一、斐波那契堆的介绍
斐波那契堆(Fibonacci heap)是堆中一种,它和二项堆一样,也是一种可合并堆;可用于实现合并优先队列。斐波那契堆比二项堆具有更好的平摊分析性能,它的合并操作的时间复杂度是O(1)。
与二项堆一样,它也是由一组堆最小有序树组成,并且是一种可合并堆。
与二项堆不同的是,斐波那契堆中的树不一定是二项树;而且二项堆中的树是有序排列的,但是斐波那契堆中的树都是有根而无序的。
二、斐波那契堆的基本操作
1. 基本定义
1 template <class T> 2 class FibNode { 3 public: 4 T key; // 关键字(键值) 5 int degree; // 度数 6 FibNode<T> *left; // 左兄弟 7 FibNode<T> *right; // 右兄弟 8 FibNode<T> *child; // 第一个孩子节点 9 FibNode<T> *parent; // 父节点 10 bool marked; // 是否被删除第一个孩子 11 12 FibNode(T value):key(value), degree(0), marked(false), 13 left(NULL),right(NULL),child(NULL),parent(NULL) { 14 key = value; 15 degree = 0; 16 marked = false; 17 left = this; 18 right = this; 19 parent = NULL; 20 child = NULL; 21 } 22 };
FibNode是斐波那契堆的节点类,它包含的信息较多。key是用于比较节点大小的,degree是记录节点的度,left和right分别是指向节点的左右兄弟,child是节点的第一个孩子,parent是节点的父节点,marked是记录该节点是否被删除第1个孩子(marked在删除节点时有用)。
1 template <class T> 2 class FibHeap { 3 private: 4 int keyNum; // 堆中节点的总数 5 int maxDegree; // 最大度 6 FibNode<T> *min; // 最小节点(某个最小堆的根节点) 7 FibNode<T> **cons; // 最大度的内存区域 8 9 public: 10 FibHeap(); 11 ~FibHeap(); 12 13 // 新建key对应的节点,并将其插入到斐波那契堆中 14 void insert(T key); 15 // 移除斐波那契堆中的最小节点 16 void removeMin(); 17 // 将other合并到当前堆中 18 void combine(FibHeap<T> *other); 19 // 获取斐波那契堆中最小键值,并保存到pkey中;成功返回true,否则返回false。 20 bool minimum(T *pkey); 21 // 将斐波那契堆中键值oldkey更新为newkey 22 void update(T oldkey, T newkey); 23 // 删除键值为key的节点 24 void remove(T key); 25 // 斐波那契堆中是否包含键值key 26 bool contains(T key); 27 // 打印斐波那契堆 28 void print(); 29 // 销毁 30 void destroy(); 31 32 private: 33 // 将node从双链表移除 34 void removeNode(FibNode<T> *node); 35 // 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中) 36 void addNode(FibNode<T> *node, FibNode<T> *root); 37 // 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面 38 