backbone库学习-model
backbone库的结构:
http://www.cnblogs.com/nuysoft/archive/2012/03/19/2404274.html
本文所有例子来自于http://blog.csdn.net/eagle_110119/article/details/8842007
1.1 先看model块的结构
var Model = Backbone.Model = function(attributes, options){} _.extend(Model.prototype, Events,{..}) var modelMethods = ['keys', 'values', 'pairs', 'invert', 'pick', 'omit']; _.each(modelMethods, function(method) {})
第一个是Model的构造器,第二个是Model的原型。注意,这里将Events和一系列的自定义参数都放进了Model的原型上,backbone必须依赖一个underscore库,我们在underscore库中找到相对应的方法。
_.extend = function(obj) { each(slice.call(arguments, 1), function(source) { if (source) { for (var prop in source) { obj[prop] = source[prop]; } } }); return obj; };
model上的方法非常多,我们先从实例化开始,先上例子
//定义Book模型类 var Book = Backbone.Model.extend({ defaults: { name: 'unknow', author: 'unknow', price: 0 } })
第一句话:
var Model = Backbone.Model = function(attributes, options){...} Model.extend = Collection.extend = Router.extend = View.extend = History.extend = extend
找到extend方法
var extend = function(protoProps, staticProps) { var parent = this; var child; // The constructor function for the new subclass is either defined by you // (the "constructor" property in your `extend` definition), or defaulted // by us to simply call the parent's constructor. if (protoProps && _.has(protoProps, 'constructor')) {//检查protoProps是否拥有constructor属性(不考虑原型上) child = protoProps.constructor; } else { child = function(){ return parent.apply(this, arguments); };//借用构造器,this指向model构造器,让子类实例化时,可以获取父类构造器的成员 } // Add static properties to the constructor function, if supplied. _.extend(child, parent, staticProps);//将父类和staticProps上的属性成员统统传给child的构造器上 // Set the prototype chain to inherit from `parent`, without calling // `parent`'s constructor function. var Surrogate = function(){ this.constructor = child; }; Surrogate.prototype = parent.prototype; child.prototype = new Surrogate;//临时构造器的方式完成继承,Surrogate属于中间件,子类实例修改不会影响父类原型,可以让子类实例获取父类原型上的成员 // Add prototype properties (instance properties) to the subclass, // if supplied. if (protoProps) _.extend(child.prototype, protoProps);//将自定义信息绑定到子类原型上 // Set a convenience property in case the parent's prototype is needed // later. child.__super__ = parent.prototype; //_super_属性方便子类直接访问父类原型 return child; //返回子类构造器 };
所以我们最后得到那个Book其实是一个继承了Model的子类构造器。ok,使用它,必须要实例化它。
var javabook = new Book();
这里,我们可以在实例化的时候,传入我们的参数,如下:
var javabook = new Book({ name : 'Thinking in Java', author : 'Bruce Eckel', price : 395.70 })
我们看一下构造器
var Model = Backbone.Model = function(attributes, options) { var defaults; var attrs = attributes || {}; options || (options = {}); this.cid = _.uniqueId('c');//生成唯一id this.attributes = {}; if (options.collection) this.collection = options.collection; if (options.parse) attrs = this.parse(attrs, options) || {}; options._attrs || (options._attrs = attrs);//让options的属性中拥有attributes,这在插件,库中很常见的写法 if (defaults = _.result(this, 'defaults')) {//this指向Book的实例,因为defaults对象被绑定到了Book的原型上,所以this是可以访问的 attrs = _.defaults({}, attrs, defaults);//合并 } this.set(attrs, options);//执行原型上的set方法 this.changed = {};//将changed(变化的)清空 this.initialize.apply(this, arguments);//实例化时执行 }
在进入set方法之前,系统会将你传进去的参数与原型上的默认参数进行合并,不清楚的可以看一下_.defaults方法
