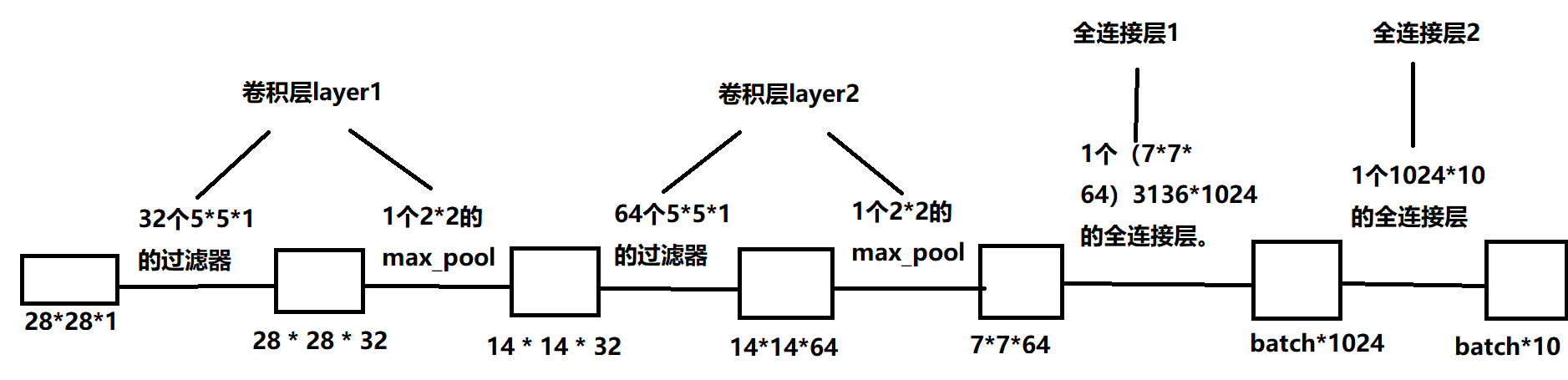
#w,b filter_w = tf.get_variable('weight',[5,5,3,16],initializer = tf.truncated_normal_initializer(stddev = 0.1)) filter_b = tf.get_variable('biases',[16],initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) #卷积的前向传播:将【32,32,3】输入通过 16个 【5,5,3】的过滤器得到【28,28,16】。w :【5,5,3,16】,b:【16】 conv = tf.nn.conv2d(input,filter_w,strides = [1,1,1,1],padding = 'SAME') # tf.nn.bias_add表示【5,5,3】个数都要加上biases。 bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv,biases) #结果通过Relu激活函数 actived_conv = tf.nn.relu(bias)
3、池化层:可加快计算速度也可防止过拟合。tf.nn.max_pool
卷积层之间加一个池化层,可缩小矩阵的尺寸,减少全连接层中的参数。
tf.nn.max_pool(传入当前层的节点矩阵,ksize = 池化层过滤器的尺寸,strides,padding),ksize的第一维和最后一维必须为1
实现了最大池化层的前向传播过程,参数和conv2d相似。

4、全部代码:
#加载模块和数据 import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examplesamples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/",one_hot = True) #参数的设置 def weight_variable(shape): initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape,stddev = 0.1) return tf.Variable(initial) def biase_variable(shape): initial = tf.constant(0.1,shape = shape) return tf.Variable(initial) def conv2d(x,w): conv = tf.nn.conv2d(x,w,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME') return conv def max_pool(x): return tf.nn.max_pool(x,ksize = [1,2,2,1],strides = [1,2,2,1],padding = 'SAME') #训练 def train(mnist): x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10]) keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32) x_image = tf.reshape(x,[-1,28,28,1]) #前向传播 #layer1 with tf.variable_scope('layer1'): w = weight_variable([5,5,1,32]) b = biase_variable([32]) conv1 = tf.nn.bias_add(conv2d(x_image,w),b) relu_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv1) pool1 = max_pool(relu_conv1) with tf.variable_scope('layer2'): w = weight_variable([5,5,32,64]) b = biase_variable([64]) conv2 = tf.nn.bias_add(conv2d(pool1,w),b) relu_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2) pool2 = max_pool(relu_conv2) with tf.variable_scope('func1'): w = weight_variable([7*7*64,1024]) b = biase_variable([1024]) pool2_reshape = tf.reshape(pool2,[-1,7*7*64]) func1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(pool2_reshape,w) + b) func1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(func1,keep_prob) with tf.variable_scope('func2'): w = weight_variable([1024,10]) b = biase_variable([10]) prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(func1_drop,w) + b) #后向传播 cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y * tf.log(prediction), reduction_indices=[1])) # loss train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy) #会话训练 sess = tf.Session() if int((tf.__version__).split('.')[1]) < 12 and int((tf.__version__).split('.')[0]) < 1: init = tf.initialize_all_variables() else: init = tf.global_variables_initializer() sess.run(init) for i in range(1000): batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(100) sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y, keep_prob: 0.5}) if i % 50 == 0: correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(prediction,1), tf.argmax(y,1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) result = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images[:1000], y: mnist.test.labels[:1000], keep_prob: 1}) print(result) if __name__ == '__main__': train(mnist)
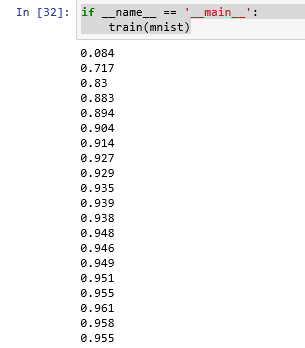
训练结果:迭代结束为95%的准确率。