来源:
1.https://ww2.mathworks.cn/help/images/ref/fspecial.html?searchHighlight=fspecial&s_tid=doc_srchtitle#d117e81237
2.https://www.cnblogs.com/leegod/p/8202731.html
简单的原理:
基于MATLAB的中值滤波均值滤波以及高斯滤波的实现
作者:lee神
1. 背景知识
中值滤波法是一种非线性平滑技术,它将每一像素点的灰度值设置为该点某邻域窗口内的所有像素点灰度值的中值.
中值滤波是基于排序统计理论的一种能有效抑制噪声的非线性信号处理技术,中值滤波的基本原理是把数字图像或数字序列中一点的值用该点的一个邻域中各点值的中值代替,让周围的像素值接近的真实值,从而消除孤立的噪声点。
方法是用某种结构的二维滑动模板,将板内像素按照像素值的大小进行排序,生成单调上升(或下降)的为二维数据序列。二维中值滤波输出为g(x,y)=med{f(x-k,y-l),(k,l∈W)} ,其中,f(x,y),g(x,y)分别为原始图像和处理后图像。W为二维模板,通常为3*3,5*5区域,也可以是不同的的形状,如线状,圆形,十字形,圆环形等。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
9 |
|
|
|
5 |
7 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
g(x,y)=med{f(x-k,y-l),(k,l∈W)}
g = med[2,4,8;1,3,9;5,7,6] = 5
中值滤波后的结果
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
均值滤波是典型的线性滤波算法,它是指在图像上对目标像素给一个模板,该模板包括了其周围的临近像素(以目标像素为中心的周围8个像素,构成一个滤波模板,即去掉目标像素本身),再用模板中的全体像素的平均值来代替原来像素值。
均值滤波也称为线性滤波,其采用的主要方法为邻域平均法。线性滤波的基本原理是用均值代替原图像中的各个像素值,即对待处理的当前像素点(x,y),选择一个模板,该模板由其近邻的若干像素组成,求模板中所有像素的均值,再把该均值赋予当前像素点(x,y),作为处理后图像在该点上的灰度g(x,y),即g(x,y)=1/m ∑f(x,y) m为该模板中包含当前像素在内的像素总个数。
均值滤波本身存在着固有的缺陷,即它不能很好地保护图像细节,在图像去噪的同时也破坏了图像的细节部分,从而使图像变得模糊,不能很好地去除噪声点。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
8 |
|
|
|
1 |
3 |
9 |
|
|
|
5 |
7 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