_.defaults = function(obj) { each(slice.call(arguments, 1), function(source) { if (source) { for (var prop in source) { console.log(obj[prop]); if (obj[prop] === void 0) obj[prop] = source[prop]; } } }); return obj; }
这里我们又有了一个新的判断方法,记得在原型上的默认参数,都是unknow和0,作者这样写也可以判断,大家学习一下。经过这个过滤,留下的基本都是我们自定义的参数了。
进入set方法。
set: function(key, val, options) { var attr, attrs, unset, changes, silent, changing, prev, current; if (key == null) return this; // Handle both `"key", value` and `{key: value}` -style arguments. if (typeof key === 'object') { attrs = key; options = val; } else { (attrs = {})[key] = val; } options || (options = {}); // Run validation. // 执行自定义的validation if (!this._validate(attrs, options)) return false;//validate为false时不能通过 // Extract attributes and options. // 提取属性和选项 unset = options.unset; silent = options.silent; changes = []; changing = this._changing; this._changing = true; if (!changing) { this._previousAttributes = _.clone(this.attributes); this.changed = {}; } //current表示当前状态,prev表示上一个状态。 current = this.attributes, prev = this._previousAttributes; // Check for changes of `id`. if (this.idAttribute in attrs) this.id = attrs[this.idAttribute];//检测id // For each `set` attribute, update or delete the current value. for (attr in attrs) { val = attrs[attr]; if (!_.isEqual(current[attr], val)) changes.push(attr);//将变化了属性名加入数组 if (!_.isEqual(prev[attr], val)) { this.changed[attr] = val;//跟上此状态不相同的,修改为现在的值 } else { delete this.changed[attr]; } unset ? delete current[attr] : current[attr] = val;//第一次赋完值后,将值放入current中。 } // Trigger all relevant attribute changes. // silent配置用于忽略验证规则,并且它不会触发change和error等事件 if (!silent) { if (changes.length) this._pending = true; for (var i = 0, l = changes.length; i < l; i++) { //console.log(current[changes[i]]); this.trigger('change:' + changes[i], this, current[changes[i]], options); } } // You might be wondering why there's a `while` loop here. Changes can // be recursively nested within `"change"` events. // 在所有事件结束后,触发一次change事件 if (changing) return this; if (!silent) { while (this._pending) { this._pending = false; this.trigger('change', this, options); } } this._pending = false; this._changing = false; return this; }
验证和silent这块,我们在例子上再说。set中很重要的一步就是处理当前状态和上一个状态,保存相应状态。
最后,我们执行
this.changed = {};//将changed(变化的)清空 this.initialize.apply(this, arguments);//实例化时执行
看一下原型上的initialize方法
initialize: function(){ }
英文注释是:Initialize is an empty function by default. Override it with your own,用到的时候,我们需要重载下。
以上完成了一个Book的实例化。
1.2 关于model实例读取数据
看个例子:
console.log(javabook.get('name'));
console.log(javabook.get('author'));
console.log(javabook.get('price'));
显示结果:

1.2.1 get方法
看一下get方法
get: function(attr) { return this.attributes[attr]; }
留心一下我们会发现,这个this.attributes在哪出现。
current = this.attributes, prev = this._previousAttributes; // Check for changes of `id`. if (this.idAttribute in attrs) this.id = attrs[this.idAttribute];//检测id // For each `set` attribute, update or delete the current value. for (attr in attrs) { val = attrs[attr]; if (!_.isEqual(current[attr], val)) changes.push(attr);//将变化了属性名加入数组 if (!_.isEqual(prev[attr], val)) { this.changed[attr] = val;//跟上此状态不相同的,修改为现在的值 } else { delete this.changed[attr]; } unset ? delete current[attr] : current[attr] = val;//第一次赋完值后,将值放入current中。 }
