摘自:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangye3017/article/details/80382496
1. 线程的查看
首先创建两个线程:
1 #include <stdio.h> 2 #include <unistd.h> 3 #include <pthread.h> 4 #include <stdlib.h> 5 #include <string.h> 6 7 void* pthread_run1(void* arg) 8 { 9 (void)arg; 10 11 while(1) 12 { 13 printf("I am thread1,ID: %d ",pthread_self()); 14 sleep(1); 15 } 16 } 17 18 void* pthread_run2(void* arg) 19 { 20 (void)arg; 21 22 while(1) 23 { 24 printf("I am thread2,ID: %d ",pthread_self()); 25 sleep(1); 26 } 27 } 28 29 30 int main() 31 { 32 33 pthread_t tid1; 34 pthread_t tid2; 35 36 pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,pthread_run1,NULL); 37 pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,pthread_run2,NULL); 38 39 printf("I am main thread "); 40 41 pthread_join(tid1,NULL); 42 pthread_join(tid2,NULL); 43 return 0; 44 }
分析:上面程序中创建了两个线程,程序执行起来,main函数所在程序为主线程,在这个主线程中有两个新线程运行
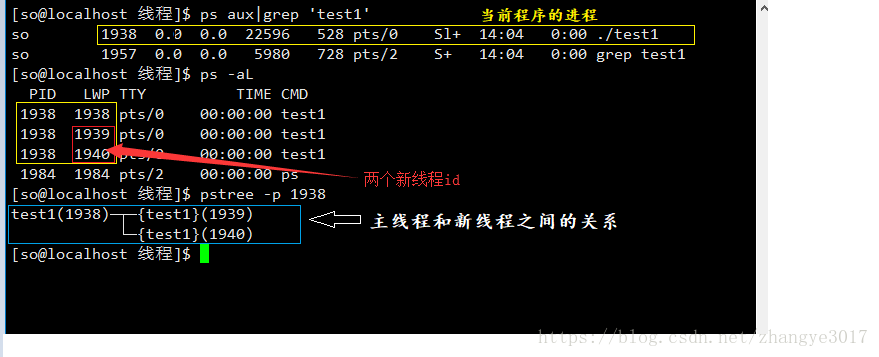
命令行查看:
//查看当前运行的进程 ps aux|grep a.out //查看当前运行的轻量级进程 ps -aL|grep a.out //查看主线程和新线程的关系 pstree -p 主线程id
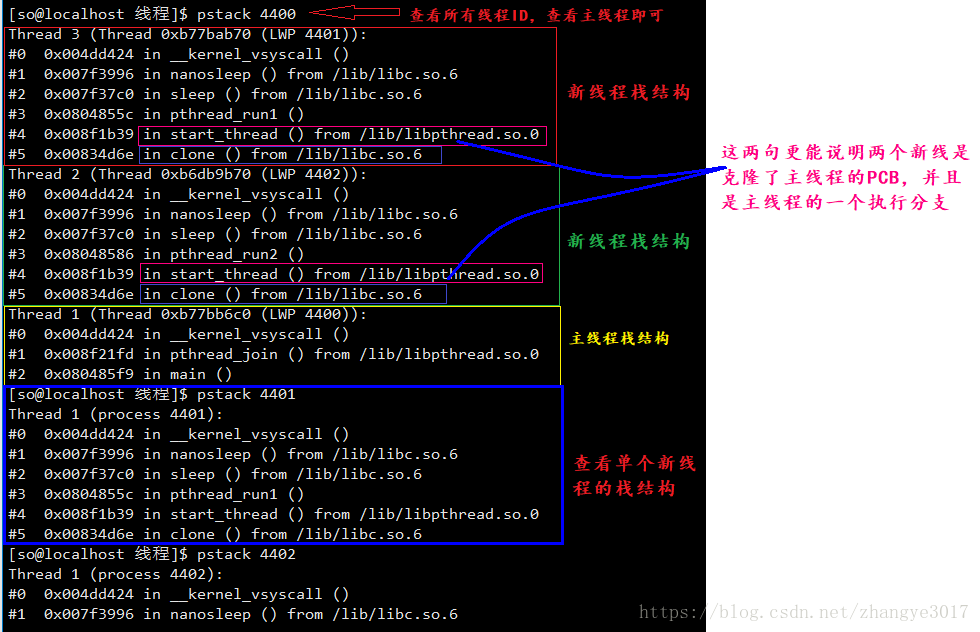
2. 线程栈结构的查看
1. 获取线程ID 2. 通过命令查看栈结构 ps stack 线程ID
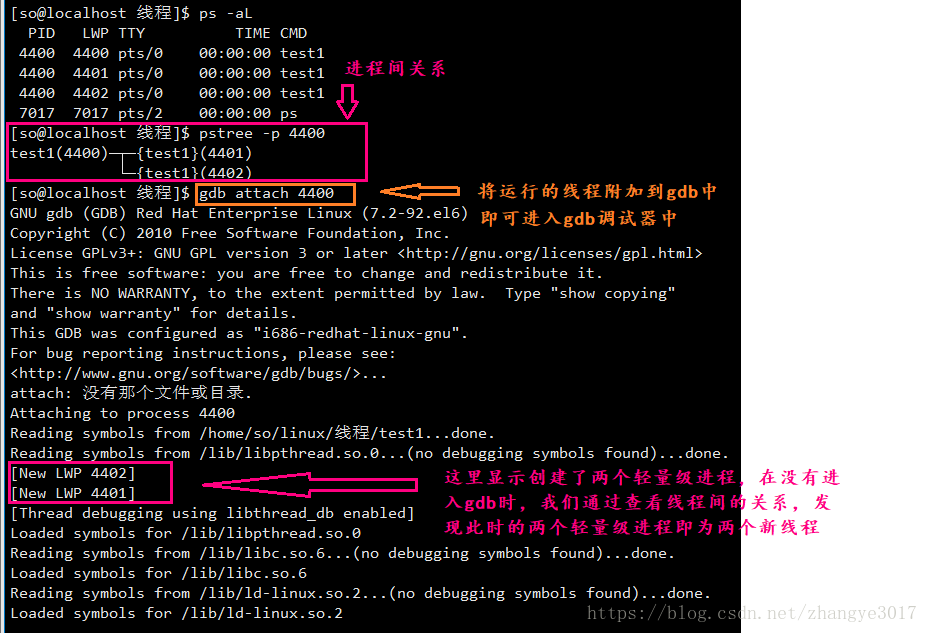
3. 利用gdb查看线程信息
将进程附加到gdb调试器当中,查看是否创建了新线程:gdb attach 主线程ID
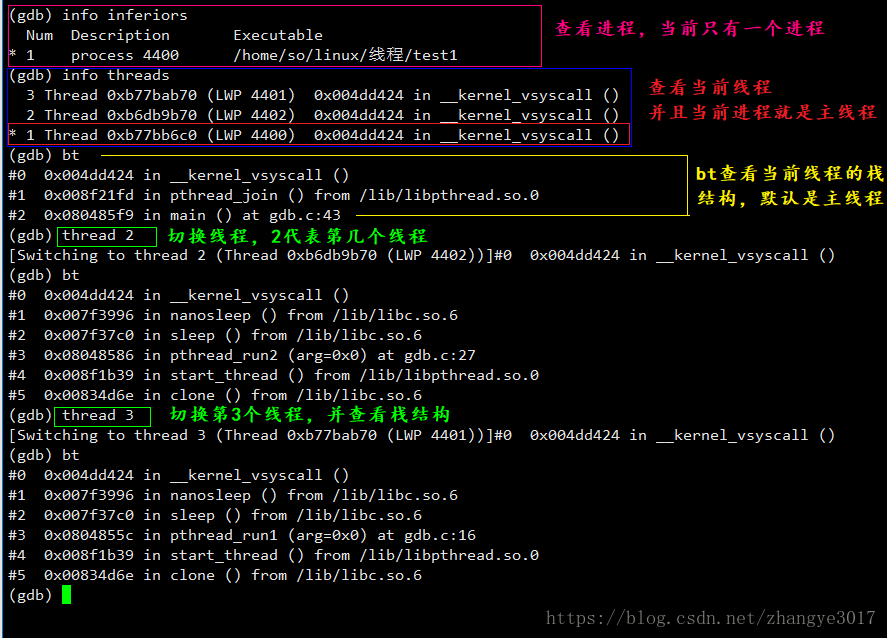
查看线程的一些信息
//1.查看进程:info inferiors //2.查看线程:info threads //3.查看线程栈结构:bt //4.切换线程:thread n(n代表第几个线程)
4. 利用gdb调试多线程
当程序没有启动,线程还没有执行,此时利用gdb调试多线程和调试普通程序一样,通过设置断点,运行,查看信息等等,在这里不在演示,最后会加上调试线程的命令
设置断点
//1. 设置断点:break 行号/函数名 //2. 查看断点:info b
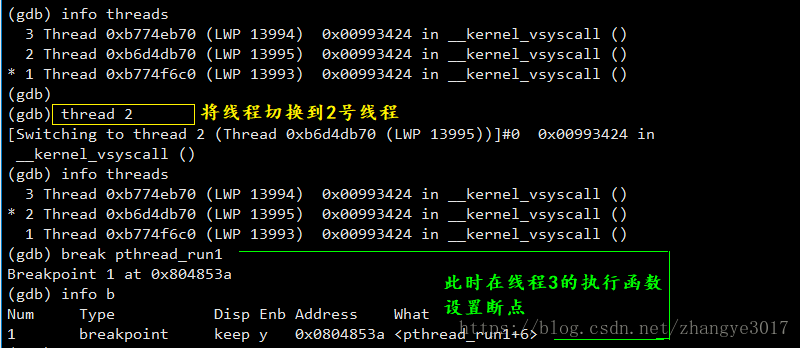
执行线程2的函数,指行完毕继续运行到断点处
1. 继续使某一线程运行:thread apply 1-n(第几个线程) n 2. 重新启动程序运行到断点处:r