g(x,y)=1/m ∑f(x,y)
g = (1/8)*(2+4+8+1+9+5+7+6) = 5
均值滤波后的结果:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
高斯滤波是一种线性平滑滤波,适用于消除高斯噪声,广泛应用于图像处理的减噪过程。通俗的讲,高斯滤波就是对整幅图像进行加权平均的过程,每一个像素点的值,都由其本身和邻域内的其他像素值经过加权平均后得到。高斯滤波的具体操作是:用一个模板(或称卷积、掩模)扫描图像中的每一个像素,用模板确定的邻域内像素的加权平均灰度值去替代模板中心像素点的值。
- 2. MATLAB实现
源码:
%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
%% 2018/01/03
%% lee
%% 137194782@qq.com
%% 微信公众号:FPGA开源工作室
%%-------------------------------------------------------------------
clear all;
clc;
M = imread('timg.jpg'); %读取MATLAB中的名为timg的图像
figure,imshow(M); %显示原始图像
title('original');
gray = rgb2gray(M);
figure,imshow(gray); %显示灰度图像
title('gray');
P1 = imnoise(gray,'gaussian',0.02); %加入高斯躁声
figure,imshow(P1); %加入高斯躁声后显示图像
title('gaussian noise');
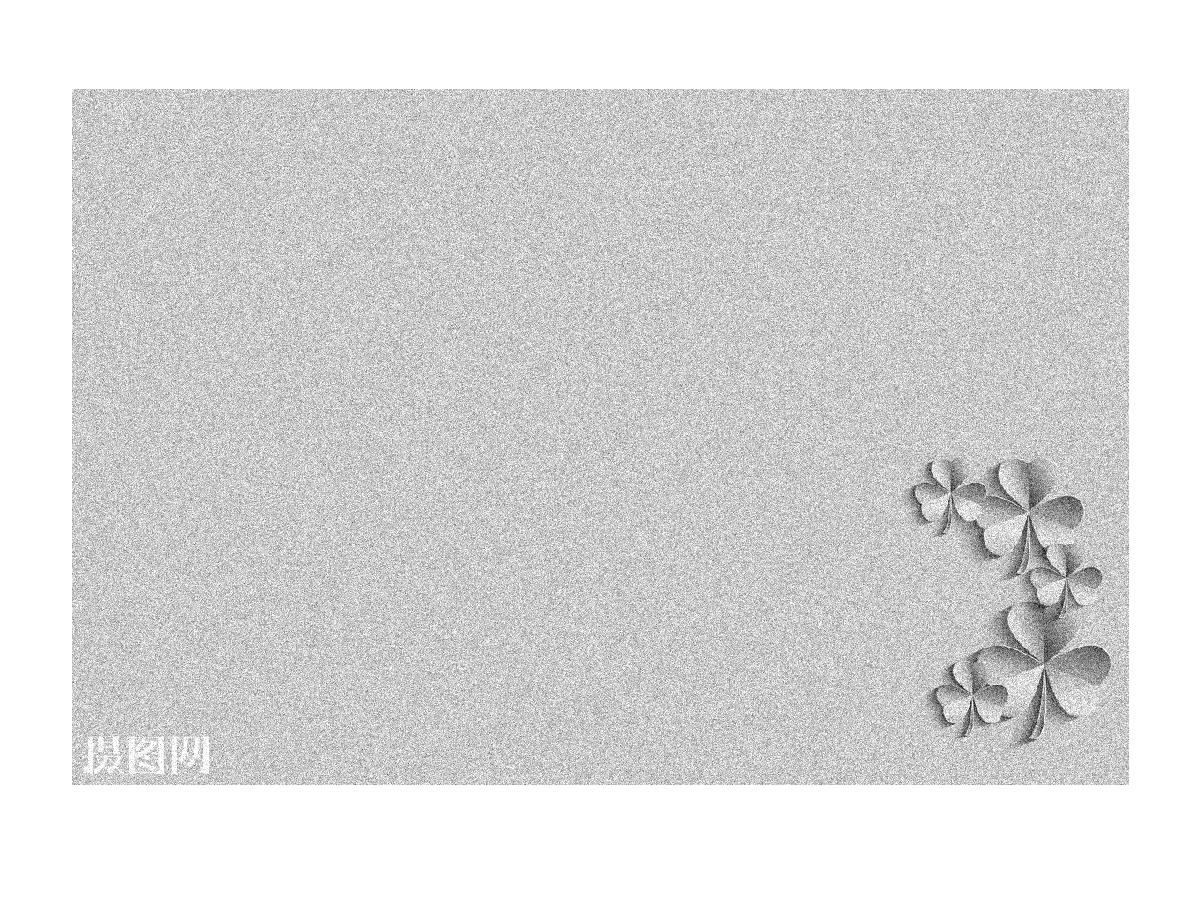
P2 = imnoise(gray,'salt & pepper',0.02); %加入椒盐躁声
figure,imshow(P2); %加入椒盐躁声后显示图像
title('salt & pepper noise');
g = medfilt2(P1); %对高斯躁声中值滤波
figure,imshow(g);
title('medfilter gaussian');
h = medfilt2(P2); %对椒盐躁声中值滤波
figure,imshow(h);
title('medfilter salt & pepper noise');
a=[1 1 1 %对高斯躁声算术均值滤波
1 1 1
1 1 1];
l=1/9*a;
k = conv2(double(P1),double(l));
figure,imshow(k,[]);
title('arithmeticfilter gaussian');
d = conv2(double(P2),double(l)); %对椒盐躁声算术均值滤波