void catList(FibNode<T> *a, FibNode<T> *b); 39 // 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中 40 void insert(FibNode<T> *node); 41 // 将"堆的最小结点"从根链表中移除, 42 FibNode<T>* extractMin(); 43 // 将node链接到root根结点 44 void link(FibNode<T>* node, FibNode<T>* root); 45 // 创建consolidate所需空间 46 void makeCons(); 47 // 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树 48 void consolidate(); 49 // 修改度数 50 void renewDegree(FibNode<T> *parent, int degree); 51 // 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来,并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。 52 void cut(FibNode<T> *node, FibNode<T> *parent); 53 // 对节点node进行"级联剪切" 54 void cascadingCut(FibNode<T> *node) ; 55 // 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key 56 void decrease(FibNode<T> *node, T key); 57 // 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key 58 void increase(FibNode<T> *node, T key); 59 // 更新斐波那契堆的节点node的键值为key 60 void update(FibNode<T> *node, T key); 61 // 在最小堆root中查找键值为key的节点 62 FibNode<T>* search(FibNode<T> *root, T key); 63 // 在斐波那契堆中查找键值为key的节点 64 FibNode<T>* search(T key); 65 // 删除结点node 66 void remove(FibNode<T> *node); 67 // 销毁斐波那契堆 68 void destroyNode(FibNode<T> *node); 69 // 打印"斐波那契堆" 70 void print(FibNode<T> *node, FibNode<T> *prev, int direction); 71 };
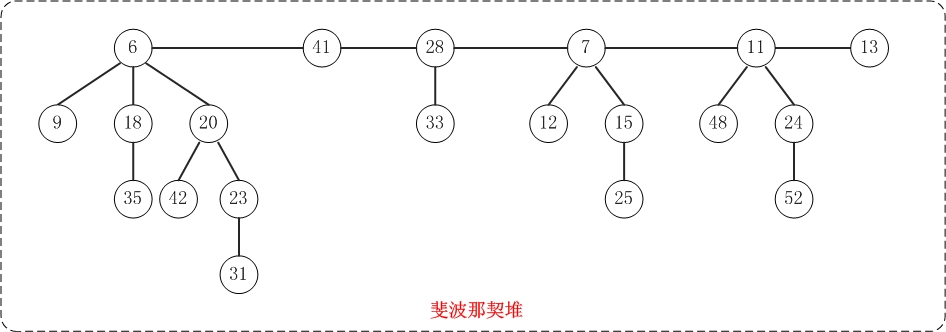
FibHeap是斐波那契堆对应的类。min是保存当前堆的最小节点,keyNum用于记录堆中节点的总数,maxDegree用于记录堆中最大度,而cons在删除节点时来暂时保存堆数据的临时空间。下面是斐波那契堆的属性结构图和内存结构图的对比示例。
从中可以看出,斐波那契堆是由一组最小堆组成,这些最小堆的根节点组成了双向链表(后文称为"根链表");斐波那契堆中的最小节点就是"根链表中的最小节点"!
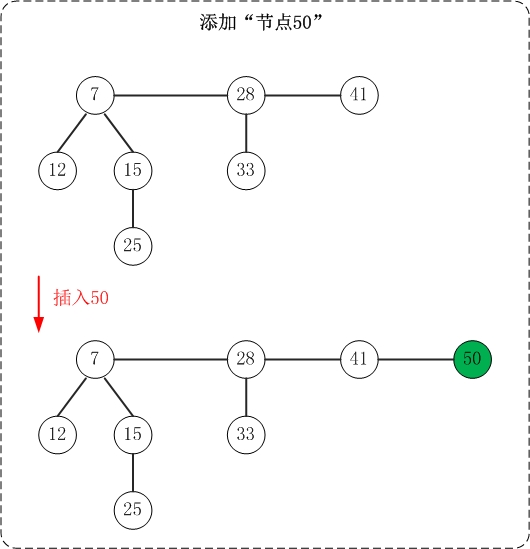
2. 插入操作
插入操作非常简单:插入一个节点到堆中,直接将该节点插入到"根链表的min节点"之前即可;若被插入节点比"min节点"小,则更新"min节点"为被插入节点。
上面是插入操作的示意图。
斐波那契堆的根链表是"双向链表",这里将min节点看作双向联表的表头(后文也是如此)。在插入节点时,每次都是"将节点插入到min节点之前(即插入到双链表末尾)"。此外,对于根链表中最小堆都只有一个节点的情况,插入操作就很演化成双向链表的插入操作。
