MapReduce篇之InputFormat
1. 概述
我们在设置MapReduce输入格式的时候,会调用这样一条语句:
|
1
|
job.setInputFormatClass(KeyValueTextInputFormat.class); |
这条语句保证了输入文件会按照我们预设的格式被读取。KeyValueTextInputFormat即为我们设定的数据读取格式。
所有的输入格式类都继承自InputFormat,这是一个抽象类。其子类有例如专门用于读取普通文件的FileInputFormat,还有用来读取数据库的DBInputFormat等等。相关类图简单画出如下(推荐新标签中打开图片查看):
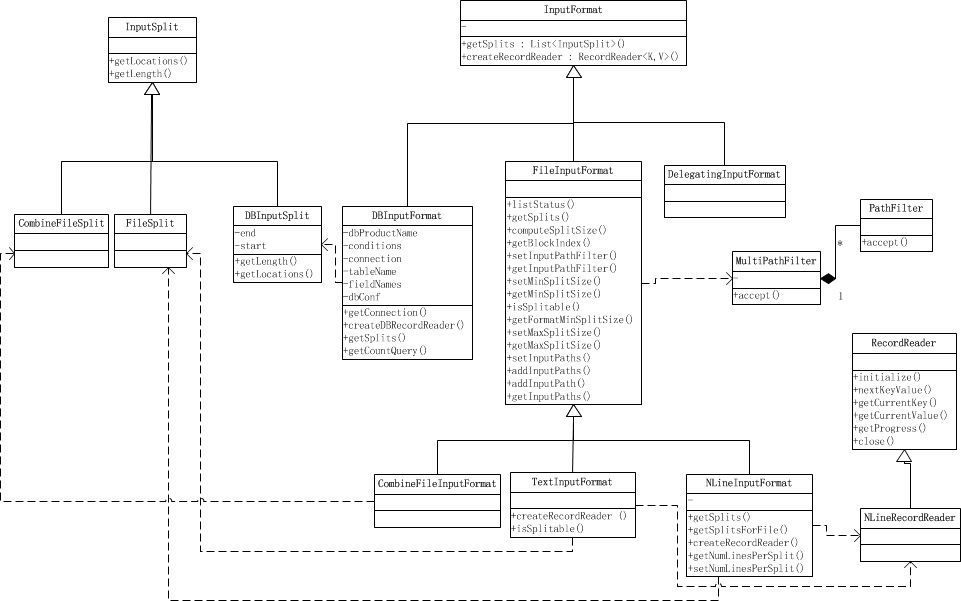
2. InputFormat
从InputFormat类图看,InputFormat抽象类仅有两个抽象方法:
- List<InputSplit> getSplits(), 获取由输入文件计算出输入分片(InputSplit),解决数据或文件分割成片问题。
- RecordReader<K,V> createRecordReader(),创建RecordReader,从InputSplit中读取数据,解决读取分片中数据问题。
在后面说到InputSplits的时候,会介绍在getSplits()时需要验证输入文件是否可分割、文件存储时分块的大小和文件大小等因素,所以总体来说,通过InputFormat,Mapreduce框架可以做到:
- 验证作业输入的正确性
- 将输入文件切割成逻辑分片(InputSplit),一个InputSplit将会被分配给一个独立的MapTask
- 提供RecordReader实现,读取InputSplit中的“K-V对”供Mapper使用
InputFormat抽象类源码也很简单,如下供参考(文章格式考虑,删除了部分注释,添加了部分中文注释):
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
public abstract class InputFormat<K, V> { /** * 仅仅是逻辑分片,并没有物理分片,所以每一个分片类似于这样一个元组 <input-file-path, start, offset> */ public abstract List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * Create a record reader for a given split. */ public abstract RecordReader<K, V> createRecordReader(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException;} |
不同的InputFormat会各自实现不同的文件读取方式以及分片方式,每个输入分片会被单独的map task作为数据源。下面详细介绍输入分片(inputSplit)是什么。
3.InputSplit
Mappers的输入是一个一个的输入分片,称InputSplit。看源码可知,InputSplit也是一个抽象类,它在逻辑上包含了提供给处理这个InputSplit的Mapper的所有K-V对。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public abstract class InputSplit { /** * 获取Split的大小,支持根据size对InputSplit排序. */ public abstract long getLength() throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * 获取存储该分片的数据所在的节点位置. */ public abstract String[] getLocations() throws IOException, InterruptedException;} |
下面深入看一个InputSplit的子类:FileSplit类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