figure,imshow(d,[]);
title('arithmeticfilter salt & pepper noise');
sigma=8;% 标准差大小
window=double(uint8(3*sigma)*2+1);% 窗口大小一半为3*sigma
H=fspecial('gaussian', window, sigma);% fspecial('gaussian', hsize, sigma)产生滤波模板
img_gauss=imfilter(P1,H,'replicate'); %为了不出现黑边,使用参数'replicate'(输入图像的外部边界通过复制内部边界的值来扩展)
figure, imshow(img_gauss);
title('gaussian filting gauss noise');
img_salt=imfilter(P2,H,'replicate');
figure, imshow(img_salt);
title('gaussian filting salt pepper noise');
结果展示:

原始图像
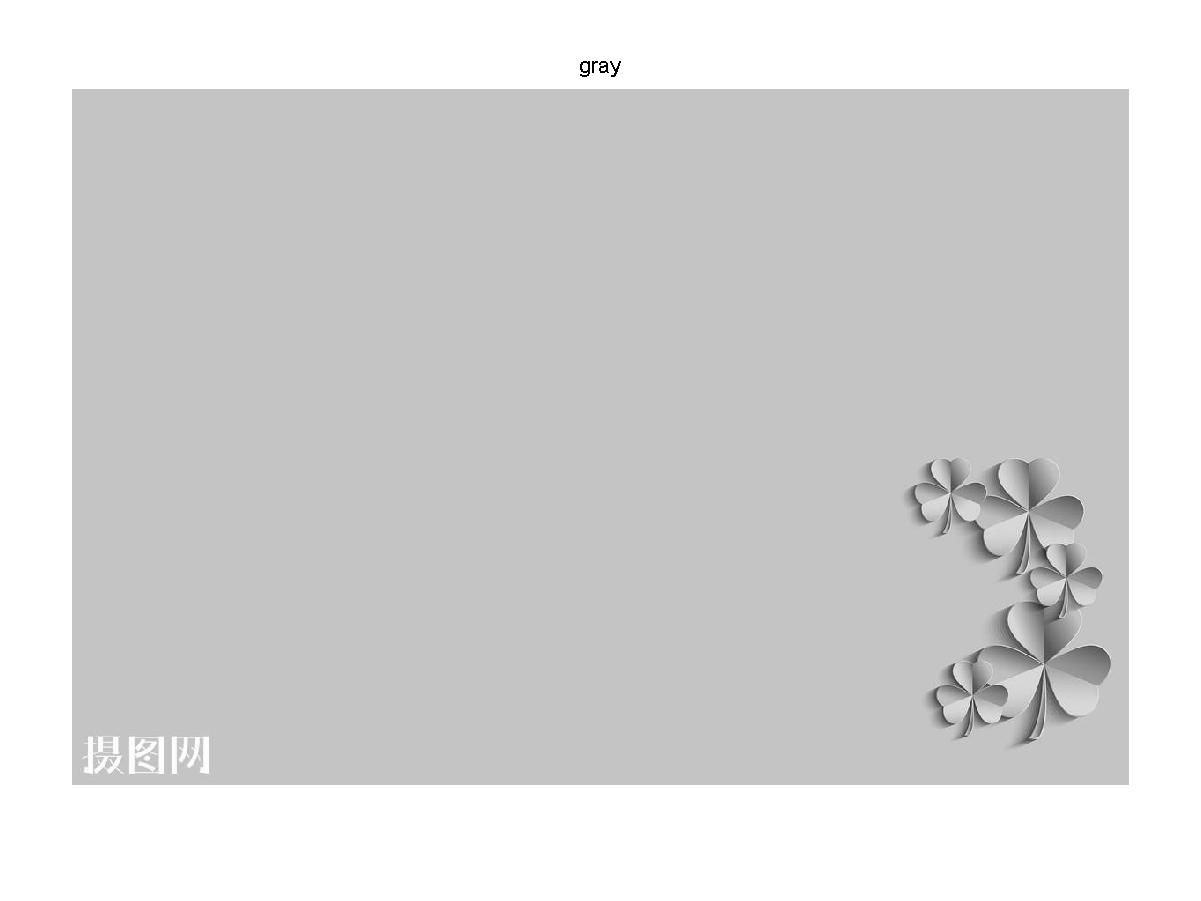

灰度图像
加入高斯噪声的灰度图像
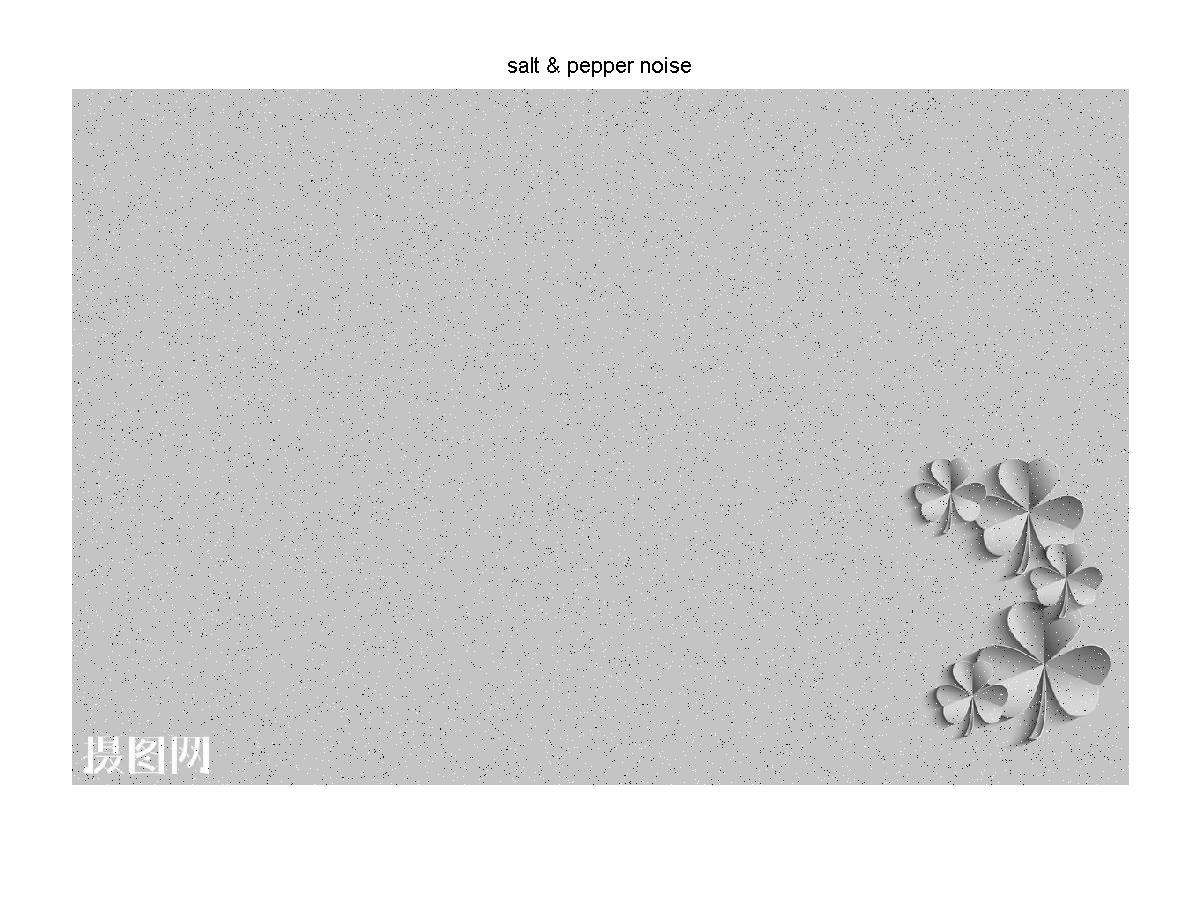
加入椒盐噪声的灰度图像
