目录
4.1 控制结构
4.1.1 条件分支
if ....:
suite1
elif ...:
suite2
...
elif ...:
suiteN
else:
suite_else
条件表达式
expression1 if boolean_expression else expression2
import random
999 if random.random() > 0.5 else 0 #999 or 0
999 + 1 if random.random() > 0.5 else 0 # 1000 or 0
999 + (1 if random.random() > 0.5 else 0) # 1000 or 999
4.1.2 循环
4.1.2.1 while循环
while boolean_expression:
while_suite
else: #有些时候还蛮有用的 循环正常执行结束后执行
else_suite
4.1.2.2 for循环
for expression in iterable:
for_suite
else: #循环正常结束后执行
else_suite
for i in range(5):
print(i)
else:
print('!!!!')
0
1
2
3
4
!!!!
for i in range(5):
if i == 3:
break
print(i)
else:
print('!!!!')
0
1
2
return 同样会跳过else_suite
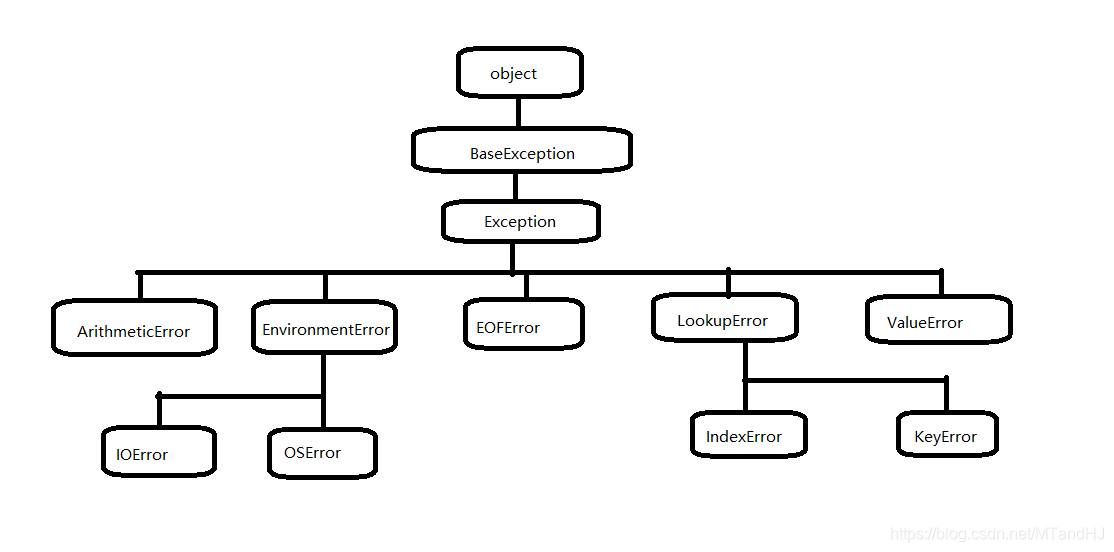
4.2 异常处理
4.2.1 捕获与产生异常
try:
try_suite
except exception_group1 as variable1:
except_suite1
...
except exception_group1 as variable1:
except_suiteN
else: #try部分正常执行才会执行这部分
else_suite
finally: #总会执行 即便异常没有被捕获到 往往用于确保资源被正确释放
finally_suite
更加简单的try...finally...
try:
try_suite
finally:
finally_suite
产生异常 raise
raise exception(args)
raise exception(args) from original_exception
raise
raise KeyError('dasd') # KeyError: 'dasd'
4.2.2 自定义异常
class exceptionName(baseException): pass
注意:上面的baseException是指某个已存在的关于异常的类
class WAWAWAError(KeyError):
pass
tips 用异常跳出深层嵌套循环
flag = False
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
for k in range(9):
if i + j +k > 10:
flag = True
break
if flag:
break
if flag:
break
else:
print(flag)
当i + j + k > 10的时候,我们希望能跳出循环,虽然这个代码块的样子还挺帅的,但是很蠢吧。
class ExitException(Exception): pass
try:
for i in range(9):
for j in range(9):
for k in range(9):
if i + j +k > 10:
raise ExitException()
except ExitException:
print('Come on!')
else:
print('You will not see me!')