public class FileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable { private Path file; private long start; private long length; private String[] hosts; /** * Constructs a split with host information * * @param file * the file name * @param start * the position of the first byte in the file to process * @param length * the number of bytes in the file to process * @param hosts * the list of hosts containing the block, possibly null */ public FileSplit(Path file, long start, long length, String[] hosts) { this.file = file; this.start = start; this.length = length; this.hosts = hosts; } /** The number of bytes in the file to process. */ @Override public long getLength() { return length; } @Override public String[] getLocations() throws IOException { if (this.hosts == null) { return new String[] {}; } else { return this.hosts; } } // 略掉部分方法} |
从源码中可以看出,FileSplit有四个属性:文件路径,分片起始位置,分片长度和存储分片的hosts。用这四项数据,就可以计算出提供给每个Mapper的分片数据。在InputFormat的getSplit()方法中构造分片,分片的四个属性会通过调用FileSplit的Constructor设置。
再看一个InputSplit的子类:CombineFileSplit。源码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
public class CombineFileSplit extends InputSplit implements Writable { private Path[] paths; private long[] startoffset; private long[] lengths; private String[] locations; private long totLength; public CombineFileSplit(Path[] files, long[] start, long[] lengths, String[] locations) { initSplit(files, start, lengths, locations); } private void initSplit(Path[] files, long[] start, long[] lengths, String[] locations) { this.startoffset = start; this.lengths = lengths; this.paths = files; this.totLength = 0; this.locations = locations; for (long length : lengths) { totLength += length; } } public long getLength() { return totLength; } /** Returns all the Paths where this input-split resides */ public String[] getLocations() throws IOException { return locations; } //省略了部分构造函数和方法,深入学习请阅读源文件} |
为什么介绍该类呢,因为接下来要学习《Hadoop学习(五) – 小文件处理》,深入理解该类,将有助于该节学习。
上面我们介绍的FileSplit对应的是一个输入文件,也就是说,如果用FileSplit对应的FileInputFormat作为输入格式,那么即使文件特别小,也是作为一个单独的InputSplit来处理,而每一个InputSplit将会由一个独立的Mapper Task来处理。在输入数据是由大量小文件组成的情形下,就会有同样大量的InputSplit,从而需要同样大量的Mapper来处理,大量的Mapper Task创建销毁开销将是巨大的,甚至对集群来说,是灾难性的!