此外,插入操作示意图与测试程序中的"插入操作"相对应,感兴趣的可以亲自验证。
插入操作代码
1 /* 2 * 将node堆结点加入root结点之前(循环链表中) 3 * a …… root 4 * a …… node …… root 5 */ 6 template <class T> 7 void FibHeap<T>::addNode(FibNode<T> *node, FibNode<T> *root) 8 { 9 node->left = root->left; 10 root->left->right = node; 11 node->right = root; 12 root->left = node; 13 } 14 15 /* 16 * 将节点node插入到斐波那契堆中 17 */ 18 template <class T> 19 void FibHeap<T>::insert(FibNode<T> *node) 20 { 21 if (keyNum == 0) 22 min = node; 23 else 24 { 25 addNode(node, min); 26 if (node->key < min->key) 27 min = node; 28 } 29 keyNum++; 30 }
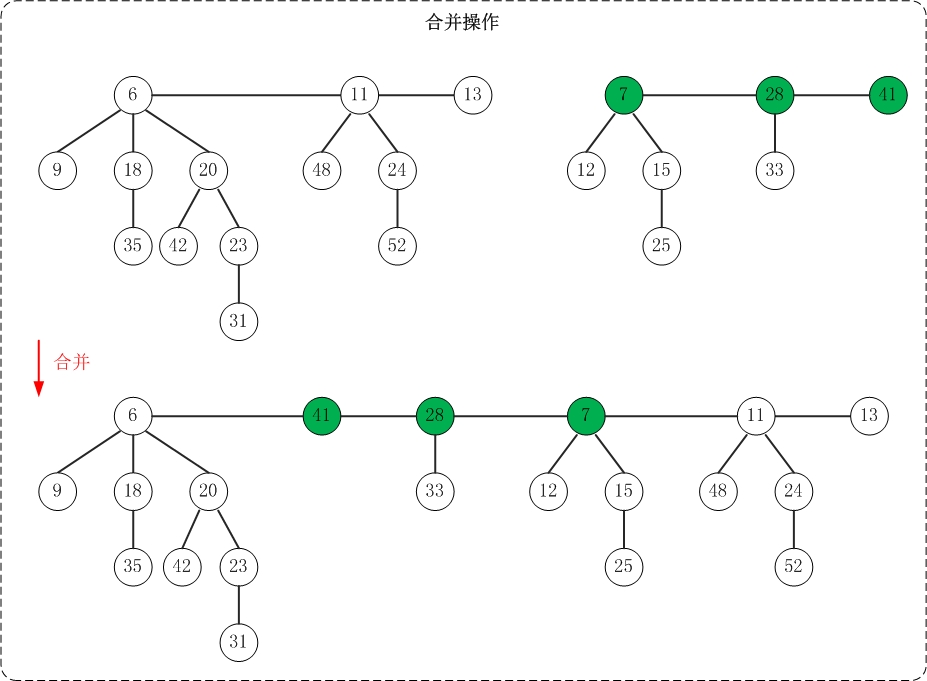
3. 合并操作
合并操作和插入操作的原理非常类似:将一个堆的根链表插入到另一个堆的根链表上即可。简单来说,就是将两个双链表拼接成一个双向链表。
上面是合并操作的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"合并操作"相对应!
合并操作代码
1 /* 2 * 将双向链表b链接到双向链表a的后面 3 * 4 * 注意: 此处a和b都是双向链表 5 */ 6 template <class T> 7 void FibHeap<T>::catList(FibNode<T> *a, FibNode<T> *b) 8 { 9 FibNode<T> *tmp; 10 11 tmp = a->right; 12 a->right = b->right; 13 b->right->left = a; 14 b->right = tmp; 15 tmp->left = b; 16 } 17 18 19 /* 20 * 将other合并到当前堆中 21 */ 22 template <class T> 23 void FibHeap<T>::combine(FibHeap<T> *other) 24 { 25 if (other==NULL) 26 return ; 27 28 if(other->maxDegree > this->maxDegree) 29 swap(*this, *other); 30 31 if((this->min) == NULL) // this无"最小节点" 32 { 33 this->min = other->min; 34 this->keyNum = other->keyNum; 35 free(other->cons); 36 delete other; 37 } 38 else if((other->min) == NULL) // this有"最小节点" && other无"最小节点" 39 { 40 free(other->cons); 41 delete other; 42 } // this有"最小节点" && other有"最小节点" 43 else 44 { 45 // 将"other中根链表"添加到"this"中 46 catList(this->min, other->min); 47 48 if (this->min->key > other->min->key) 49 this->min = other->min; 50 this->keyNum += other->keyNum; 51 free(other->cons); 52 delete other; 53 } 54 }