将this.attributes和current之间是引用传递,当current[attr]的值变化时,this.attributes中的值也发生了变化,刚开始current为一个空对象,它会根据你自定义传入的对象,去复制过来。另外attributes是实例上的属性,所以我们可以这样取值。
console.log(javabook.attributes['name']) console.log(javabook.attributes['author']) console.log(javabook.attributes['price'])
其实结果是一样的。
1.2.2 escape()
我们看一下,另外一种取值方法:escape()
escape: function(attr) { return _.escape(this.get(attr)); }
看似做了层过滤,看下_.escape方法
_.each(['escape', 'unescape'], function(method) { _[method] = function(string) { if (string == null) return '';//为空将返回 return ('' + string).replace(entityRegexes[method], function(match) {//匹配到正则的部分执行function方法,实际上就是将<,>,&,",'等进行转换 return entityMap[method][match]; }); }; }); var entityRegexes = { escape: new RegExp('[' + _.keys(entityMap.escape).join('') + ']', 'g'),//拼正则 unescape: new RegExp('(' + _.keys(entityMap.unescape).join('|') + ')', 'g') }; var entityMap = {//需要转换的部分 escape: { '&': '&', '<': '<', '>': '>', '"': '"', "'": ''' } };
如果需要添加新的转换部分,可以添加到entityMap中。
1.3 修改数据
看例子:
var javabook = new Book(); // 通过set方法设置模型数据 javabook.set('name', 'Java7入门经典'); javabook.set('author', 'Ivor Horton'); javabook.set('price', 88.50); // 获取数据并将数据输出到控制台 var name = javabook.get('name'); var author = javabook.get('author'); var price = javabook.get('price'); console.log(name); // 输出Java7入门经典 console.log(author); // 输出Ivor Horton console.log(price); // 输出88.50
原型上的set方法,刚才我们已经看过了,set方法会将我们传入的值与上一次状态的值进行比较,同样也与没赋这次值的当前值进行比较。如果改变了,则将新的值覆盖旧的值,不过this._previousAttributes中保存着model上一次状态的值。
set可以单独一个个赋值,同样也可以一起赋值
//set()方法也允许同时设置多个属性,例如: javabook.set({ name : 'Java7入门经典', author : 'Ivor Horton', price : 88.50 });
1.4 修改数据吗,触发事件
当调用set()方法修改模型中的数据时,会触发一系列事件,我们常常通过监听这些事件,来动态调整界面中数据的显示,我们先来看一个例子:
// 定义Book模型类 var Book = Backbone.Model.extend({ defaults : { name : 'unknown', author : 'unknown', price : 0 } }); // 实例化模型对象 var javabook = new Book(); // 监听模型"change"事件 javabook.on('change', function(model) { console.log('change事件被触发'); }); // 监听模型"change:name"事件 javabook.on('change:name', function(model, value) { console.log('change:name事件被触发'); }); // 监听模型"change:author"事件 javabook.on('change:author', function(model, value) { console.log('change:author事件被触发'); }); // 通过set()方法设置数据 javabook.set({ name : 'Thinking in Java', author : 'unknown', price : 395.70 }); // 控制台输出结果: // change:name事件被触发 // change事件被触发
问题在set方法中,一般情况我们不设置slient的情况下,会执行事件,看代码:
// silent配置用于忽略验证规则,并且它不会触发change和error等事件 if (!silent) { if (changes.length) this._pending = true; for (var i = 0, l = changes.length; i < l; i++) { this.trigger('change:' + changes[i], this, current[changes[i]], options); } }
如果我们修改的数据,changes数组中是会有值的。遍历changes数组,将修改过的属性名找到,执行类似'change:属性名'为名称的事件,这里,告诉我们在页面,如果想通过数据修改触发事件的话,这个事件的命名按照'change'+'属性名'来定义。
另外,set源码中,还有一段:
// 在所有事件结束后,触发一次change事件 if (changing) return this; if (!silent) { while (this._pending) { this._pending = false; this.trigger('change', this, options); } }
一旦数据不真正修改了,那this._pending将变为true,将默认执行一遍change方法。我们可能监听change方法来判断数据是否被修改(但是你也可以通过获取实例的_pending属性来判断)
除了get方法之外,还有两种方法获取上一次状态的值
previous()
previousAttributes()
先看previous()
previous: function(attr) { if (attr == null || !this._previousAttributes) return null; return this._previousAttributes[attr]; }
很简单,this._previousAttributes存放着上一个状态的参数。
previousAttributes()
previousAttributes: function() { return _.clone(this._previousAttributes); }
克隆一份返回,这样修改不会影响原来的状态值。
1.5 数据验证
Backbone模型提供了一套数据验证机制,确保我们在模型中存储的数据都是通过验证的,我们通过下面的例子来说明这套验证机制:
var Book = Backbone.Model.extend({ validate : function(data) { if(data.price < 1) { return '书籍价格不应低于1元.'; } } }); var javabook = new Book(); // 监听error事件,当验证失败时触发 javabook.on('error', function(model, error) { console.log(error); }); javabook.set('price', 0);
找到set方法中的相应方法:
if (!this._validate(attrs, options)) return false;
大家注意,上述的例子没有作用,为什么?因为this._validate()中传入的两个参数为空,定义Book时传入的validate实际上绑定到Book的原型上。实例化时根本没有传入任何数据。这里源码存在错误,看看我们该如何修改。
先看_validate方法:
_validate: function(attrs, options) { //if (!options.validate || !this.validate) return true;//这里的this.validate是你自己定义的,所以validate需要定义在model类中 if(!this.validate || !options.validate) return true//没有验证,直接通过
attrs = _.extend({}, this.attributes, attrs); var error = this.validationError = this.validate(attrs, options) || null; if (!error) return true;//没有报错内容,返回true
this.trigger('invalid', this, error, _.extend(options, {validationError: error})); //如果是false,则表示验证正确,否则则自动执行下面的trigger方法,抛出异常 return false; }
因为options没值,所以!options.validate恒为true,这也就是为什么validate不验证的关键。修改下判断为:
if(!this.validate || !options.validate) return true//没有验证,直接通过
继续向下,看这段代码:
this.trigger('invalid', this, error, _.extend(options, {validationError: error}));
如果抛出错误,会执行事件名为invalid的事件,那我们再看看页面的绑定事件名,是error,不相符,导致从this._events中按事件名取事件取不到,导致验证失败。ok,简单修改下页面
// 监听error事件,当验证失败时触发 javabook.on('invalid', function(model, error) { console.log(error); });
ok,修改完成,我们再运行一遍,看结果
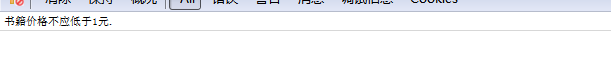
对于修改validate这块,我只是列举了一种办法,还有很多方法,你选择你喜欢。再说一句,绑定validate还有一种方式:
javabook.set('price', 0, {
error : function(model, error) {
console.log('自定义错误:' + error);
}
});
options将会有值,这样就不会跳出validate判断了。
1.6 slient配置
这个东西搁了一段没看,现在我们根据例子来过一遍。上例子:
javabook.set('price', 0, {
silent : true
});
如果传入silent,那将不触发change和change:属性名的事件,但记住,它只在定义它的时候生效,换言之,如下代码:
javabook.set('price', 0, {
silent : true
});
javabook.set('name', 'Thinking in Java');
第一次set不会抛异常,第二次会,为什么,因为传入的参数不一样。第二次没有silent,就可以触发change等事件了。
1.7 删除数据
Backbone提供了unset和clear方法,看下API
unset()方法用于删除对象中指定的属性和数据
clear()方法用于删除模型中所有的属性和数据
例子:
// 定义Book模型类 var Book = Backbone.Model.extend(); // 实例化模型对象 var javabook = new Book({ name : 'Java7入门经典', author : 'Ivor Horton', price : 88.50 }); // 输出: Java7入门经典 console.log(javabook.get('name')); // 删除对象name属性 javabook.unset('name'); // 输出: undefined console.log(javabook.get('name')); 当我们对模型的name属性执行unset()方法后,模型内部会使用delete关键字将name属性从对象中删除。 clear()方法与unset()方法执行过程类似,但clear()方法会删除模型中的所有数据,例如: // 定义Book模型类 var Book = Backbone.Model.extend(); // 实例化模型对象 var javabook = new Book({ name : 'Java7入门经典', author : 'Ivor Horton', price : 88.50 }); // 删除对象name属性 javabook.clear(); // 以下均输出: undefined console.log(javabook.get('name')); console.log(javabook.get('author')); console.log(javabook.get('price'));
先从unset开始
javabook.unset('name');
找到相应的unset方法
unset: function(attr, options) { return this.set(attr, void 0, _.extend({}, options, {unset: true})); }
可以看的很清楚,unset还是用到set方法,注意它传入的{unset:true}的,回到之前的set方法中,去找相应的unset部分,我们会找到这段代码。
unset ? delete current[attr] : current[attr] = val;//第一次赋完值后,将值放入current中。
unset为true之后,delete current[attr],即删除current['name']。表示删除了name属性。
再来看clear方法
