There is an m x n matrix that is initialized to all 0's. There is also a 2D array indices where each indices[i] = [ri, ci] represents a 0-indexed location to perform some increment operations on the matrix.
For each location indices[i], do both of the following:
- Increment all the cells on row
ri. - Increment all the cells on column
ci.
Given m, n, and indices, return the number of odd-valued cells in the matrix after applying the increment to all locations in indices.
Example 1:
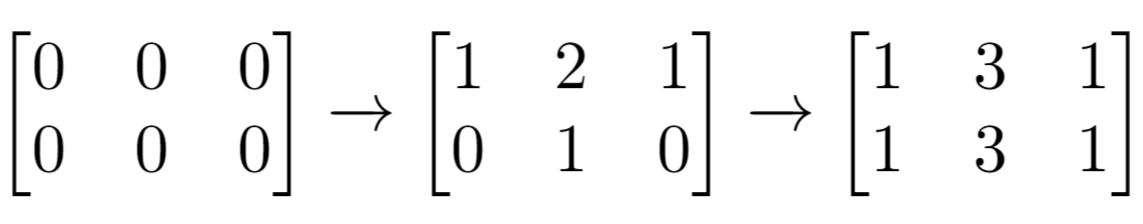
Input: m = 2, n = 3, indices = [[0,1],[1,1]] Output: 6 Explanation: Initial matrix = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]]. After applying first increment it becomes [[1,2,1],[0,1,0]]. The final matrix is [[1,3,1],[1,3,1]], which contains 6 odd numbers.
Constraints:
1 <= m, n <= 501 <= indices.length <= 1000 <= ri < m0 <= ci < n-
class Solution { public: int oddCells(int m, int n, vector<vector<int>>& indices) { vector<int> r(m); vector<int> c(n); int ans=0; for(auto &idx:indices){ r[idx[0]]^=1; c[idx[1]]^=1; } for(int i=0;i<m;++i) for(int j=0;j<n;j++) ans+=r[i]^c[j]; return ans; } };
以上代码参考 花花酱 。异或运算(^) ,两个相同则为假,两个不同则为真。每一行或一列的数都当成整体操作。0与1进行异或运算偶数次结果为0,奇数次异或操作结果为0