4. 取出最小节点
抽取最小结点的操作是斐波那契堆中较复杂的操作。
(1)将要抽取最小结点的子树都直接串联在根表中;
(2)合并所有degree相等的树,直到没有相等的degree的树。
上面是取出最小节点的示意图。图中应该写的非常明白了,若有疑问,看代码。
此外,该操作示意图与测试程序中的"删除最小节点"相对应!有兴趣的可以亲自验证。
取出最小节点代码
1 /* 2 * 将"堆的最小结点"从根链表中移除, 3 * 这意味着"将最小节点所属的树"从堆中移除! 4 */ 5 template <class T> 6 FibNode<T>* FibHeap<T>::extractMin() 7 { 8 FibNode<T> *p = min; 9 10 if (p == p->right) 11 min = NULL; 12 else 13 { 14 removeNode(p); 15 min = p->right; 16 } 17 p->left = p->right = p; 18 19 return p; 20 } 21 22 /* 23 * 将node链接到root根结点 24 */ 25 template <class T> 26 void FibHeap<T>::link(FibNode<T>* node, FibNode<T>* root) 27 { 28 // 将node从双链表中移除 29 removeNode(node); 30 // 将node设为root的孩子 31 if (root->child == NULL) 32 root->child = node; 33 else 34 addNode(node, root->child); 35 36 node->parent = root; 37 root->degree++; 38 node->marked = false; 39 } 40 41 /* 42 * 创建consolidate所需空间 43 */ 44 template <class T> 45 void FibHeap<T>::makeCons() 46 { 47 int old = maxDegree; 48 49 // 计算log2(keyNum),"+1"意味着向上取整! 50 // ex. log2(13) = 3,向上取整为3+1=4。 51 maxDegree = (log(keyNum)/log(2.0)) + 1; 52 if (old >= maxDegree) 53 return ; 54 55 // 因为度为maxDegree可能被合并,所以要maxDegree+1 56 cons = (FibNode<T> **)realloc(cons, 57 sizeof(FibHeap<T> *) * (maxDegree + 1)); 58 } 59 60 /* 61 * 合并斐波那契堆的根链表中左右相同度数的树 62 */ 63 template <class T> 64 void FibHeap<T>::consolidate() 65 { 66 int i, d, D; 67 FibNode<T> *x, *y, *tmp; 68 69 makeCons();//开辟哈希所用空间 70 D = maxDegree + 1; 71 72 for (i = 0; i < D; i++) 73 cons[i] = NULL; 74 75 // 合并相同度的根节点,使每个度数的树唯一 76 while (min != NULL) 77 { 78 x = extractMin(); // 取出堆中的最小树(最小节点所在的树) 79 d = x->degree; // 获取最小树的度数 80 // cons[d] != NULL,意味着有两棵树(x和y)的"度数"相同。 81 while (cons[d] != NULL) 82 { 83 y = cons[d]; // y是"与x的度数相同的树" 84 if (x->key > y->key) // 保证x的键值比y小 85 swap(x, y); 86 87 link(y, x); // 将y链接到x中 88 cons[d] = NULL; 89 d++; 90 } 91 cons[d] = x; 92 } 93 min = NULL; 94 95 // 将cons中的结点重新加到根表中 96 for (i=0; i<D; i++) 97 { 98 if (cons[i] != NULL) 99 { 100 if (min == NULL) 101 min = cons[i]; 102 else 103 { 104 addNode(cons[i], min); 105 if ((cons[i])->key < min->key) 106 min = cons[i]; 107 } 108 } 109 } 110 } 111 112 /* 113 * 移除最小节点 114 */ 115 template <class T> 116 void FibHeap<T>::removeMin() 117 { 118 if (min==NULL) 119 return ; 120 121 FibNode<T> *child = NULL; 122 FibNode<T> *m = min; 123 // 将min每一个儿子(儿子和儿子的兄弟)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中 124 while (m->child != NULL) 125 { 126 child = m->child; 127 removeNode(child); 128 if (child->right == child) 129 m->child = NULL; 130 else 131 m->child = child->right; 132 133 addNode(child, min); 134 child->parent = NULL; 135 } 136 137 // 将m从根链表中移除 138 removeNode(m); 139 // 若m是堆中唯一节点,则设置堆的最小节点为NULL; 140 // 否则,设置堆的最小节点为一个非空节点(m->right),然后再进行调节。 141 if (m->right == m) 142 min = NULL; 143 else 144 { 145 min = m->right; 146 consolidate(); 147 } 148 keyNum--; 149 150 delete m; 151 }
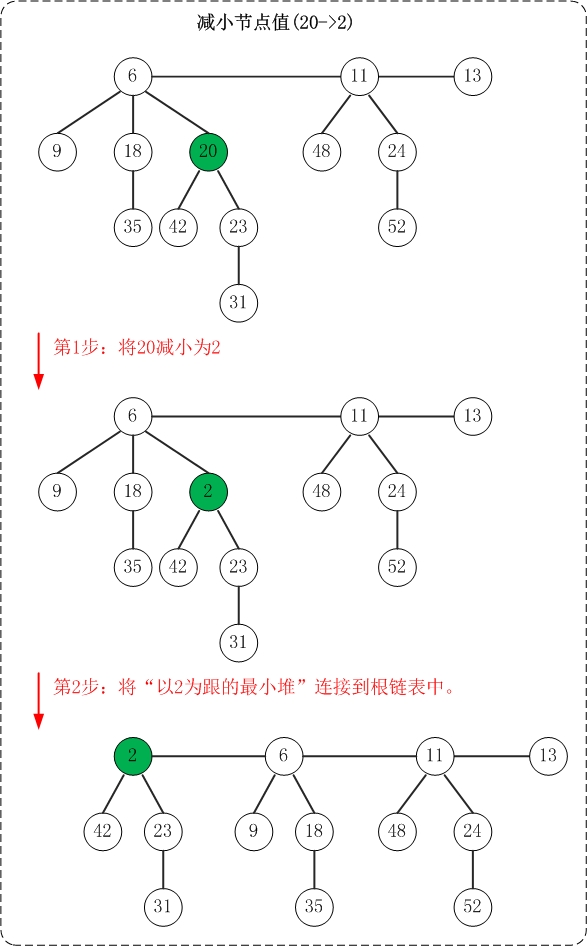
5. 减小节点值
减少斐波那契堆中的节点的键值,这个操作的难点是:如果减少节点后破坏了"最小堆"性质,如何去维护呢?下面对一般性情况进行分析。
(1) 首先,将"被减小节点"从"它所在的最小堆"剥离出来;然后将"该节点"关联到"根链表"中。 倘若被减小的节点不是单独一个节点,而是包含子树的树根。则是将以"被减小节点"为根的子树从"最小堆"中剥离出来,然后将该树关联到根链表中。
(2) 接着,对"被减少节点"的原父节点进行"级联剪切"。所谓"级联剪切",就是在被减小节点破坏了最小堆性质,并被切下来之后;再从"它的父节点"进行递归级联剪切操作。
而级联操作的具体动作则是:若父节点(被减小节点的父节点)的marked标记为false,则将其设为true,然后退出。
否则,将父节点从最小堆中切下来(方式和"切被减小节点的方式"一样);然后递归对祖父节点进行"级联剪切"。
marked标记的作用就是用来标记"该节点的子节点是否有被删除过",它的作用是来实现级联剪切。而级联剪切的真正目的是为了防止"最小堆"由二叉树演化成链表。
(3) 最后,别忘了对根链表的最小节点进行更新。
上面是减小节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"减小节点"相对应!
