一、任务:采用基本的LSTM识别MNIST图片,将其分类成10个数字。
为了使用RNN来分类图片,将每张图片的行看成一个像素序列,因为MNIST图片的大小是28*28像素,所以我们把每一个图像样本看成一行行的序列。因此,共有(28个元素的序列)×(28行),然后每一步输入的序列长度是28,输入的步数是28步。
二、LSTM模型:
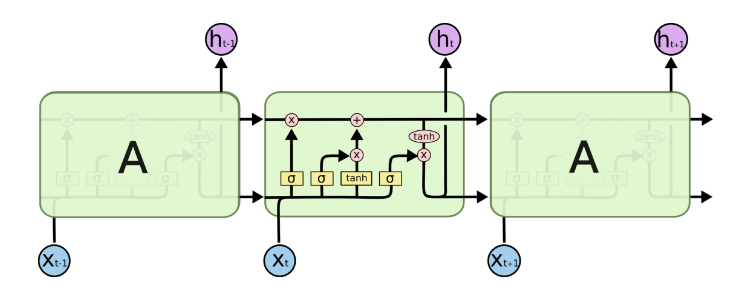
输入:x(t-1)的大小为一个28维的向量。……x(t-1),x(t)、x(t+1)……有28个。【将一张图片拆成28*28】
隐藏层大小:128
输出:10
U:28*128
V:128*10
三、LSTM代码:
加载数据:
import tensorflow as tf from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot = True)
构建模型:
#定义RNN模型: def RNN(X,w,b,input_size,unit,batch_size): ################################ #输入层,先处理x的shape #将输入的x转换成(128 batch * 28 time_steps,28 input_size) X = tf.reshape(X,[-1,input_size]) ##################################### #隐藏层 #输入的大小转换: # x_in的大小:(128 batch * 28 time_steps ,128 unit) X_in = tf.matmul(X,w['in']) + b['in'] #将x_in转换成:(128 batch , 28 input_size,128 unit),因为要将其转成张量才能输入LSTM的结构中 X_in = tf.reshape(X_in,[-1,input_size,unit]) #隐藏层模型结构: #BasicLSTMCell 是最简单的LSTMCell. with tf.variable_scope('lstm',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): lstm = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(num_units = unit , forget_bias= 1.0 ,state_is_tuple= True) #初始化状态:lstm单元由两个部分组成:(c_state,h_state)状态值和输出值 init_state = lstm.zero_state(batch_size , dtype = tf.float32) #dynamic_rnn接收张量(batch , steps , inputs) 或者(steps,batch,inputs)作为X_in,其需要输入、隐藏层结构【遗忘门】以及细胞状态 outputs , final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm , X_in,initial_state = init_state , time_major = False) ######################################################### #输出层 results = tf.matmul(final_state[1],w['out']) + b['out'] return results
训练模型:
1、设置参数(超参数、神经网络参数)
2、前向传播(构建RNN模型)【即构建模型的过程】
3、后向传播(求损失函数、设置优化器)
4、设置会话、训练模型。
def train(mnist):
#设置参数
######################## #设置训练的超参数,学习率、训练次数和每轮训练大小 lr = 0.001 training_iters = 100000 batch_size = 128 #设置神经网络的参数 input_size = 28 #一个输入的向量大小 time_steps = 28 #序列长度 unit = 128 #隐藏层的神经元个数 output_size = 10 #输出 #定义输入数据以及权重 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,time_steps,input_size]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,output_size]) # with tf.variable_scope("canshu", reuse=True): #in大小:(28*128),out大小:(128*10)。 w = { 'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size,unit])), 'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([unit,output_size])) } b = { 'in':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [unit])), 'out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [output_size])) } ################################# ##构建模型,定义损失函数和优化器,优化器采用AdamOptimizer
with tf.variable_scope('train_op',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): pred = RNN(x,w,b,input_size,unit,batch_size) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = pred , labels = y)) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss) #################################### #计算模型预测结果以及准确率计算方法 correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1)) acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32)) ###################################### #训练数据及评估模型 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) step = 0 while step * batch_size < training_iters: batch_xs , batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size,time_steps,input_size]) sess.run([train_op],feed_dict = { x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys, }) if step % 20 == 0: print(sess.run(acc,feed_dict = { x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys, })) step += 1
原本代码中没有加红的两句,然后报错:
Variable basic/rnn/basic_lstm_cell/weights does not exist, or was not created with tf.get_variable(). Did you mean to set reuse=None in VarScope?