4.3 自定义函数
Tips 参数默认值为可变时 危险
给定默认值的时候,参数时在程序执行def时就建立的了,所以,当参数默认值为可变对象的时候,危险。
def append_if_even(x, lst=[]): #从对象绑定的角度考虑,合情合理
if x % 2 == 0:
lst.append(x)
print(lst)
append_if_even(2) #[2]
append_if_even(2) #[2, 2]
append_if_even(2) #[2, 2, 2]
append_if_even(2) #[2, 2, 2, 2]
字符串 数字 元组等都是固定变量
def append_if_even(x, lst=''):
if x % 2 == 0:
lst += '?'
print(lst)
append_if_even(2) # '?'
append_if_even(2) # '?'
append_if_even(2) # '?'
append_if_even(2) # '?'
def append_if_even(x, lst=None):
lst = [] if lst is None else lst
if x % 2 == 0:
lst += '?'
print(lst)
4.3.1 名称与Docstrings
def simpledoc(real, dream='sky'):
""" Returns the text I can not control now...
real is any string; dream is the same as well, while it has default value 'sky'.
Of course, your different people has various dreams, but we all need to confront
the real life.
>>> simpledoc('god')
"haha happy"
>>> simpledoc('god', 'earth')
"don't cry, go forward..."
"""
if real == 'god' and dream == 'sky':
return 'haha happy'
else:
return "don't cry, go forward..."
4.3.2 参数与参数拆分
def product(*args):
print(args)
result = 1
for arg in args:
result += arg
return result
product(2,3,4,5) # (2, 3, 4, 5) 15
*args 后面仍然可以使用关键词参数
def sum_of_powers(*args, power=1): #虽然power不添加默认值不会报错,但是使用的时候必须用关键词参数的形式传入值
result = 0
for arg in args:
result += arg ** power
return result
* 用于区分位置参数和关键词参数 def f(a, b, *, c = 0): ...
def sum_and_add(a, b, *, c = 0):
return a + b + c
sum_and_add(1, 2) # 3
sum_and_add(1, 2, 1) #TypeError
sum_and_add(1, 2, c = 1) # 4
f(**options)
**用于传入参数
options = dict(a = 1, b = 2, c = 1) #如果有多余的参数,会TypeError
sum_and_add(**options) # 4
**用于函数构建
def add(prime = 0, **adds):
for key, value in adds.items():
print(key)
prime += value
return prime
add(a = 1, b = 2, c = 3) # a b c 6
4.3.3 存取全局范围的变量 global
def remain():
global REMAIN
REMAIN = 3
def sum_and_add(a, b):
remain() #得执行一次
return a + b + REMAIN
sum_and_add(1, 2) # 6
4.3.4 Lambda 函数
lambda parameters: expression
expression 不能包含分支或循环,也不能包含return或yield。如果expression是一个元组,那么应该用括号包起来。
f = lambda : (1, 2)
f() # (1, 2)
f = lambda x: "" if x == 1 else 's'
f(1) # ''
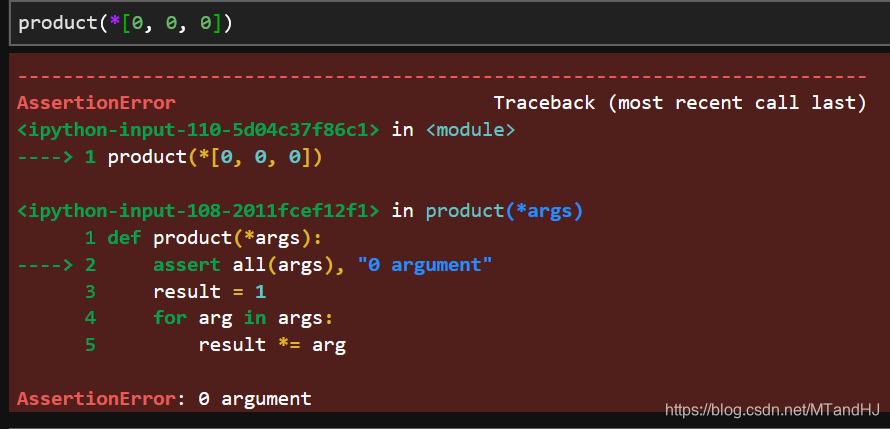
4.3.5 断言 assert
assert boolean_expression, optional_expression
def product(*args):
assert all(args), "0 argument"
result = 1
for arg in args:
result *= arg
return result
product(*[1, 2, 3, 4]) # 24
练习
import os
import sys
WORD_FORWARD = "Choose filename: "
WORD_CONTINUE = "Press Enter to continue..."
