一、今日学习的内容:
今天学习了6.3和6.4的内容。
二、遇到的问题:
无。
三、明日计划:
明天计划学习6.5的内容。
今天学习的具体内容如下:
1.使用接口
(1)接口不能单独实例化,需要通过接口的实现类来进行实例化,接口的实现类必须实现接口内的全部方法,
(2)接口的使用
接口的实现类的形式:
[修饰符] class <类名> [extends 父类名] [implements 接口列表]
| 修饰符 | 用于指定类的访问权限,可选public、abstract、final |
| 类名 | 用于指定类的名称,需要是合法的Java标识符,首字母大写 |
| extends 父类名 | 可选,用于指定要定义的类继承于哪个类 |
| implements 接口列表 | 可选,用于指定该类实现的是哪些接口,当有多个接口时,用逗号隔开 |
实例如下:
接口的实例化:接口名 对象=new 接口的实现类();
例如下面代码中的 Student2 inter=new Interface();
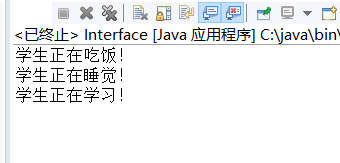
package test1; interface Student2{ int clas=0604; void learning(); void eat(); void sleep(); } public class Interface implements Student2{ @Override public void learning() { System.out.println("学生正在学习!"); } @Override public void eat() { System.out.println("学生正在吃饭!"); } @Override public void sleep() { System.out.println("学生正在睡觉!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Student2 inter=new Interface(); inter.eat(); inter.sleep(); inter.learning(); } }
测试截图;
(3)Java接口的特征归纳
| 1 | 接口中的成员变量默认值是public、static、final,这些是可以省略的,接口中的成员变量都是常量,用大写字母,单词之间用“_”相连。 |
| 2 | 接口中的方法默认是public abstract 类型的,可省略,这些方法在接口中没有方法体,不能被实例化。 |
| 3 | 接口中只能接受成员变量是public、static、final 类型,方法默认是public abstract 类型。接口中的变量必须初始化,且方法必须是抽象方法。 |
| 4 | 接口中没有构造方法,不能被实例化。 |
| 5 | 一个接口不能实现另一个接口,但它可以继承多个其他接口 |
| 6 | Java接口必须通过类来实现它的实现类来它的抽象方法。 |
| 7 | 当类实现了某个接口时,就必须实现接口内的所有方法,否则就将该类设为抽象类。 |
| 8 | 不允许创建接口的实例,但允许定义接口类型的引用变量,该引用变量引用实现了这个接口的类的实例。 |
| 9 | 一个类只能继承一个直接的父类,但可以实现多个接口,间接的实现了多继承。 |
2.接口的继承
(1)接口继承接口
接口只能继承接口,不能继承普通类和抽象类。
interface Student2{ int clas=0604; void learning(); void eat(); void sleep(); } interface Student3{ void play(); } interface Student4 extends Student2,Student3{ public abstract void gohome(); }
(2)间接实现多重继承
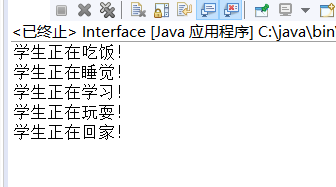
package test1; interface Student2{ int clas=0604; void learning(); void eat(); void sleep(); } interface Student3{ void play(); } interface Student4 extends Student2,Student3{ public abstract void gohome(); } public class Interface implements Student4{ @Override public void learning() { System.out.println("学生正在学习!"); } public void eat() { System.out.println("学生正在吃饭!"); } public void sleep() { System.out.println("学生正在睡觉!"); } public void play() { System.out.println("学生正在玩耍!"); } public void gohome() { System.out.println("学生正在回家!"); } public static void main(String[] args) { Student4 inter=new Interface(); inter.eat(); inter.sleep(); inter.learning(); inter.play(); inter.gohome(); } }
测试截图: