目录
背景图的基本概念图的程序表示图的常见算法遍历深度优先遍历广度优先遍历最小生成树拓扑排序完整代码备注
背景返回目录
不同的数据结构有不同的用途,像:数组、链表、队列、栈多数是用来做为基本的工具使用,二叉树多用来作为已排序元素列表的存储,B 树用在存储中,本文介绍的 Graph 多数是为了解决现实问题(说到底,所有的数据结构都是这个目的),如:网络布局、任务安排等。
图的基本概念返回目录
示例
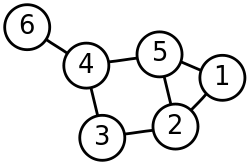
顶点(Vertex)
上图的 1、2、3、4、5、6 就是顶点。
邻接(Adjoin)
如果 A 和 B 通过定向边相连,且方向为 A -> B,则 B 为 A 的邻接,如果相连的边是没有方向的,则 A 和 B 互为邻接。
边(Edge)
顶点之间的连线就是边。
连通图(Connected Graph)
不考虑边的方向性,从任何一个节点都可以遍历到其它节点。本文的所有算法(除了拓扑排序)只适合连通图。
定向图(Directed Graph)
图中的所有边都带方向。
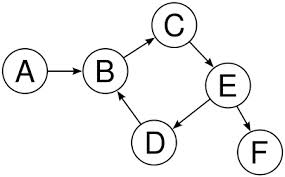
权重图(Weighted Graph)
图中的所有边都有权重。
图的程序表示返回目录
如果图 T 有 A、B、C 三个节点,有 A -> B,B -> C,C -> A 三个边(没有方向),如何在程序中表示 T 呢?
邻接矩阵
A B C
A 0 1 0
B 0 0 1
C 1 0 0
矩阵的行代表了定向边的起始顶点,矩阵的列代表了定向边的介绍顶点,矩阵中的值:1 代表了列是行的邻接,0 则反之。如果边没有方向,则矩阵是相对于正对角线是对称的。
邻接列表
A:[ B ]
B:[ C ]
C:[ A ]
这个就不多说了,多数书籍使用都是邻接矩阵。
代码
1 class Vertex<T> 2 { 3 public T Value { get; set; } 4 5 public bool WasVisited { get; set; } 6 } 7 8 class Graph<T> 9 { 10 #region 私有字段 11 12 private int _maxSize; 13 private Vertex<T>[] _vertexs; 14 private bool[][] _edges; 15 private int _vertexCount = 0; 16 17 #endregion 18 19 #region 构造方法 20 21 public Graph(int maxSize) 22 { 23 _maxSize = maxSize; 24 _vertexs = new Vertex<T>[_maxSize]; 25 _edges = new bool[_maxSize][]; 26 for (var i = 0; i < _maxSize; i++) 27 { 28 _edges[i] = new bool[_maxSize]; 29 } 30 } 31 32 #endregion 33 34 #region 添加顶点 35 36 public Graph<T> AddVertex(T value) 37 { 38 _vertexs[_vertexCount++] = new Vertex<T> { Value = value }; 39 40 return this; 41 } 42 43 #endregion 44 45 #region 添加边 46 47 public Graph<T> AddUnDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 48 { 49 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 50 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 51 52 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 53 _edges[endIndex][startIndex] = true; 54 55 return this; 56 } 57 58 public Graph<T> AddDirectedEdge(T startItem, T endItem) 59 { 60 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 61 var endIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(endItem); 62 63 _edges[startIndex][endIndex] = true; 64 65 return this; 66 } 67 68 #endregion 69 }
图的常见算法返回目录
遍历返回目录
本文的遍历算法只适合一般的无向图。
深度优先遍历返回目录
深度优先遍历的原则是:尽可能的离开始节点远,二叉树的三种遍历算法都属于这种算法。
示例

从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):ABCEDBF。
栈版本
1 #region 深度优先遍历:栈版本 2 3 public void DepthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var stack = new Stack<int>(); 7 8 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, startIndex, action); 9 while (stack.Count > 0) 10 { 11 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(stack.Peek()); 12 if (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 13 { 14 this.DepthFirstSearchVisit(stack, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 15 } 16 else 17 { 18 stack.Pop(); 19 } 20 } 21 22 this.ResetVisited(); 23 } 24 25 private void DepthFirstSearchVisit(Stack<int> stack, int index, Action<T> action) 26 { 27 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 28 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 29 stack.Push(index); 30 } 31 32 #endregion
递归版本
1 #region 深度优先遍历:递归版本 2 3 public void DepthFirstSearchRecursion(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 7 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(startIndex, action); 8 9 this.ResetVisited(); 10 } 11 12 private void DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(int index, Action<T> action) 13 { 14 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 15 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 16 17 var adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 18 while (adjoinVertexIndex >= 0) 19 { 20 this.DepthFirstSearchRecursionVisit(adjoinVertexIndex, action); 21 adjoinVertexIndex = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndex(index); 22 } 23 } 24 25 #endregion
广度优先遍历返回目录
广度优先遍历的原则是:尽可能的离开始节点近。这个算法没有办法通过递归实现,多数都是使用的队列(终于发现了队列的又一个用处)。
示例