减小节点值的代码
1 /* 2 * 修改度数 3 */ 4 template <class T> 5 void FibHeap<T>::renewDegree(FibNode<T> *parent, int degree) 6 { 7 parent->degree -= degree; 8 if (parent-> parent != NULL) 9 renewDegree(parent->parent, degree); 10 } 11 12 /* 13 * 将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来, 14 * 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员。 15 */ 16 template <class T> 17 void FibHeap<T>::cut(FibNode<T> *node, FibNode<T> *parent) 18 { 19 removeNode(node); 20 renewDegree(parent, node->degree); 21 // node没有兄弟 22 if (node == node->right) 23 parent->child = NULL; 24 else 25 parent->child = node->right; 26 27 node->parent = NULL; 28 node->left = node->right = node; 29 node->marked = false; 30 // 将"node所在树"添加到"根链表"中 31 addNode(node, min); 32 } 33 34 /* 35 * 对节点node进行"级联剪切" 36 * 37 * 级联剪切:如果减小后的结点破坏了最小堆性质, 38 * 则把它切下来(即从所在双向链表中删除,并将 39 * 其插入到由最小树根节点形成的双向链表中), 40 * 然后再从"被切节点的父节点"到所在树根节点递归执行级联剪枝 41 */ 42 template <class T> 43 void FibHeap<T>::cascadingCut(FibNode<T> *node) 44 { 45 FibNode<T> *parent = node->parent; 46 if (parent != NULL) 47 { 48 if (node->marked == false) 49 node->marked = true; 50 else 51 { 52 cut(node, parent); 53 cascadingCut(parent); 54 } 55 } 56 } 57 58 /* 59 * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值减少为key 60 */ 61 template <class T> 62 void FibHeap<T>::decrease(FibNode<T> *node, T key) 63 { 64 FibNode<T> *parent; 65 66 if (min==NULL ||node==NULL) 67 return ; 68 69 if ( key>=node->key) 70 { 71 cout << "decrease failed: the new key(" << key <<") " 72 << "is no smaller than current key(" << node->key <<")" << endl; 73 return ; 74 } 75 76 node->key = key; 77 parent = node->parent; 78 if (parent!=NULL && node->key < parent->key) 79 { 80 // 将node从父节点parent中剥离出来,并将node添加到根链表中 81 cut(node, parent); 82 cascadingCut(parent); 83 } 84 85 // 更新最小节点 86 if (node->key < min->key) 87 min = node; 88 }
6. 增加节点值
增加节点值和减少节点值类似,这个操作的难点也是如何维护"最小堆"性质。思路如下:
(1) 将"被增加节点"的"左孩子和左孩子的所有兄弟"都链接到根链表中。
(2) 接下来,把"被增加节点"添加到根链表;但是别忘了对其进行级联剪切。
上面是增加节点值的示意图。该操作示意图与测试程序中的"增大节点"相对应!
增加节点值的代码
1 /* 2 * 将斐波那契堆中节点node的值增加为key 3 */ 4 template <class T> 5 void FibHeap<T>::increase(FibNode<T> *node, T key) 6 { 7 FibNode<T> *child, *parent, *right; 8 9 if (min==NULL ||node==NULL) 10 return ; 11 12 if (key <= node->key) 13 { 14 cout << "increase failed: the new key(" << key <<") " 15 << "is no greater than current key(" << node->key <<")" << endl; 16 return ; 17 } 18 19 // 将node每一个儿子(不包括孙子,重孙,...)都添加到"斐波那契堆的根链表"中 20 while (node->child != NULL) 21 { 22 child = node->child; 23 removeNode(child); // 将child从node的子链表中删除 24 if (child->right == child) 25 node->child = NULL; 26 else 27 node->child = child->right; 28 29 addNode(child, min); // 将child添加到根链表中 30 child->parent = NULL; 31 } 32 node->degree = 0; 33 node->key = key; 34 35 // 如果node不在根链表中, 36 // 则将node从父节点parent的子链接中剥离出来, 37 // 并使node成为"堆的根链表"中的一员, 38 // 然后进行"级联剪切" 39 // 否则,则判断是否需要更新堆的最小节点 40 parent = node->parent; 41 if(parent != NULL) 42 { 43 cut(node, parent); 44 cascadingCut(parent); 45 } 46 else if(min == node) 47 { 48 right = node->right; 49 while(right != node) 50 { 51 if(node->key > right->key) 52 min = right; 53 right = right->right; 54 } 55 } 56 }
7. 删除节点
删除节点,本文采用了操作是:"取出最小节点"和"减小节点值"的组合。
(1) 先将被删除节点的键值减少。减少后的值要比"原最小节点的值"即可。
(2) 接着,取出最小节点即可。
删除节点值的代码
1 /* 2 * 删除结点node 3 */ 4 template <class T> 5 void FibHeap<T>::remove(FibNode<T> *node) 6 { 7 T m = min->key-1; 8 decrease(node, m-1); 9 removeMin(); 10 }