原因:是因为在BasicRNNCell 使用到了get_variable操作,第一次的时候创建新的variable,第二次调用的时候检测到命名冲突,报错。
加上以下代码:
with tf.variable_scope('lstm',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
with tf.variable_scope('train_op',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE):
四、MultiLSTM代码:比普通的LSTM多了两行红色的代码
加载数据:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot = True)
构建模型:
def mLSTM(X,w,b,input_size,unit,batch_size,layer_num): ################################ #输入层,先处理x的shape #将输入的x转换成(128 batch * 28 time_steps,28 input_size) X = tf.reshape(X,[-1,input_size]) ##################################### #隐藏层 #输入的大小转换: # x_in的大小:(128 batch * 28 time_steps ,128 unit) X_in = tf.matmul(X,w['in']) + b['in'] #将x_in转换成:(128 batch , 28 input_size,128 unit),因为要将其转成张量才能输入LSTM的结构中 X_in = tf.reshape(X_in,[-1,input_size,unit]) #隐藏层模型结构: #BasicLSTMCell 是最简单的LSTMCell. #state_is_tuple 官方建议设置为True。此时,输入和输出的states为c(cell状态)和h(输出)的二元组 #forget_bias遗忘门的初始值设为 1,一开始不能遗忘 #num_units:num_units这个参数的大小就是LSTM输出结果的维度。例如num_units=128, 那么LSTM网络最后输出就是一个128维的向量。 with tf.variable_scope('lstm',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): lstm = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(num_units = unit , forget_bias= 1.0 ,state_is_tuple= True) lstm = tf.nn.rnn_cell.DropoutWrapper(lstm,0.5) mlstm = tf.nn.rnn_cell.MultiRNNCell([lstm for i in range(layer_num)]) init_state = mlstm.zero_state(batch_size,dtype = tf.float32) outputs , final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(mlstm,X_in,initial_state = init_state,time_major=False) #初始化状态:lstm单元由两个部分组成:(c_state,h_state)状态值和输出值 # init_state = lstm.zero_state(batch_size , dtype = tf.float32) #dynamic_rnn接收张量(batch , steps , inputs) 或者(steps,batch,inputs)作为X_in,其需要输入、隐藏层结构【遗忘门】以及细胞状态 # outputs , final_state = tf.nn.dynamic_rnn(lstm , X_in,initial_state = init_state , time_major = False) #########################################################33333 #输出层
#final_state的【【维度(128,128)的张量】,【维度为(128,128)的张量】】,因为两层的LSTM。
print(final_state) results = tf.matmul(final_state[1][1],w['out']) + b['out'] return results
训练模型:
def train(mnist): #构建模型 ######################## #设置训练的超参数,学习率、训练次数和每轮训练大小 lr = 0.001 training_iters = 100000 batch_size = 128 #设置神经网络的参数 input_size = 28 #一个输入的向量大小 time_steps = 28 #序列长度 unit = 128 #隐藏层的神经元个数 output_size = 10 #输出 layer_num = 3 #定义输入数据以及权重 x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,time_steps,input_size]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,output_size]) # with tf.variable_scope("canshu", reuse=True): #in大小:(28*128),out大小:(128*10)。 w = { 'in':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([input_size,unit])), 'out':tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([unit,output_size])) } b = { 'in':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [unit])), 'out':tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.1,shape = [output_size])) } ################################# #定义损失函数和优化器,优化器采用AdamOptimizer with tf.variable_scope('train_op',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): pred = mLSTM(x,w,b,input_size,unit,batch_size,layer_num) loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = pred , labels = y)) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss) #################################### #计算模型预测结果以及准确率计算方法 correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(y,1)) acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32)) ###################################### #训练数据及评估模型 with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) step = 0 while step * batch_size < training_iters: batch_xs , batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size,time_steps,input_size]) sess.run([train_op],feed_dict = { x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys, }) if step % 20 == 0: print(sess.run(acc,feed_dict = { x:batch_xs, y:batch_ys, })) step += 1
五、双向循环神经网络的代码:
加载模型:
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot = True)
构建模型:
def BiRNN(x,w,b): x = tf.transpose(x , [1,0,2]) x = tf.reshape(x,[-1,input_size]) x = tf.split(x,time_steps) with tf.variable_scope('BiRNN',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): lstm_fw_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_size,forget_bias=1.0,state_is_tuple=True) lstm_bw_cell = tf.contrib.rnn.BasicLSTMCell(hidden_size,forget_bias=1.0,state_is_tuple=True) #x为一个长度为T的list,list中的每个Tensor元素shape为[batch_size,input_size] output , _ , _ = tf.contrib.rnn.static_bidirectional_rnn(lstm_fw_cell,lstm_bw_cell,x,dtype = tf.float32) result = tf.nn.bias_add(tf.matmul(output[-1],w) , b) return result
设置参数、训练会话
#设置参数 lr = 0.001 batch_size = 128 training_iters = 20000 input_size = 28 time_steps = 28 output_size = 10 hidden_size = 256 #占位符 X = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,time_steps,input_size]) Y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,output_size]) with tf.variable_scope('out',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): w = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([2 * hidden_size , output_size],stddev = 0.1)) b = tf.get_variable('biases',[output_size],initializer = tf.constant_initializer(0.1)) #后向传播 with tf.variable_scope('train_op',reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE): pred = BiRNN(X,w,b) cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = pred,labels =Y)) train_op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(cost) correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1),tf.argmax(Y,1)) acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred,tf.float32)) #训练会话 init = tf.global_variables_initializer() with tf.Session() as sess: sess.run(init) step = 1 while step * batch_size < training_iters: batch_xs , batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size) batch_xs = batch_xs.reshape([batch_size,time_steps,input_size]) sess.run(train_op,feed_dict = {X:batch_xs,Y:batch_ys}) if step % 20 == 0: accuracy = sess.run(acc,feed_dict = {X:batch_xs,Y:batch_ys}) print(accuracy) step += 1