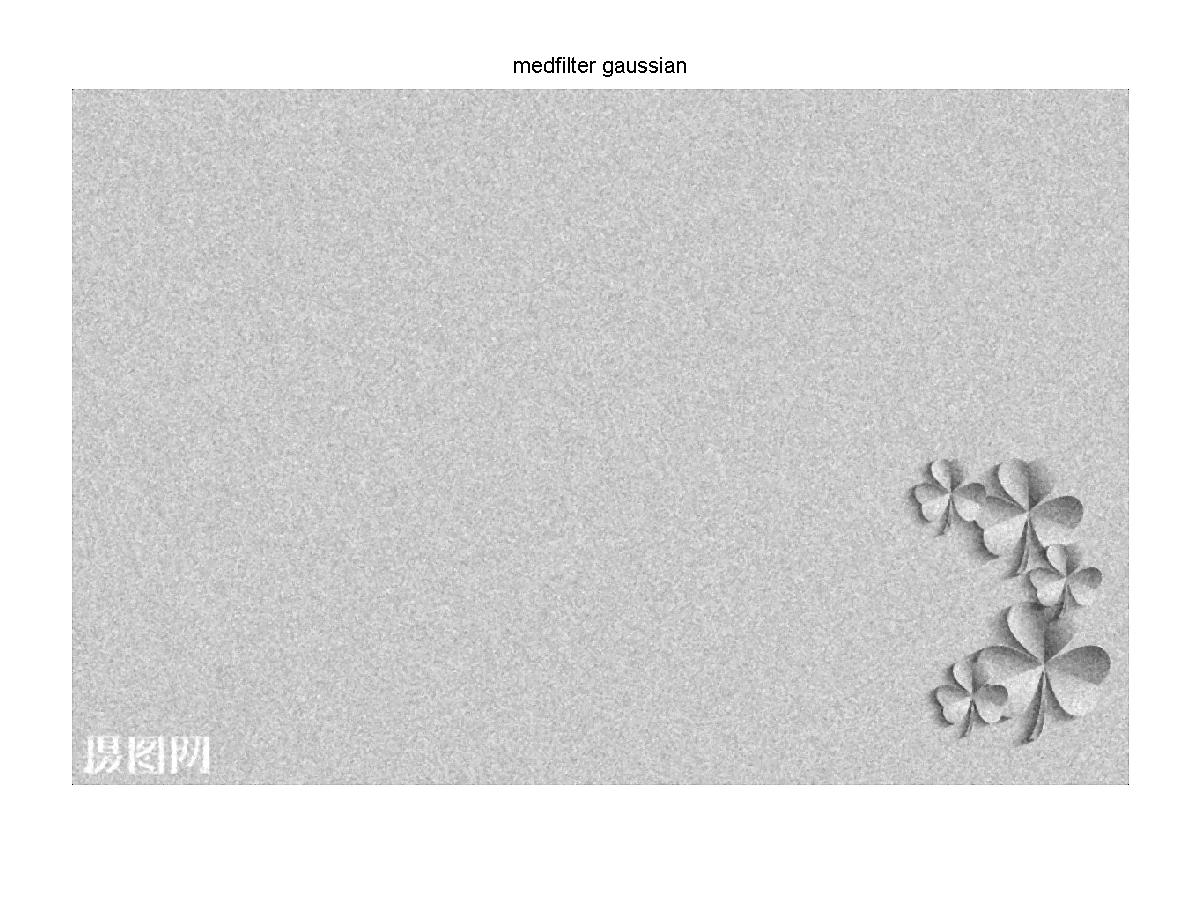

经过中值滤波后的高斯噪声灰度图像
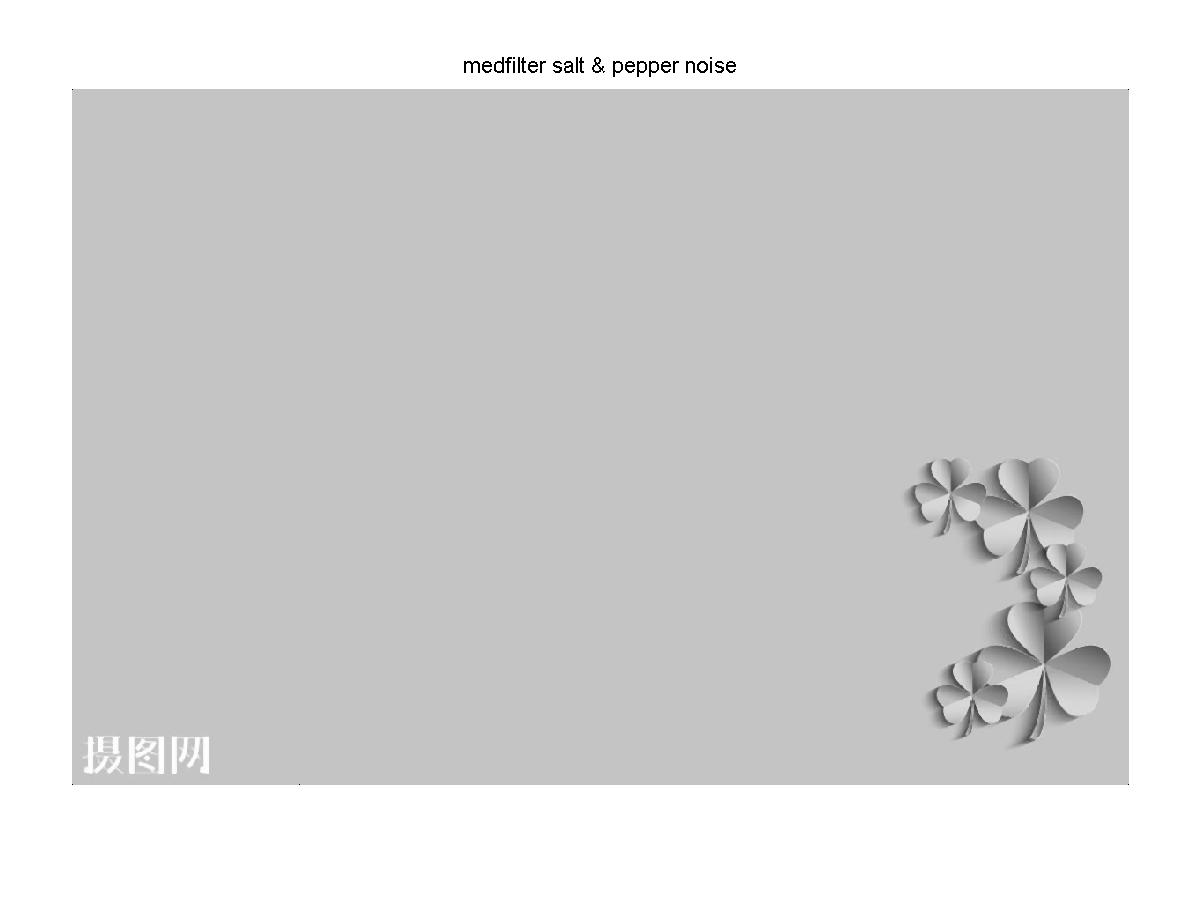
经过中值滤波后的椒盐噪声灰度图像
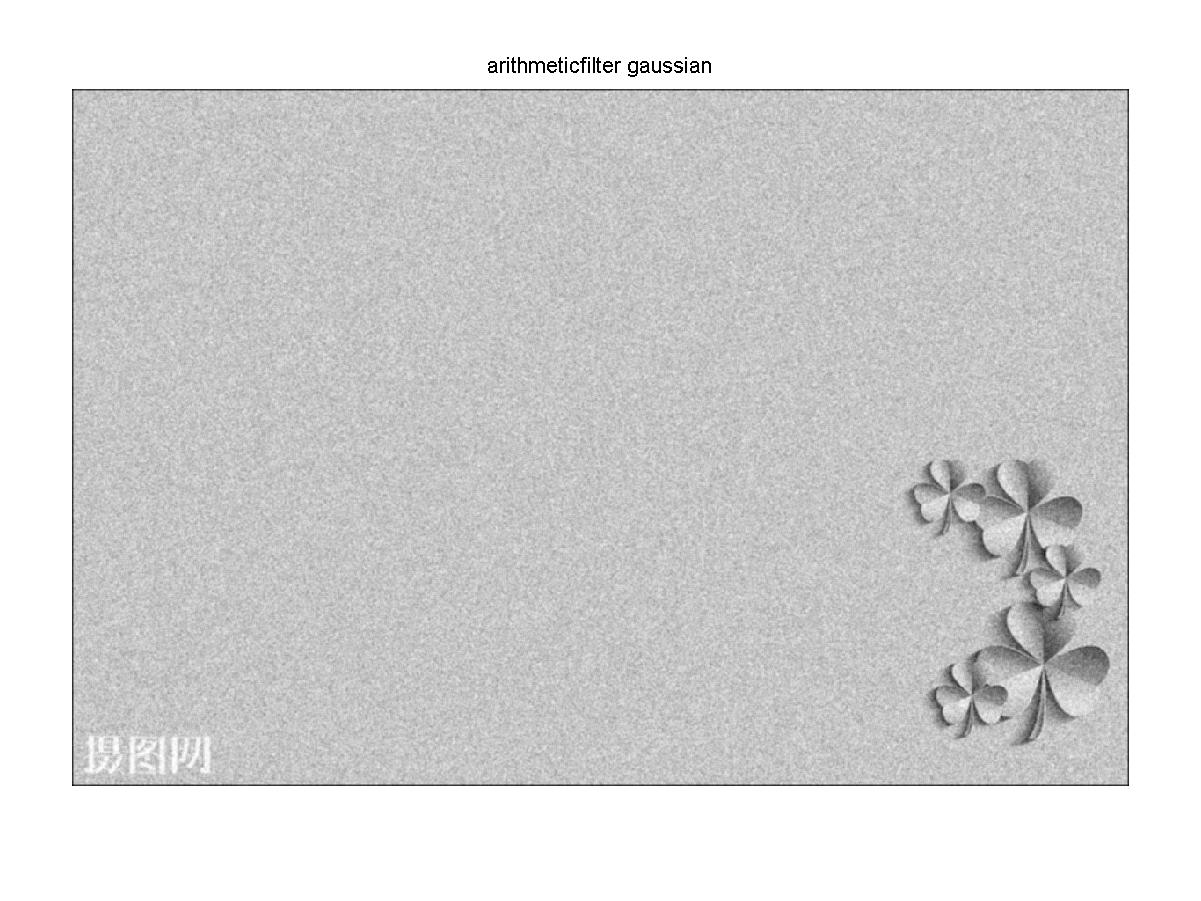

经过均值滤波后的高斯噪声灰度图像
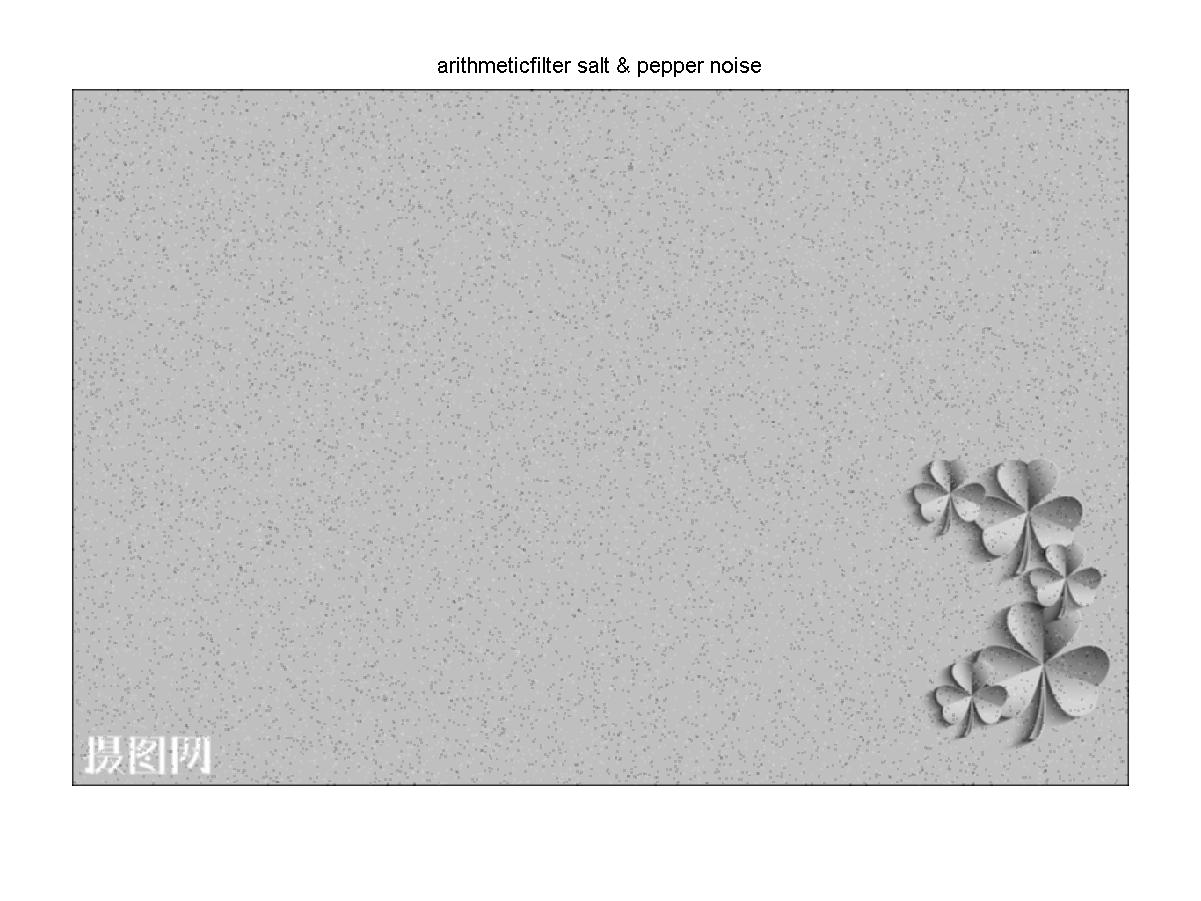
经过均值滤波后的椒盐噪声灰度图像
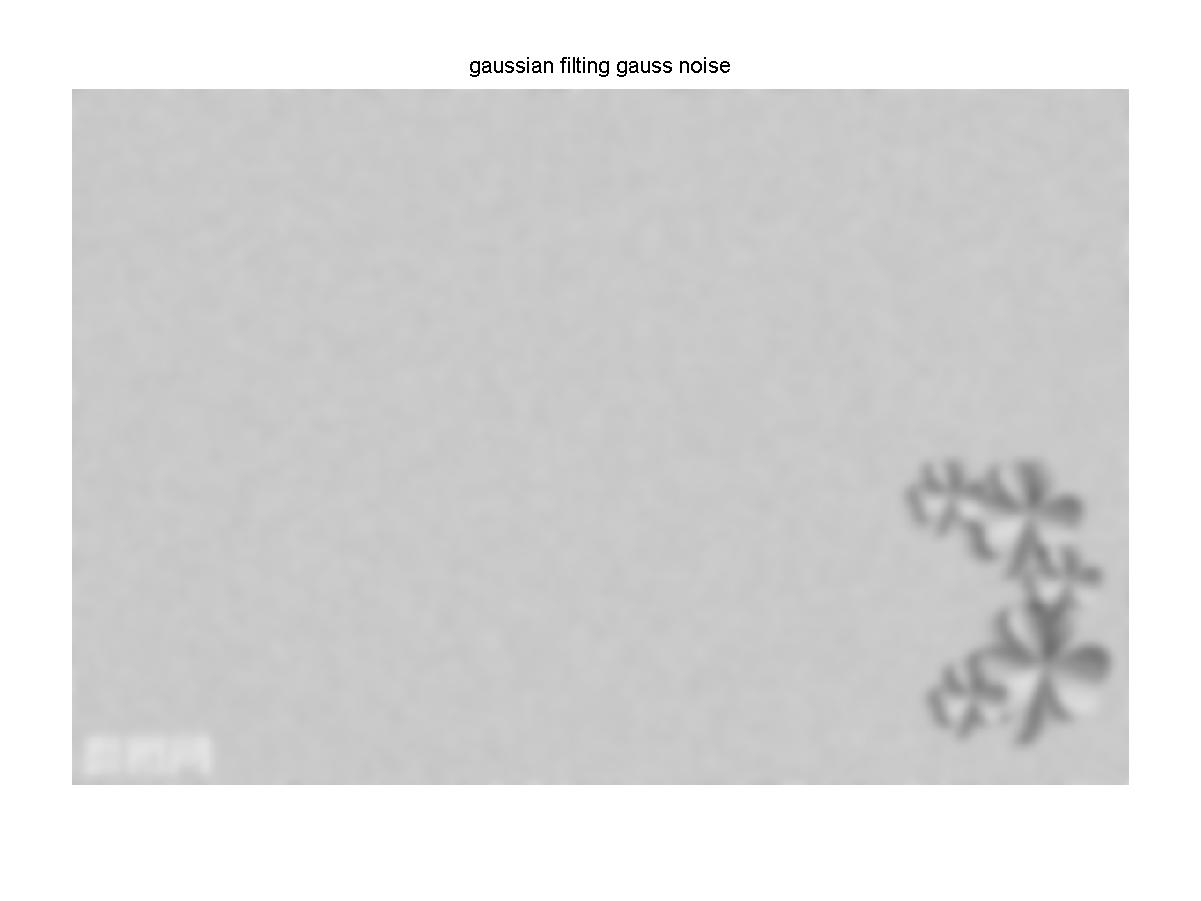

经过高斯滤波后的高斯噪声灰度图像

经过高斯滤波的椒盐噪声的灰度图像
结果分析:图像经过中值滤波后,高斯噪声没有被完全去除,椒盐噪声几乎被完全去除效果较好。经过均值滤波后不管是高斯噪声还是椒盐噪声大部分都没有被去除,只是稍微模糊化。经过高斯滤波后,高斯噪声和椒盐噪声几乎被很大程度的模糊化,原图好像被加上了一层蒙版。
fspecial函数的简介
fspecial
Syntax
Description
h = fspecial('gaussian',hsize,sigma)hsize with standard deviation sigma. Not recommended. Use imgaussfilt or imgaussfilt3 instead.