WORD_OPTION1 = "[A/a]dd [D/d]elete [S/s]ave [Q/q]uit [a]: "
WORD_OPTION2 = "[A/a]dd [Q/q]uit [a]: "
WORD_ERROR_FILENAME = "Sorry, {0} is not found..."
WORD_ERROR_OPTION1 = "ERROR: invalid choice--enter one of 'AaDdSsQq'"
WORD_ERROR_OPTION2 = "ERROR: invalid choice--enter one of 'AaQq'"
WORD_FILES_ZERO = "-- no items are in list --"
WORD_ADD_ITEM = "Add item: "
WORD_DELETE_ITEM = "Delete item number (or 0 to cancel): "
WORD_ERROR_DELETE = "The number exceeds the limits..."
WORD_SAVE_ITEM = "Saved {0} item{1} to {2}"
WORD_SAVE_UNSAVED = "Save unsaved changes (y/n) [y]: "
def filename_and_set():
f = None
files = []
global filename
try:
filename = input(WORD_FORWARD)
if filename[-4:] != '.txt': #.txt 代替.lst
filename += '.txt'
f = open(filename)
for item in f:
files.append(item.rstrip())
except FileNotFoundError:
pass
finally:
if f is not None:
f.close()
return files
def delete_item(files):
flag = input(WORD_DELETE_ITEM)
try:
flag = int(flag)
if flag is 0:
pass
else:
files.pop(flag - 1)
except ValueError:
print("Integer is need...")
except IndexError:
print(WORD_ERROR_DELETE)
def save_item(files):
f = None
n = len(files)
try:
f = open(filename, 'w', encoding='utf8')
for item in files:
f.write(item + '
')
print(WORD_SAVE_ITEM.format(n,
's' if n > 1 else '',
filename))
except:
print('ERROR: SAVE...')
finally:
if f is not None:
f.close()
def quit_item(files):
n = len(files)
flag = input(WORD_SAVE_UNSAVED)
if flag is 'y' or not flag:
save_item(files)
sys.exit()
def option1(files, label):
if label == 'A' or label == 'a' or not label:
files.append(input(WORD_ADD_ITEM))
elif label == 'D' or label == 'd':
delete_item(files)
elif label == 'S' or label =='s':
save_item(files)
elif label == 'Q' or label == 'q':
quit_item(files)
else:
print(WORD_ERROR_OPTION1)
def option2(files, label):
if label == 'A' or label == 'a' or not label:
files.append(input(WORD_ADD_ITEM))
elif label == 'Q' or label == 'q':
quit_item(files)
else:
print(WORD_ERROR_OPTION2)
def screen_show(files):
n = len(files)
if n != 0:
files.sort()
if not n:
print(WORD_FILES_ZERO)
label = input(WORD_OPTION2)
option2(files, label)
else:
for i in range(n):
print("{0}: {1}".format(i+1, files[i]))
label = input(WORD_OPTION1)
option1(files, label)
def main():
files = filename_and_set()
count = 1
while True:
count += 1
if count > 10:
break
screen_show(files)
print('
')
main()