clear: function(options) { var attrs = {}; for (var key in this.attributes) attrs[key] = void 0;//将this.attributes中所有的成员清空,这里undefined可能会被重写,所以用void 0代替 return this.set(attrs, _.extend({}, options, {unset: true})); }
clear方法依旧是调用set方法,由于成员被清空,再传入set中,删除掉current[attr],释放掉内存。
1.8 将模型数据同步到服务器
1.8.1 save
Backbone提供了与服务器数据的无缝连接,我们只需要操作本地Model对象,Backbone就会按照规则自动将数据同步到服务器。如果需要使用Backbone默认的数据同步特性,请确定你的服务器数据接口已经支持了REST架构。具体概念,大家可以看http://blog.csdn.net/eagle_110119/article/details/8842007部分的讲解,或者上网搜些资料看。
数据标识:Backbone中每一个模型对象都有一个唯一标识,默认名称为id,你可以通过idAttribute属性来修改它的名称。
URL: Backbone默认使用PATHINFO的方式来访问服务器接口。
先看例子
// 定义Book模型类 var Book = Backbone.Model.extend({ urlRoot : '/service' }); // 创建实例 var javabook = new Book({ id : 1001, name : 'Thinking in Java', author : 'Bruce Eckel', price : 395.70 }); // 保存数据 javabook.save();
看一下save方法
save: function(key, val, options) { var attrs, method, xhr, attributes = this.attributes; // Handle both `"key", value` and `{key: value}` -style arguments. if (key == null || typeof key === 'object') { attrs = key; options = val; } else { (attrs = {})[key] = val; } options = _.extend({validate: true}, options); // If we're not waiting and attributes exist, save acts as // `set(attr).save(null, opts)` with validation. Otherwise, check if // the model will be valid when the attributes, if any, are set. if (attrs && !options.wait) { if (!this.set(attrs, options)) return false; } else { if (!this._validate(attrs, options)) return false;//验证通过了 } // Set temporary attributes if `{wait: true}`. if (attrs && options.wait) { this.attributes = _.extend({}, attributes, attrs); } // After a successful server-side save, the client is (optionally) // updated with the server-side state. if (options.parse === void 0) options.parse = true; var model = this; var success = options.success; options.success = function(resp) {//返回成功的回调 // Ensure attributes are restored during synchronous saves. model.attributes = attributes; var serverAttrs = model.parse(resp, options); if (options.wait) serverAttrs = _.extend(attrs || {}, serverAttrs); if (_.isObject(serverAttrs) && !model.set(serverAttrs, options)) { return false; } if (success) success(model, resp, options); model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options); }; wrapError(this, options);//将options绑定一个error方法 method = this.isNew() ? 'create' : (options.patch ? 'patch' : 'update');//判断id,如果没有则新建,如果有再判断options.patch,改为更新 if (method === 'patch') options.attrs = attrs; xhr = this.sync(method, this, options); // Restore attributes. if (attrs && options.wait) this.attributes = attributes; return xhr; }
这里,我们先只从前端的角度看save方法,有条件的朋友,可以搭建一个环境,与服务器交互下,效果会更好(目前我也再搞,我使用的是node+mongodb)
在save方法中,我们调用了validate进行了验证。验证不通过,则不允许发送请求。其中的options.success是一个返回成功的回调函数。看一下wrapError
var wrapError = function(model, options) { var error = options.error; options.error = function(resp) { if (error) error(model, resp, options); model.trigger('error', model, resp, options); }; };
这个方法,给options添加了一个error方法,主要是为了防止当ajax请求失败时,捕获错误信息。
其中ajax的请求,主要包含:url,method,async,datatype,success,error等。看一下save如果处理method
method = this.isNew() ? 'create' : (options.patch ? 'patch' : 'update');//判断id,如果没有则新建,如果有再判断options.patch,改为更新
接着是
xhr = this.sync(method, this, options);
ajax归根结底是通过XMLHttpRequest实例来操作的,来看如何创建一个xhr实例,进入原型的sync方法
sync: function() { return Backbone.sync.apply(this, arguments); }