CombineFileSplit是针对小文件的分片,它将一系列小文件封装在一个InputSplit内,这样一个Mapper就可以处理多个小文件。可以有效的降低进程开销。与FileSplit类似,CombineFileSplit同样包含文件路径,分片起始位置,分片大小和分片数据所在的host列表四个属性,只不过这些属性不再是一个值,而是一个列表。
需要注意的一点是,CombineFileSplit的getLength()方法,返回的是这一系列数据的数据的总长度。
现在,我们已深入的了解了InputSplit的概念,看了其源码,知道了其属性。我们知道数据分片是在InputFormat中实现的,接下来,我们就深入InputFormat的一个子类,FileInputFormat看看分片是如何进行的。
4. FileInputFormat
FileInputFormat中,分片方法代码及详细注释如下,就不再详细解释该方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
public List<InputSplit> getSplits(JobContext job) throws IOException { // 首先计算分片的最大和最小值。这两个值将会用来计算分片的大小。 // 由源码可知,这两个值可以通过mapred.min.split.size和mapred.max.split.size来设置 long minSize = Math.max(getFormatMinSplitSize(), getMinSplitSize(job)); long maxSize = getMaxSplitSize(job); // splits链表用来存储计算得到的输入分片结果 List<InputSplit> splits = new ArrayList<InputSplit>(); // files链表存储由listStatus()获取的输入文件列表,listStatus比较特殊,我们在下面详细研究 List<FileStatus> files = listStatus(job); for (FileStatus file : files) { Path path = file.getPath(); FileSystem fs = path.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration()); long length = file.getLen(); // 获取该文件所有的block信息列表[hostname, offset, length] BlockLocation[] blkLocations = fs.getFileBlockLocations(file, 0, length); // 判断文件是否可分割,通常是可分割的,但如果文件是压缩的,将不可分割 // 是否分割可以自行重写FileInputFormat的isSplitable来控制 if ((length != 0) && isSplitable(job, path)) { long blockSize = file.getBlockSize(); // 计算分片大小 // 即 Math.max(minSize, Math.min(maxSize, blockSize)); // 也就是保证在minSize和maxSize之间,且如果minSize<=blockSize<=maxSize,则设为blockSize long splitSize = computeSplitSize(blockSize, minSize, maxSize); long bytesRemaining = length; // 循环分片。 // 当剩余数据与分片大小比值大于Split_Slop时,继续分片, 小于等于时,停止分片 while (((double) bytesRemaining) / splitSize > SPLIT_SLOP) { int blkIndex = getBlockIndex(blkLocations, length - bytesRemaining); splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length - bytesRemaining, splitSize, blkLocations[blkIndex].getHosts())); bytesRemaining -= splitSize; } // 处理余下的数据 if (bytesRemaining != 0) { splits.add(new FileSplit(path, length - bytesRemaining, bytesRemaining, blkLocations[blkLocations.length - 1].getHosts())); } } else if (length != 0) { // 不可split,整块返回 splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, blkLocations[0] .getHosts())); } else { // 对于长度为0的文件,创建空Hosts列表,返回 splits.add(new FileSplit(path, 0, length, new String[0])); } } // 设置输入文件数量 job.getConfiguration().setLong(NUM_INPUT_FILES, files.size()); return splits;} |
在getSplits()方法中,我们提到了一个方法,listStatus(),我们先来看一下这个方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
protected List<FileStatus> listStatus(JobContext job) throws IOException { // 省略部分代码... List<PathFilter> filters = new ArrayList<PathFilter>(); filters.add(hiddenFileFilter); PathFilter jobFilter = getInputPathFilter(job); if (jobFilter != null) { filters.add(jobFilter); } // 创建了一个MultiPathFilter,其内部包含了两个PathFilter // 一个为过滤隐藏文件的Filter,一个为用户自定义Filter(如果制定了) PathFilter inputFilter = new MultiPathFilter(filters); for (int i = 0; i < dirs.length; ++i) { Path p = dirs[i]; FileSystem fs = p.getFileSystem(job.getConfiguration()); FileStatus[] matches = fs.globStatus(p, inputFilter); if (matches == null) { errors.add(new IOException("Input path does not exist: " + p)); } else if (matches.length == 0) { errors.add(new IOException("Input Pattern " + p + " matches 0 files")); } else { for (FileStatus globStat : matches) { if (globStat.isDir()) { for (FileStatus stat : fs.listStatus( globStat.getPath(), inputFilter)) { result.add(stat); } } else { result.add(globStat); } } } } // 省略部分代码}NLineInputFormat是一个很有意思的FileInputFormat的子类,有时间可以了解一下。 |
5. PathFilter