从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):ABCEDFB。
代码
1 #region 广度优先遍历 2 3 public void BreadthFirstSearch(T startItem, Action<T> action) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 7 8 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, startIndex, action); 9 while (queue.Count > 0) 10 { 11 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(queue.Dequeue()); 12 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 13 { 14 this.BreadthFirstSearchVisit(queue, adjoinVertexIndex, action); 15 } 16 } 17 18 this.ResetVisited(); 19 } 20 21 private void BreadthFirstSearchVisit(Queue<int> queue, int index, Action<T> action) 22 { 23 _vertexs[index].WasVisited = true; 24 action(_vertexs[index].Value); 25 queue.Enqueue(index); 26 } 27 28 #endregion
最小生成树返回目录
本文的最小生成树算法只适合一般的无向图。
将 N 个顶点连接起来的最小树叫:最小生成树。
给定一个颗有 N 个顶点的连通图,则最小生成树的边为:N - 1。
不同的遍历算法生成的最小生成树是不同的,下面使用广度优先遍历来生成最小树。
示例

从 A 开始的遍历顺序为(邻接的遍历顺序为字母升序):A->B、B->C、C->E、E->D、E->F、D->B。
代码
1 #region 最小生成树 2 3 public void DisplayMinimumSpanningTree(T startItem) 4 { 5 var startIndex = this.GetVertexIndex(startItem); 6 var queue = new Queue<int>(); 7 8 _vertexs[startIndex].WasVisited = true; 9 queue.Enqueue(startIndex); 10 while (queue.Count > 0) 11 { 12 var currentIndex = queue.Dequeue(); 13 var adjoinVertexIndexs = this.GetNextUnVisitedAdjoinVertexIndexs(currentIndex); 14 foreach (var adjoinVertexIndex in adjoinVertexIndexs) 15 { 16 Console.WriteLine(_vertexs[currentIndex].Value + "->" + _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].Value); 17 18 _vertexs[adjoinVertexIndex].WasVisited = true; 19 queue.Enqueue(adjoinVertexIndex); 20 } 21 } 22 23 this.ResetVisited(); 24 } 25 26 #endregion
拓扑排序返回目录
拓扑排序只适合定向图,且图中不存在循环结构。其算法非常简单,依次获取图中的没有邻接顶点的顶点,然后删除该顶点。
示例

上图出现了循环结构,假如没有顶点 C,拓扑排序的结果为(顶点的遍历顺序为字母升序):EFDAB。
算法
1 #region 拓扑排序 2 3 public List<T> TopologySort() 4 { 5 var cloneVertexs = (Vertex<T>[])_vertexs.Clone(); 6 var cloneEdges = (bool[][])_edges.Clone(); 7 var cloneVertexCount = _vertexCount; 8 9 var results = new List<T>(); 10 while (_vertexCount > 0) 11 { 12 var successor = this.NextSuccessor(); 13 if (successor == -1) 14 { 15 throw new InvalidOperationException("出现循环了!"); 16 } 17 18 results.Insert(0, _vertexs[successor].Value); 19 20 this.RemoveVertex(successor); 21 _vertexCount--; 22 } 23 24 _vertexs = cloneVertexs; 25 _edges = cloneEdges; 26 _vertexCount = cloneVertexCount; 27 28 return results; 29 } 30 31 private int NextSuccessor() 32 { 33 for (var row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 34 { 35 if (_edges[row].Take(_vertexCount).All(x => !x)) 36 { 37 return row; 38 } 39 } 40 41 return -1; 42 } 43 44 private void RemoveVertex(int successor) 45 { 46 for (int i = successor; i < _vertexCount - 1; i++) 47 { 48 _vertexs[i] = _vertexs[i + 1]; 49 } 50 51 for (int row = successor; row < _vertexCount - 1; row++) 52 { 53 for (int column = 0; column < _vertexCount; column++) 54 { 55 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row + 1][column]; 56 } 57 } 58 59 for (int column = successor; column < _vertexCount - 1; column++) 60 { 61 for (int row = 0; row < _vertexCount; row++) 62 { 63 _edges[row][column] = _edges[row][column + 1]; 64 } 65 } 66 } 67 68 #endregion
完整代码返回目录
 View Code
View Code备注返回目录
本文没有解释权重图,下篇再介绍。
