-
解法一
因为前面已经有
Merge Two Sorted Lists这道题目的铺垫,所以第一个想法是合并k个链表,那就两两合并,所以解法一的思路比较简单。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
int k = lists.size(); //一共有多少个链表
ListNode* newhead = NULL;
int i = 0;
while(i < k)
{
ListNode* head1 = lists[i];
newhead = mergeTwoLists(head1,newhead);
i++;
}
return newhead;
}
private:
/*每次合并两个链表*/
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
{
ListNode* headnode = new ListNode(0);
headnode->next = NULL;
ListNode* pre = headnode; //尾指针初始状态下指向头节点
//注意题目中l1和l2都没有头节点
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
if(l1->val > l2->val)
{
pre->next = l2;
pre = pre->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
//相等 或 l1 比 l2小 都应该执行这里
pre->next = l1;
pre = pre->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
pre->next = l1;
l1 = NULL;
}
if(l2)
{
pre->next = l2;
l2= NULL;
}
return headnode->next;
}
};
- 解法二 使用最小堆
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
ListNode dummy(0);
ListNode* tail = &dummy;
auto comp = [](ListNode* a,ListNode* b){return a->val > b->val;};
priority_queue<ListNode*,vector<ListNode*>,decltype(comp)> dataqueue(comp);
//ListNode* head;
for(ListNode* list : lists)
{
if(list)
{
dataqueue.push(list);
}
}
while(!dataqueue.empty())
{
tail->next = dataqueue.top();
dataqueue.pop();
tail = tail->next;
if(tail->next)
{
dataqueue.push(tail->next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}
};
首先建立一个最小堆,将l1 l2 l3头部的三个元素依次插入到最小堆中,此时最小堆内的元素为{1,1,2},将最小堆的堆顶1弹出,链接到tail后面,同时由于这个1来自l1,则将l1中的下一个元素4插入最小堆,此时最小堆内的元素为{1,2,4},再弹出最小堆的堆顶,链接到tail后面,同时由于这个1来自链表l2,因此将l2中的下一个元素插入到最小堆中,此时最小堆内元素为{2,3,4},重复这个过程,直到最小堆内的元素为空。

假设有k个链表,每个链表的长度为n,则时间复杂度为:O(kn * log k) 空间复杂度为O(k) + O(n)
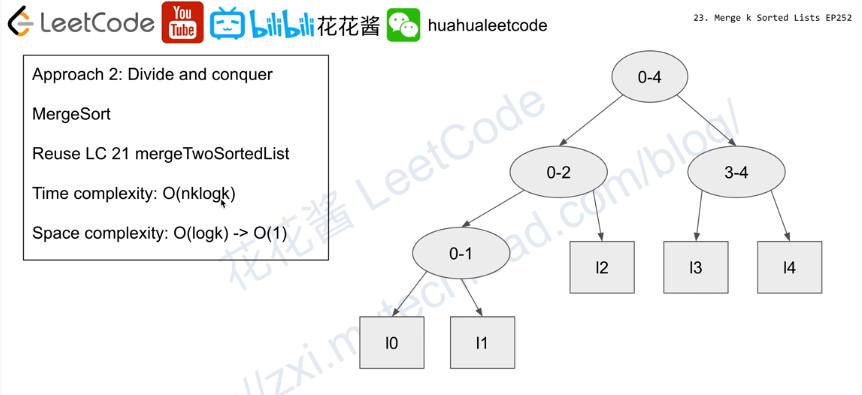
- 解法三 分治思想
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
/*分治思想解决*/
class Solution
{
public:
ListNode* mergeKLists(vector<ListNode*>& lists)
{
int r = 0;
int l = lists.size();
return merge(lists,r,l - 1);
}
private:
ListNode* merge(vector<ListNode*>& lists,int r,int l)
{
int center = 0;
if(r > l)
{
return NULL;
}
if(r == l)
{
return lists[r];
}
if(r + 1 == l)
{
return mergeTwoLists(lists[r],lists[l]);
}
ListNode* left = NULL;
ListNode* right = NULL;
center = (r + l) / 2;
left = merge(lists,r,center); //递归解决左边
right = merge(lists,center + 1,l); //递归解决右边
return mergeTwoLists(left,right);
}
/*合并两个链表*/
ListNode* mergeTwoLists(ListNode* l1, ListNode* l2)
{
ListNode* headnode = new ListNode(0);
headnode->next = NULL;
ListNode* pre = headnode; //尾指针初始状态下指向头节点
//注意题目中l1和l2都没有头节点
while(l1 != NULL && l2 != NULL)
{
if(l1->val > l2->val)
{
pre->next = l2;
pre = pre->next;
l2 = l2->next;
}
else
{
//相等 或 l1 比 l2小 都应该执行这里
pre->next = l1;
pre = pre->next;
l1 = l1->next;
}
}
if(l1)
{
pre->next = l1;
l1 = NULL;
}
if(l2)
{
pre->next = l2;
l2= NULL;
}
return headnode->next;
}
};
分治思想是如果想解决lists中链表合并,就先解决左半部分的链表合并,得到合并后的链表left,再解决右半部分的链表合并,得到合并后的链表right,然后再将左半部分和右半部分分别合并起来即可。而想要得到left,就需要重复上面的过程。
- 参考资料
1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XqA8bBoEdIY 《花花酱 LeetCode 23. Merge k Sorted Lists - 刷题找工作 EP252》