jdk1.8、MyBatis3.4.6、MySQL数据库5.6.45、Eclipse Version: 2019-12 M2 (4.14.0)
MyBatis从入门到精通(第5章):MyBatis代码生成器
在 MBG 的 context 中将 targetRuntime 配置为 MyBatis3 时,MBG 会生成和 Example 相关的对象和方法,这一节就来介绍与 Example 相关的方法。
新建一个针对 country 表相关的 Example MBG 配置文件,新增的配置文件 generatorConfig-country.xml 如下。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE generatorConfiguration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD MyBatis Generator Configuration 1.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-generator-config_1_0.dtd"> <generatorConfiguration> <classPathEntry location="C:Userskangy.m2 epositorymysqlmysql-connector-java5.1.45mysql-connector-java-5.1.45.jar"/> <context id="MySqlContext" targetRuntime="MyBatis3" defaultModelType="flat"> <property name="javaFileEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <commentGenerator> <property name="suppressDate" value="true"/> <property name="addRemarkComments" value="true"/> </commentGenerator> <jdbcConnection driverClass="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" connectionURL="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/testmybatis" userId="root" password="root"> </jdbcConnection> <javaModelGenerator targetPackage="tk.mybatis.simple.model" targetProject="simplesrcmainjava"> <property name="trimStrings" value="true" /> </javaModelGenerator> <sqlMapGenerator targetPackage="tk.mybatis.simple.mapper" targetProject="simplesrcmain esources"/> <javaClientGenerator type="XMLMAPPER" targetPackage="tk.mybatis.simple.mapper" targetProject="simplesrcmainjava"/> <table tableName="country"> <generatedKey column="id" sqlStatement="MySql"/> </table> </context> </generatorConfiguration>
这个配置是针对 Eclipse 插件进行的,所以如果使用其他方式,请注意修改 targetProject 属性。
上面这个配置中的包名都是按照第 2 章中的规范来写的,因此会和原有的 Country 对象冲突(XML 和 Mapper 接口因为使用 Eclipse 插件,所以不会有冲突)。这种情况下,先生成代码,然后处理不一致的地方。
生成代码后,可以发现 CountryMapper 接口中增加了大量的基础方法, CountryMapper.xml 中也增加了相应的 SQL 语句。
下面通过在原有的 CountryMapperTest 测试类中添加新测试来了解 Example 的相关用法。先通过全面调用 Example 对象中的方法来了解 Example,代码如下。
@Test public void testExample() { // 获取 sqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(); try { // 获取 CountryMapper 接口 CountryMapper countryMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CountryMapper.class); //创建 Example 对象 CountryExample example = new CountryExample(); //设置排序规则 example.setOrderByClause("id desc, countryname asc"); //设置是否 distinct 去重 example.setDistinct(true); //创建条件,只能有一个 createCriteria CountryExample.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); //id >= 1 criteria.andIdGreaterThanOrEqualTo(1); //id < 4 criteria.andIdLessThan(4); //countrycode like '%U%' //最容易出错的地方,注意 like 必须自己写上通配符的位置,不可能默认两边加 %,like 可以是任何情况 criteria.andCountrycodeLike("%U%"); //or 的情况,可以有多个 or CountryExample.Criteria or = example.or(); //countryname = 中国 or.andCountrynameEqualTo("中国"); //执行查询 List<Country> countryList = countryMapper.selectByExample(example); printCountryList(countryList); } finally { // 不要忘记关闭 sqlSession sqlSession.close(); } }
