
有一点我们很容易忽略的是排序算法的稳定性(腾讯校招2016笔试题曾考过)。
排序算法稳定性的简单形式化定义为:如果Ai = Aj,排序前Ai在Aj之前,排序后Ai还在Aj之前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的。通俗地讲就是保证排序前后两个相等的数的相对顺序不变。
对于不稳定的排序算法,只要举出一个实例,即可说明它的不稳定性;而对于稳定的排序算法,必须对算法进行分析从而得到稳定的特性。需要注意的是,排序算法是否为稳定的是由具体算法决定的,不稳定的算法在某种条件下可以变为稳定的算法,而稳定的算法在某种条件下也可以变为不稳定的算法。
例如,对于冒泡排序,原本是稳定的排序算法,如果将记录交换的条件改成A[i] >= A[i + 1],则两个相等的记录就会交换位置,从而变成不稳定的排序算法。
其次,说一下排序算法稳定性的好处。排序算法如果是稳定的,那么从一个键上排序,然后再从另一个键上排序,前一个键排序的结果可以为后一个键排序所用。基数排序就是这样,先按低位排序,逐次按高位排序,低位排序后元素的顺序在高位也相同时是不会改变的。
一.冒泡排序(Bubble Sort)
1.基本思想:两个数比较大小,较大的数下沉,较小的数冒起来。
2.过程:
1.比较相邻的两个数据,如果第二个数小,就交换位置。
2.从后向前两两比较,一直到比较最前两个数据。最终最小数被交换到起始的位置,这样第一个最小数的位置就排好了。
3.继续重复上述过程,依次将第2.3...n-1个最小数排好位置。

3.平均时间复杂度:O(n2)
4.C#代码实现:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace BubbleSort { //冒泡排序类 public class BubbleSorter { public void Sort(int[] list) { int i, j, temp; bool done = false; j = 1; while ((j < list.Length) && (!done)) { done = true; for (i = 0; i < list.Length - j; i++) { if (list[i] > list[i + 1]) { done = false; temp = list[i]; list[i] = list[i + 1]; list[i + 1] = temp; } } j++; } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] iArrary = new int[] { 1, 5, 13, 6, 10, 55, 99, 2, 87, 12, 34, 75, 33, 47 }; BubbleSorter sh = new BubbleSorter(); sh.Sort(iArrary); for (int m = 0; m < iArrary.Length; m++) Console.Write("{0}", iArrary[m]+","); Console.WriteLine(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
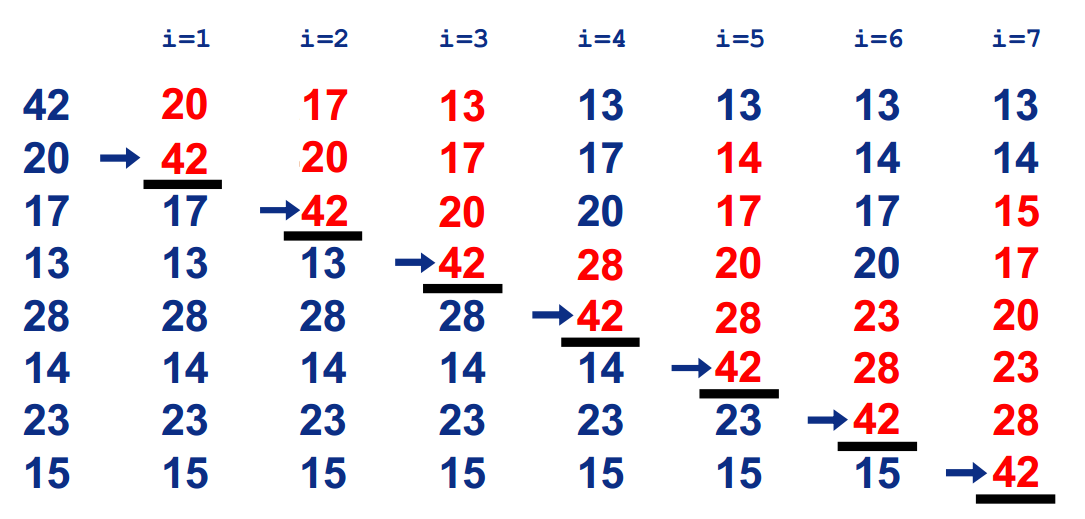
二. 选择排序(SelctionSort)
1.基本思想:
在长度为N的无序数组中,第一次遍历n-1个数,找到最小的数值与第一个元素交换;
第二次遍历n-2个数,找到最小的数值与第二个元素交换;
。。。
第n-1次遍历,找到最小的数值与第n-1个元素交换,排序完成。
2.过程:
3.平均时间复杂度:O(n2)
4.C#代码实现:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace SelectionSort { //Selection Sort //在长度为N的无序数组中,第一次遍历n-1个数,找到最小的数值与第一个元素交换; //第二次遍历n-2个数,找到最小的数值与第二个元素交换; //。。。 //第n-1次遍历,找到最小的数值与第n-1个元素交换,排序完成。 public class SelectionSorter { private int min; public void Sort(int[] list) { for (int i = 0; i < list.Length - 1; i++) { min = i; for (int j = i + 1; j < list.Length; j++) { if (list[j] < list[min]) min = j; } int t = list[min]; list[min] = list[i]; list[i] = t; } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] iArrary = new int[] { 1, 5, 3, 6, 10, 55, 9, 2, 87, 12, 34, 75, 33, 47 }; SelectionSorter ss = new SelectionSorter(); ss.Sort(iArrary); for (int m = 0; m < iArrary.Length; m++) Console.Write("{0}", iArrary[m]+","); Console.WriteLine(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
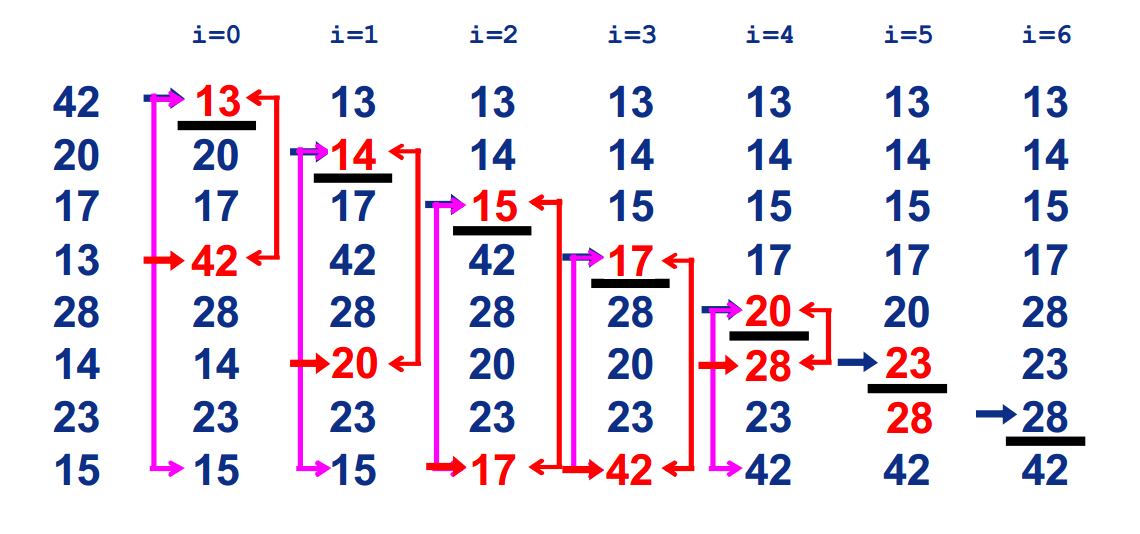
三. 插入排序(Insertion Sort)
1.基本思想:
在要排序的一组数中,假定前n-1个数已经排好序,现在将第n个数插到前面的有序数列中,使得这n个数也是排好顺序的。如此反复循环,直到全部排好顺序。
2.过程:

3.平均时间复杂度:O(n2)
4.C#代码实现:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace InsertionSort { public class InsertionSorter { public void Sort(int[] list) { for (int i = 1; i < list.Length; i++) { int t = list[i]; int j = i; while ((j > 0) && (list[j - 1] > t)) { list[j] = list[j - 1]; --j; } list[j] = t; } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] iArrary = new int[] { 1, 13, 3, 6, 10, 55, 98, 2, 87, 12, 34, 75, 33, 47 }; InsertionSorter ii = new InsertionSorter(); ii.Sort(iArrary); for (int m = 0; m < iArrary.Length; m++) Console.Write("{0}", iArrary[m]+","); Console.WriteLine(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
四. 希尔排序(Shell Sort)
1.前言:
数据序列1: 13-17-20-42-28 利用插入排序,13-17-20-28-42. Number of swap:1;
数据序列2: 13-17-20-42-14 利用插入排序,13-14-17-20-42. Number of swap:3;
如果数据序列基本有序,使用插入排序会更加高效。
2.基本思想:
在要排序的一组数中,根据某一增量分为若干子序列,并对子序列分别进行插入排序。
然后逐渐将增量减小,并重复上述过程。直至增量为1,此时数据序列基本有序,最后进行插入排序。
3.过程:

4.平均时间复杂度:O(nlogn) ~ O(n^2)
5.C#代码实现:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace ShellSort { public class ShellSorter { public void Sort(int[] list) { int inc; for (inc = 1; inc <= list.Length / 9; inc = 3 * inc + 1) ; for (; inc > 0; inc /= 3) { for (int i = inc + 1; i <= list.Length; i += inc) { int t = list[i - 1]; int j = i; while ((j > inc) && (list[j - inc - 1] > t)) { list[j - 1] = list[j - inc - 1]; j -= inc; } list[j - 1] = t; } } } } class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { int[] iArrary = new int[] { 59,20,17,13,28,14,23,83 }; ShellSorter sh = new ShellSorter(); sh.Sort(iArrary); for (int m = 0; m < iArrary.Length; m++) Console.Write("{0}", iArrary[m]+","); Console.WriteLine(); Console.ReadKey(); } } }
参考:http://www.cnblogs.com/eniac12/p/5329396.html
http://www.runoob.com/w3cnote/sort-algorithm-summary.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/zxjyuan/archive/2010/01/06/1640092.html