h = fspecial('motion',len,theta)len specifies the length of the motion and theta specifies the angle of motion in degrees in a counter-clockwise direction. The filter becomes a vector for horizontal and vertical motions. The default len is 9 and the default theta is 0, which corresponds to a horizontal motion of nine pixels.
h = fspecial('prewitt')h'.
[ 1 1 1 0 0 0 -1 -1 -1 ]
h = fspecial('sobel')h'.
[ 1 2 1 0 0 0 -1 -2 -1 ]
Examples
Input Arguments
Output Arguments
Algorithms
Averaging filters:
ones(n(1),n(2))/(n(1)*n(2))
Gaussian filters:
hg(n1,n2)=e−(n21+n22)2σ2
h(n1,n2)=hg(n1,n2)n1n2hg
Laplacian filters:
∇2=∂2∂x2+∂2∂y2
∇2=4(α+1)α41−α4α41−α4−11−α4α41−α4α4
Laplacian of Gaussian (LoG) filters:
hg(n1,n2)=e−(n21+n22)2σ2
h(n1,n2)=(n21+n22−2σ2)hg(n1,n2)σ4n1n2hg
Note that fspecial shifts the equation to ensure that the sum of all elements of the kernel is zero (similar to the Laplace kernel) so that the convolution result of homogeneous regions is always zero.
Motion filters:
-
Construct an ideal line segment with the length and angle specified by the arguments
lenandtheta, centered at the center coefficient ofh. -
For each coefficient location
(i,j), compute the nearest distance between that location and the ideal line segment. -
h = max(1 - nearest_distance, 0); -
Normalize
h:h = h/(sum(h(:)))