看一下Backbone.sync
Backbone.sync = function(method, model, options) { var type = methodMap[method]; // Default options, unless specified. _.defaults(options || (options = {}), { emulateHTTP: Backbone.emulateHTTP,//false emulateJSON: Backbone.emulateJSON //false }); // Default JSON-request options. // 默认JSON请求选项 var params = {type: type, dataType: 'json'}; // Ensure that we have a URL. // 查看选项中是否有url,没有则选用实例set时的url if (!options.url) { params.url = _.result(model, 'url') || urlError(); } // Ensure that we have the appropriate request data. if (options.data == null && model && (method === 'create' || method === 'update' || method === 'patch')) { params.contentType = 'application/json';//用于定义网络文件的类型和网页的编码,决定浏览器将以什么形式、什么编码读取这个文件 params.data = JSON.stringify(options.attrs || model.toJSON(options));//转成字符串,其中model.toJSON()返回this.attributes里的信息 } // params中包含了发送给服务器的所有信息 // For older servers, emulate JSON by encoding the request into an HTML-form. if (options.emulateJSON) { params.contentType = 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded'; params.data = params.data ? {model: params.data} : {}; } // For older servers, emulate HTTP by mimicking the HTTP method with `_method` // And an `X-HTTP-Method-Override` header. if (options.emulateHTTP && (type === 'PUT' || type === 'DELETE' || type === 'PATCH')) { params.type = 'POST'; if (options.emulateJSON) params.data._method = type; var beforeSend = options.beforeSend; options.beforeSend = function(xhr) { xhr.setRequestHeader('X-HTTP-Method-Override', type); if (beforeSend) return beforeSend.apply(this, arguments); }; } // Don't process data on a non-GET request. if (params.type !== 'GET' && !options.emulateJSON) { params.processData = false; } // If we're sending a `PATCH` request, and we're in an old Internet Explorer // that still has ActiveX enabled by default, override jQuery to use that // for XHR instead. Remove this line when jQuery supports `PATCH` on IE8. if (params.type === 'PATCH' && noXhrPatch) { params.xhr = function() { return new ActiveXObject("Microsoft.XMLHTTP"); }; } // Make the request, allowing the user to override any Ajax options. var xhr = options.xhr = Backbone.ajax(_.extend(params, options)); model.trigger('request', model, xhr, options); return xhr; }
其中,整个这个方法中,主要完成的工作,就是填充params,让其包含传到服务器所需要的所有信息,包括头,编码等等。另外在ajax中存在兼容性问题,低版本的IE没有xhr对象,它们有自己的实例对象activeObject。
兼容性判断
var noXhrPatch = typeof window !== 'undefined' && !!window.ActiveXObject && !(window.XMLHttpRequest && (new XMLHttpRequest).dispatchEvent);
浏览器不支持xhr,可以使用activeObject
代码最后,调用了Backbone.ajax(_.extend(params,options))
Backbone.ajax = function() { return Backbone.$.ajax.apply(Backbone.$, arguments); }
再看
Backbone.$ = root.jQuery || root.Zepto || root.ender || root.$;
这里,我们都清楚了,Backbone在与服务器交互时,再发送请求时调用的是第三方的ajax,这里我们使用的是jQuery。最后返回xhr对象。save方法结束。(这里大家可以结合$.ajax()来理解)
例子中还将,可以这样写回调
// 将数据保存到服务器 javabook.save(null, { success : function(model) { // 数据保存成功之后, 修改price属性并重新保存 javabook.set({ price : 388.00 }); javabook.save(); } });
这样也可以,为什么呢,看源码:
var success = options.success;//你可以在save方法的时候写成功回调 options.success = function(resp) {//返回成功的回调 // Ensure attributes are restored during synchronous saves. model.attributes = attributes; var serverAttrs = model.parse(resp, options); if (options.wait) serverAttrs = _.extend(attrs || {}, serverAttrs); if (_.isObject(serverAttrs) && !model.set(serverAttrs, options)) { return false; } if (success) success(model, resp, options); model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options); };
没有自己写回调,系统帮你写,如果有回调,则使用你的回调,至于回调函数,我们最后看。
还有一个wait参数的配置,看例子
// 从将数据保存到服务器 javabook.save({ name : 'Thinking in Java', author : 'Bruce Eckel', price : 395.70 }, { wait : true });
例子中的解答是如果我们传递了wait配置为true,那么数据会在被提交到服务器之前进行验证,当服务器没有响应新数据(或响应失败)时,模型中的数据会被还原为修改前的状态。如果没有传递wait配置,那么无论服务器是否保存成功,模型数据均会被修改为最新的状态、或服务器返回的数据。
我们来看回调,里面有几个方法
if (attrs && !options.wait) { if (!this.set(attrs, options)) return false; } else { if (!this._validate(attrs, options)) return false;//验证通过了 }
如果设置了wait为true,将会进行验证(其实你不传值,也要进行验证。。。)
再看这个方法
parse: function(resp, options) { return resp; }
对照save里的方法
model.attributes = attributes; var serverAttrs = model.parse(resp, options); if (options.wait) serverAttrs = _.extend(attrs || {}, serverAttrs);
如果设置了wait,当服务器没有响应时,理论上resp是没有值,serverAttrs的值应该为attrs,这个是原来修改前的值。对于ajax请求失败,失败了服务器一般返回错误信息,数据库里的数据是不会修改原来的状态,所以原来的状态依旧是原来的状态。
其实在我们不设置wait参数时,save方法可以有参数,不需要在此之前使用set,因为他包含了这set方法看例子
javabook.save({ name: 'helloWorld' //,wait: true } );
运行结果为:

可以看到name被修改了,save完成了set的功能,前提,不要设置wait,wait可以理解为保持原有的参数不变(在ajax没有返回时,或者报错时)
很多时候,接口返回的数据是多种多样的,例子上有一种情况
{ "resultCode" : "0", "error" : "null", "data" : [{ "isNew" : "true", "bookId" : "1001", "bookName" : "Thinking in Java(修订版)", "bookAuthor" : "Bruce Eckel", "bookPrice" : "395.70" }] }
backbone提供了一个parse方法,不过之前我们已经看过,默认情况,这个方法提供传入两个参数,并返回第一个参数,解析时,自己重写parse方法解析。
1.8.2 fetch
fetch()方法用于从服务器接口获取模型的默认数据,常常用于模型的数据恢复,它的参数和原理与save()方法类似,因此你可以很容易理解它。
从fetch代码看起:
fetch: function(options) { options = options ? _.clone(options) : {}; if (options.parse === void 0) options.parse = true; var model = this; var success = options.success; options.success = function(resp) {//成功的回调 if (!model.set(model.parse(resp, options), options)) return false; if (success) success(model, resp, options); model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options); }; wrapError(this, options);//错误的回调 return this.sync('read', this, options); }
基本跟save相似,注意,这里的标识为read。如果需要在回调中绑定响应事件的,可以在页面用on绑定事件,事件名为sync,这样是正确回调后,是可以触发的。
这里,因为没有连接上服务器,所以id的部分没有给出,抱歉。
1.8.3 destroy
destroy()方法用于将数据从集合(关于集合我们将在下一章中讨论)和服务器中删除,需要注意的是,该方法并不会清除模型本身的数据,如果需要删除模型中的数据,请手动调用unset()或clear()方法)当你的模型对象从集合和服务器端删除时,只要你不再保持任何对模型对象的引用,那么它会自动从内存中移除。(通常的做法是将引用模型对象的变量或属性设置为null值)
看一下destory
destroy: function(options) { options = options ? _.clone(options) : {}; var model = this; var success = options.success; var destroy = function() { //模型会触发destroy事件,页面需要声明 model.trigger('destroy', model, model.collection, options); }; options.success = function(resp) { //成功回调 if (options.wait || model.isNew()) destroy(); if (success) success(model, resp, options); if (!model.isNew()) model.trigger('sync', model, resp, options); }; if (this.isNew()) {//查看id是否是新的。 options.success(); return false; } wrapError(this, options);//错误回调 var xhr = this.sync('delete', this, options); if (!options.wait) destroy();//设置wait之后,将不会触发destory return xhr; }
这里的标识为delete,可以看到,该方法并不会清除模型本身(也就是没有跟this.attributes打交道)。
这里基本过完一遍model。ok,好吧有点长。。
内容不多,时间刚好,以上是我的一点读码体会,如有错误,请指出,大家共通学习。