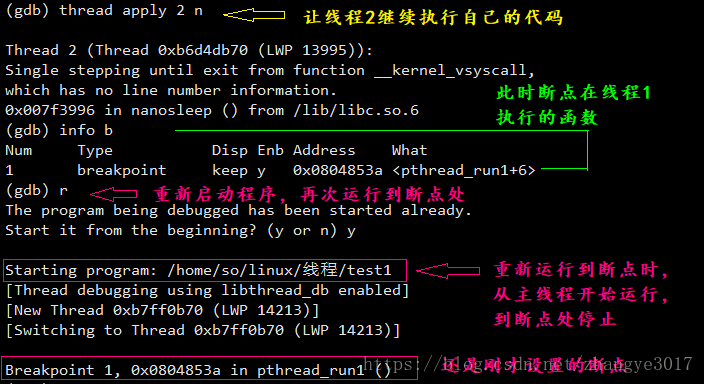
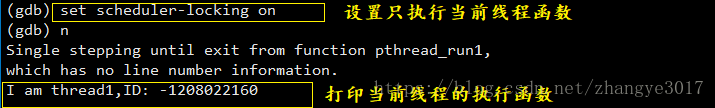
只运行当前线程
1. 设置:set scheduler-locking on 2. 运行:n
所有线程并发执行
1. 设置:set scheduler-locking off 2. 运行:n

总结调试多线程的命令
| 命令 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| info threads | 显示当前可调试的所有线程,每个线程会有一个GDB为其分配的ID,后面操作线程的时候会用到这个ID。 前面有*的是当前调试的线程 |
| thread ID(1,2,3…) | 切换当前调试的线程为指定ID的线程 |
| break thread_test.c:123 thread all(例:在相应函数的位置设置断点break pthread_run1) | 在所有线程中相应的行上设置断点 |
| thread apply ID1 ID2 command | 让一个或者多个线程执行GDB命令command |
| thread apply all command | 让所有被调试线程执行GDB命令command |
| set scheduler-locking 选项 command | 设置线程是以什么方式来执行命令 |
| set scheduler-locking off | 不锁定任何线程,也就是所有线程都执行,这是默认值 |
| set scheduler-locking on | 只有当前被调试程序会执行 |
| set scheduler-locking on step | 在单步的时候,除了next过一个函数的情况(熟悉情况的人可能知道,这其实是一个设置断点然后continue的行为)以外,只有当前线程会执行 |