PathFilter文件筛选器接口,使用它我们可以控制哪些文件要作为输入,哪些不作为输入。PathFilter有一个accept(Path)方法,当接收的Path要被包含进来,就返回true,否则返回false。可以通过设置mapred.input.pathFilter.class来设置用户自定义的PathFilter。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public interface PathFilter { /** * Tests whether or not the specified abstract pathname should be * included in a pathname list. * * @param path The abstract pathname to be tested * @return <code>true</code> if and only if <code>pathname</code> * should be included */ boolean accept(Path path);} |
FileInputFormat类有hiddenFileFilter属性:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
private static final PathFilter hiddenFileFilter = new PathFilter() { public boolean accept(Path p) { String name = p.getName(); return !name.startsWith("_") && !name.startsWith("."); }}; |
hiddenFileFilter过滤掉隐藏文件。
FileInputFormat类还有一个内部类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
private static class MultiPathFilter implements PathFilter { private List<PathFilter> filters; public MultiPathFilter(List<PathFilter> filters) { this.filters = filters; } public boolean accept(Path path) { for (PathFilter filter : filters) { if (!filter.accept(path)) { return false; } } return true; }} |
MultiPathFilter类类似于一个PathFilter代理,其内部有一个PathFilter list属性,只有符合其内部所有filter的路径,才被作为输入。在FileInputFormat类中,它被listStatus()方法调用,而listStatus()又被getSplits()方法调用来获取输入文件,也即实现了在获取输入分片前进行文件过滤。
至此,我们已经利用PathFilter过滤了文件,利用FileInputFormat 的getSplits方法,计算出了Mapreduce的Map的InputSplit。作业的输入分片有了,而这些分片,是怎么被Map读取的呢?
这由InputFormat中的另一个方法createRecordReader()来负责。FileInputFormat没有对于这个方法的实现,而是交给子类自行去实现它。
6. RecordReader
RecordReader将读入到Map的数据拆分成<key, value>对。RecordReader也是一个抽象类,下面我们通过源码看一下,RecordReader主要做哪些工作:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public abstract class RecordReader<KEYIN, VALUEIN> implements Closeable { /** * 由一个InputSplit初始化 */ public abstract void initialize(InputSplit split, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * 顾名思义,读取分片下一个<key, value>对 */ public abstract boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * Get the current key */ public abstract KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * Get the current value. */ public abstract VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * 跟踪读取分片的进度 */ public abstract float getProgress() throws IOException, InterruptedException; /** * Close the record reader. */ public abstract void close() throws IOException;} |
从源码可以看出,一个RecordReader主要来完成这几项功能。接下来,通过一个具体的RecordReader实现类,来详细了解一下各功能的具体操作。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
|
public class LineRecordReader extends RecordReader<LongWritable, Text> { private CompressionCodecFactory compressionCodecs = null; private long start; private long pos; private long end; private LineReader in; private int maxLineLength; private LongWritable key = null; private Text value = null; // initialize函数即对LineRecordReader的一个初始化 // 主要是计算分片的始末位置,打开输入流以供读取K-V对,处理分片经过压缩的情况等 public void initialize(InputSplit genericSplit, TaskAttemptContext context) throws IOException { FileSplit split = (FileSplit) genericSplit; Configuration job = context.getConfiguration(); this.maxLineLength = job.getInt("mapred.linerecordreader.maxlength", Integer.MAX_VALUE); start = split.getStart(); end = start + split.getLength(); final Path file = split.getPath(); compressionCodecs = new CompressionCodecFactory(job); final CompressionCodec codec = compressionCodecs.getCodec(file); // 打开文件,并定位到分片读取的起始位置 FileSystem fs = file.getFileSystem(job); FSDataInputStream fileIn = fs.open(split.getPath()); boolean skipFirstLine = false; if (codec != null) { // 文件是压缩文件的话,直接打开文件 in = new LineReader(codec.createInputStream(fileIn), job); end = Long.MAX_VALUE; } else { // if (start != 0) { skipFirstLine = true; --start; // 定位到偏移位置,下次读取就会从便宜位置开始 fileIn.seek(start); } in = new LineReader(fileIn, job); } if (skipFirstLine) { // skip first line and re-establish "start". start += in.readLine(new Text(), 0, (int) Math.min((long) Integer.MAX_VALUE, end - start)); } this.pos = start; } public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException { if (key == null) { key = new LongWritable(); } key.set(pos);// key即为偏移量 if (value == null) { value = new Text(); } int newSize = 0; while (pos < end) { newSize = in.readLine(value, maxLineLength, Math.max((int) Math.min(Integer.MAX_VALUE, end - pos), maxLineLength)); // 读取的数据长度为0,则说明已读完 if (newSize == 0) { break; } pos += newSize; // 读取的数据长度小于最大行长度,也说明已读取完毕 if (newSize < maxLineLength) { break; } // 执行到此处,说明该行数据没读完,继续读入 } if (newSize == 0) { key = null; value = null; return false; } else { return true; } } // 省略了部分方法} |
数据从InputSplit分片中读出已经解决,但是RecordReader是如何被Mapreduce框架利用的呢?我们先看一下Mapper类
7. Mapper
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
|
public class Mapper<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { public class Context extends MapContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { public Context(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid, RecordReader<KEYIN, VALUEIN> reader, RecordWriter<KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> writer, OutputCommitter committer, StatusReporter reporter, InputSplit split) throws IOException, InterruptedException { super(conf, taskid, reader, writer, committer, reporter, split); } } /** * 预处理,仅在map task启动时运行一次 */ protected void setup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { } /** * 对于InputSplit中的每一对<key, value>都会运行一次 */ @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") protected void map(KEYIN key, VALUEIN value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { context.write((KEYOUT) key, (VALUEOUT) value); } /** * 扫尾工作,比如关闭流等 */ protected void cleanup(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { } /** * map task的驱动器 */ public void run(Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException { setup(context); while (context.nextKeyValue()) { map(context.getCurrentKey(), context.getCurrentValue(), context); } cleanup(context); }} |
重点看一下Mapper.class中的run()方法,它相当于map task的驱动。
- run()方法首先调用setup()进行初始操作
- 然后循环对每个从context.nextKeyValue()获取的“K-V对”调用map()函数进行处理
- 最后调用cleanup()做最后的处理
事实上,content.nextKeyValue()就是使用了相应的RecordReader来获取“K-V对”。Mapper.class中的Context类,它继承自MapContext类,使用一个RecordReader进行构造。下面我们再看这个MapContext。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
|
public class MapContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> extends TaskInputOutputContext<KEYIN, VALUEIN, KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> { private RecordReader<KEYIN, VALUEIN> reader; private InputSplit split; public MapContext(Configuration conf, TaskAttemptID taskid, RecordReader<KEYIN, VALUEIN> reader, RecordWriter<KEYOUT, VALUEOUT> writer, OutputCommitter committer, StatusReporter reporter, InputSplit split) { super(conf, taskid, writer, committer, reporter); this.reader = reader; this.split = split; } /** * Get the input split for this map. */ public InputSplit getInputSplit() { return split; } @Override public KEYIN getCurrentKey() throws IOException, InterruptedException { return reader.getCurrentKey(); } @Override public VALUEIN getCurrentValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { return reader.getCurrentValue(); } @Override public boolean nextKeyValue() throws IOException, InterruptedException { return reader.nextKeyValue(); }} |
从MapContent类中的方法可见,content.getCurrentKey(),content.getCurrentValue()以及nextKeyValue(),其实都是对RecordReader方法的封装,即MapContext是直接使用传入的RecordReader来对InputSplit进行“K-V对”读取的。
至此,我们已经清楚的知道Mapreduce的输入文件是如何被过滤、读取、分片、读出“K-V对”,然后交给Mapper类来处理的。