在上一篇《C#4.0的dynamic和var及object关键字辨析》中温习了.net 4.0的dynamic关键字,今天看看C#的delegate/event/Action/Func/Predicate关键字,它们基本上.net 2.0-3.0就有了,不是新的,但新手容易晕。
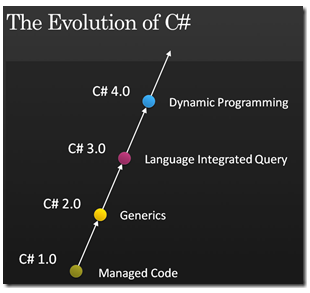
回顾C#发展的历史,C#1.0完全是模仿Java,并保留了C/C++的一些特性如struct,新学者很容易上手;C#2.0加入了泛型,也与 Java1.5的泛型如出一辙;C#3.0加入了一堆语法糖,并在没有修改CLR的情况下引入了Linq,简直是神来之笔,虽然很多项目出于各种各样如性能之类的原因没有采用,但非常适合小型程序的快速开发,减轻了程序员的工作量,也提高了代码的可读性;C#4.0增加了动态语言的特性,从里面可以看到很多javascript、python这些动态语言的影子。虽然越来越偏离静态语言的道路,但从另一个角度来说,这些特性也都是为了提高程序员的生产力。至于被接受与否,还是让时间来说话吧。
好了,看看C#的delegate/event/Action/Func/Predicate关键字,直接上代码:
1: using System;
2: using System.Collections.Generic;
3: using System.Linq;
4: using System.Text;
5:
6: namespace ConsoleApplication1
7: {
8: class Program
9: {
10: public class Test
11: {
12: public delegate void WriteName(string name); //定义委托
13: public static event WriteName WriteNameEvent; //定义事件
14: }
15:
16: static Action<string> WriteNameAction;//Action是参数从0到4,返回类型为void(即没有返回值)的委托
17: static Func<string, int> WriteNameFunction;//Func的参数从1到5个,有返回值的委托,最后一个是返回类型
18:
19: static void Main(string[] args)
20: {
21: Test.WriteName myDelegate = x => { Console.WriteLine("abc,{0}!", x); }; // 使用 Lambda 表达式
22: myDelegate("teststring");
23:
24: Test.WriteName w = (string name) => { Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}!", name); };//使用匿名委托
25: w("Jimmy");
26:
27: Test.WriteNameEvent += (string name) => { Console.WriteLine("Hello,{0}!", name); };//使用匿名委托
28: Test.WriteNameEvent += delegate(string name) { Console.Write("test"); }; //使用匿名方法(.net 2.0)
29:
30: WriteNameAction = HelloWrite; // 匿名委托,和这个一样:WriteNameAction = new Action<string>(HelloWrite);
31: WriteNameAction("test");
32:
33: WriteNameAction = (string name) => { Console.WriteLine("hello,{0}!", name); };//使用匿名委托
34: WriteNameAction("test2");
35:
36:
37: WriteNameFunction = HelloWrite2; // 匿名委托,和这个一样:WriteNameFunction = new Func<string, int>(HelloWrite2);
38: Console.WriteLine(WriteNameFunction("test3"));
39:
40: Predicate<int[]> preTest = i => i.Length == 10;
41:
42: Console.Read();
43:
44: }
45:
46: static List<String> listString = new List<String>()
47: {
48: "One","Two","Three","Four","Fice","Six","Seven","Eight","Nine","Ten"
49: };
50:
51: static List<String> GetFirstStringFromList()
52: {
53: string str = GetStringList(a => { return a.Length <= 3 && a.Contains('S'); });// 使用 Predicate 泛型委托
54:
55: return listString.FindAll((c) => { return c.Length <= 3; });// 使用 Predicate 泛型委托
56: }
57:
58: static String GetStringList(Predicate<String> p) // 使用 Predicate 泛型委托
59: {
60: foreach (string item in listString)
61: {
62: if (p(item))
63: return item;
64: }
65: return null;
66: }
67:
68: static void HelloWrite(string name)
69: {
70: Console.WriteLine("Hello world,{0}!", name);
71: }
72:
73: static int HelloWrite2(string name)
74: {
75: Console.WriteLine("Hello world,{0}!", name);
76: return 1;
77: }
78: }
79: }