some notes from coding practice, source from: GeekforGeek
-
randint(): return a random integer by given the specific range [start, end], edge included
1 # Python3 program explaining work 2 # of randint() function 3 4 # imports random module 5 import random 6 7 # Generates a random number between 8 # a given positive range 9 r1 = random.randint(0, 10) 10 print("Random number between 0 and 10 is % s" % (r1)) 11 12 # Generates a random number between 13 # two given negative range 14 r2 = random.randint(-10, -1) 15 print("Random number between -10 and -1 is % d" % (r2)) 16 17 # Generates a random number between 18 # a positive and a negative range 19 r3 = random.randint(-5, 5) 20 print("Random number between -5 and 5 is % d" % (r3))
Syntax :
randint(start, end)
Parameters :
(start, end) : Both of them must be integer type values.
Returns :
A random integer in range [start, end] including the end points.
Errors and Exceptions :
ValueError : Returns a ValueError when floating
point values are passed as parameters.
TypeError : Returns a TypeError when anything other than
numeric values are passed as parameters.
-
guess number game
# importing randint function # from random module from random import randint # Function which generates a new # random number everytime it executes def generator(): return randint(1, 10) # Function takes user input and returns # true or false depending whether the # user wins the lucky draw! def rand_guess(): random_number = generator() # defining the number of # guesses the user gets guess_left = 3 flag = 0 # looping the number of times # the user gets chances while guess_left > 0: # Taking a input from the user guess = int(input("Pick your number to " "enter the lucky draw ")) # checking whether user's guess # matches the generated win-condition if (guess == random_number): flag = 1 break elif (guess < random_number): print("opps, try larger number") else: print("opps, try smaller number") # Decrementing number of # guesses left by 1 guess_left -= 1 # If win-condition is satisfied then, # the function rand_guess returns True if flag is 1: return True # Else the function returns False else: return False # Driver code if __name__ == '__main__': if rand_guess() is True: print("Congrats!! You Win.") else : print("Sorry, You Lost!")
-
Pandas DataFrame.loc
DataFrame is a two-dimensional size-mutable, potentially heterogeneous tabular data structure with labeled axes (rows and columns). Arithmetic operations align on both row and column labels. It can be thought of as a dict-like container for Series objects. This is the primary data structure of the Pandas.
Pandas DataFrame.loc attribute access a group of rows and columns by label(s) or a boolean array in the given DataFrame.
Syntax: DataFrame.loc
Parameter: None
Returns: Scalar, Series, DataFrame
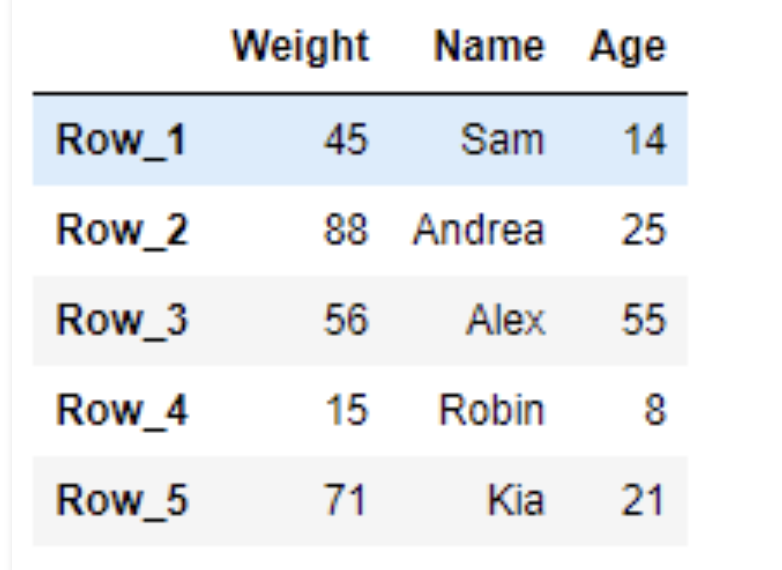
# return the value result = df.loc['Row_2', 'Name'] # Print the result print(result) #Andrea
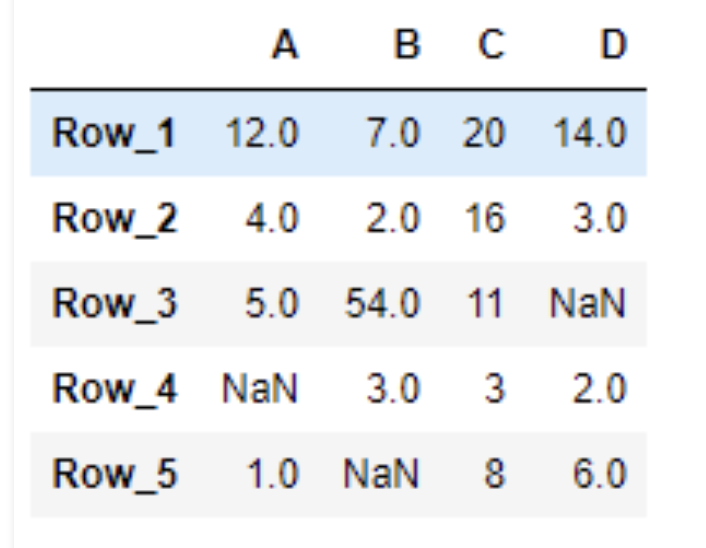
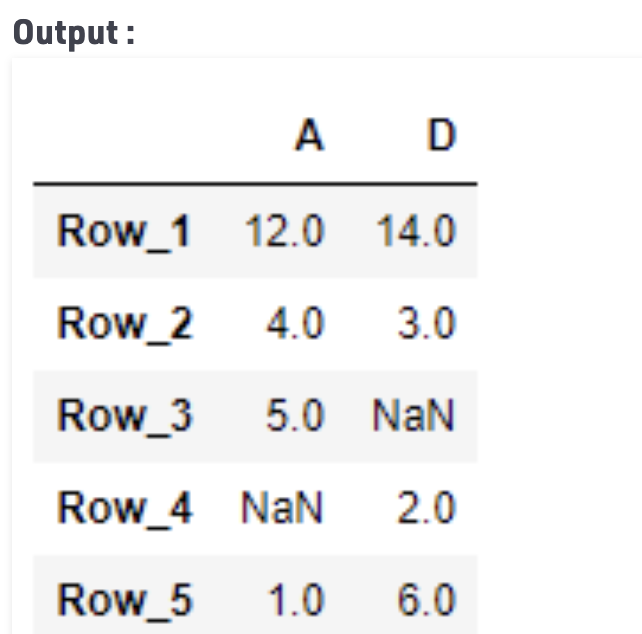
# return the values. result = df.loc[:, ['A', 'D']] # Print the result print(result)
-
numPy.sum()
numpy.sum(arr, axis, dtype, out): This function returns the sum of array elements over the specified axis.
Parameters :
arr: input array.
axis: axis along which we want to calculate the sum value. Otherwise, it will consider arr to be flattened(works on all the axis). axis = 0 means along the column and axis = 1 means working along the row.
out: Different array in which we want to place the result. The array must have the same dimensions as the expected output. Default is None.
initial : [scalar, optional] Starting value of the sum.
Return: Sum of the array elements (a scalar value if the axis is none) or array with sum values along the specified axis.
import numpy as np a = [0,1,2,3,4,5] b = [1,2,3,4,5,6] a = np.array(a) b = np.array(b) c = np.sum(np.square(a-b)) #output: c = 6
# Python Program illustrating # numpy.sum() method import numpy as np # 1D array arr = [20, 2, .2, 10, 4] print(" Sum of arr : ", np.sum(arr)) print("Sum of arr(uint8) : ", np.sum(arr, dtype = np.uint8)) print("Sum of arr(float32) : ", np.sum(arr, dtype = np.float32)) print (" Is np.sum(arr).dtype == np.uint : ", np.sum(arr).dtype == np.uint) print ("Is np.sum(arr).dtype == np.float : ", np.sum(arr).dtype == np.float)
output:
Sum of arr : 36.2 Sum of arr(uint8) : 36 Sum of arr(float32) : 36.2 Is np.sum(arr).dtype == np.uint : False Is np.sum(arr).dtype == np.uint : True
-
the function is used to create an indirect partitioned copy of the input array with its elements rearranged in such a way that the value of the element in k-th position is in the position it would be in a sorted array. All elements smaller than the kth element are moved before this element and all equal or greater are moved behind it. The ordering of the elements in the two partitions is undefined.It returns an array of indices of the same shape as arr, i.enumpy.argpartition()arr[index_array]yields a partition of arr.
Syntax: numpy.argpartition(arr, kth, axis=-1, kind=’introselect’, order=None)
Parameters :
arr : [array_like] Input array.
kth : [int or sequence of ints ] Element index to partition by.
axis : [int or None] Axis along which to sort. If None, the array is flattened before sorting. The default is -1, which sorts along the last axis.
kind: Selection algorithm. Default is ‘introselect’.
order : [str or list of str] When arr is an array with fields defined, this argument specifies which fields to compare first, second, etc.
Return : [index_array, ndarray] Array of indices that partition arr along the specified axis.
use argpartition to find top k maximum values or top k minimum values
x = np.array([3, 4, 2, 1, 0, 5]) print(x[np.argpartition(x, -5)[-5:]]) # find the top 5 maximum values print(x[np.argpartition(x, 5)[:5]]) #find the top 5 minimum values #output: [1 2 4 3 5] [1 2 0 3 4]