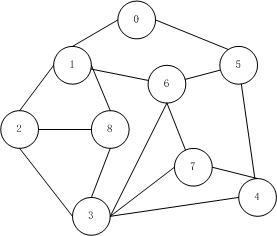
使用邻接矩阵进行存储;
package graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class DFSTraverse {
private static ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
// 邻接矩阵存储;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 初始数据;
int[] vertexs = { 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
int[][] edges = { { 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0 }, { 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1 }, { 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1 },
{ 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 }, { 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 } };
DFSTraverse(vertexs, edges);
System.out.println("深度遍历结果:" + list);
}
private static void DFSTraverse(int[] vertexs, int[][] edges) {
boolean[] visited = new boolean[vertexs.length]; // 顶点是否被访问;
for (int i = 0; i < visited.length; i++) {
visited[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vertexs.length; i++) {
if (!visited[i]) { // 没有被访问;
DFS(edges, visited, i, vertexs);
}
}
}
private static void DFS(int[][] edges, boolean[] visited, int i, int[] vertexs) {
visited[i] = true;
// System.out.println(vertexs[i]);
list.add(vertexs[i]);
for (int j = 0; j < vertexs.length; j++) {
if (edges[i][j] == 1 && !visited[i]) {
DFS(edges, visited, j, vertexs);
}
}
}
}
运行结果
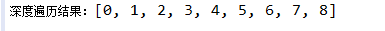
图的深度优先遍历类似于二叉树的前序遍历。