打印控制台
DEBUG [main] - ==> Preparing: select distinct id, countryname, countrycode from country WHERE ( id >= ? and id < ? and countrycode like ? ) or( countryname = ? ) order by id desc, countryname asc DEBUG [main] - ==> Parameters: 1(Integer), 4(Integer), %U%(String), 中国(String) TRACE [main] - <== Columns: id, countryname, countrycode TRACE [main] - <== Row: 3, 俄罗斯, RU TRACE [main] - <== Row: 2, 美国, US DEBUG [main] - <== Total: 2 3 俄罗斯 RU 2 美国 US
除了代码中注释的内容,特别需要注意的地方是 or 的方法。当有多个 or 的时候,SQL 语句就是类似 or(...)or(...)这样的 SQL,如果一个 or 都没有,那就只有 example.createCriteria ()中的查询条件。
除了 selectByExample ,与 UPDATE 相关的有两个方法,分别为 updateByExample 和 updateByExampleSelective 。这两个方法的区别是,当对象的属性为空时,第一个方法会将值更新为 null,第二个方法不会更新 null 属性的字段。通过 Example 的方法一般都是批量操作,由于 country 表存在主键 id,不能被批量更新,因此要使用 updateByExampleSelective 进行测试,代码如下。

@Test public void testUpdateByExampleSelective() { // 获取 sqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(); try { // 获取 CountryMapper 接口 CountryMapper countryMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CountryMapper.class); //创建 Example 对象 CountryExample example = new CountryExample(); //创建条件,只能有一个 createCriteria CountryExample.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); //更新所有 id > 2 的国家 criteria.andIdGreaterThan(2); //创建一个要设置的对象 Country country = new Country(); //将国家名字设置为 China country.setCountryname("China"); //执行查询 countryMapper.updateByExampleSelective(country, example); //在把符合条件的结果输出查看 printCountryList(countryMapper.selectByExample(example)); } finally { // 不要忘记关闭 sqlSession sqlSession.close(); } }
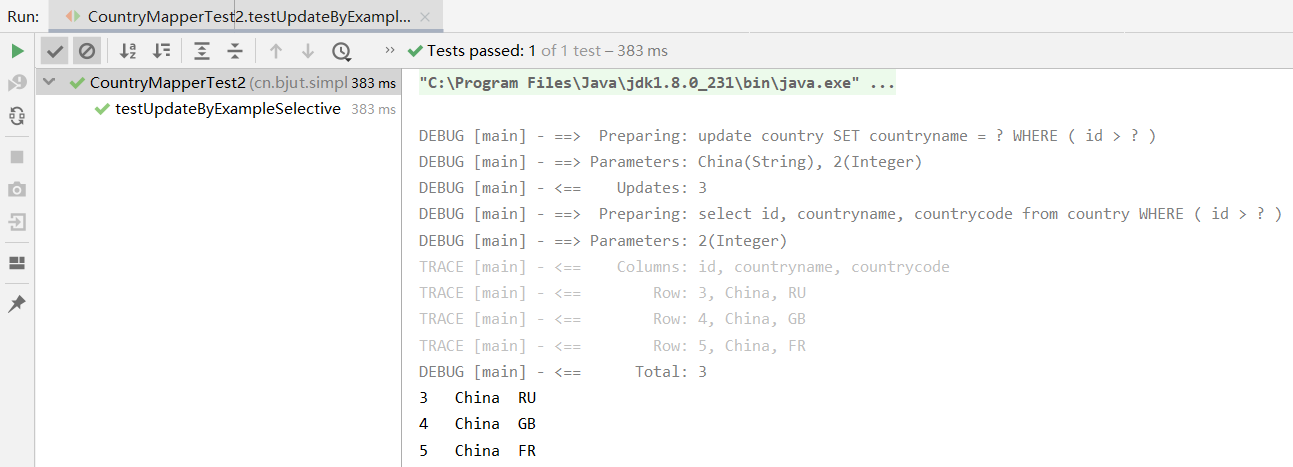
除了以上的 Example 方法,还有 deleteByExample 和 countByExample 两个方法,下面测试这两个方法。

@Test public void testDeleteByExample() { // 获取 sqlSession SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(); try { // 获取 CountryMapper 接口 CountryMapper countryMapper = sqlSession.getMapper(CountryMapper.class); //创建 Example 对象 CountryExample example = new CountryExample(); //创建条件,只能有一个 createCriteria CountryExample.Criteria criteria = example.createCriteria(); //删除所有 id > 2 的国家 criteria.andIdGreaterThan(2); //执行查询 countryMapper.deleteByExample(example); //使用 countByExample 查询符合条件的数量,因为删除了,所以这里应该是 0 Assert.assertEquals(0, countryMapper.countByExample(example)); } finally { // 不要忘记关闭 sqlSession sqlSession.close(); } }
测试代码输出结果如下。
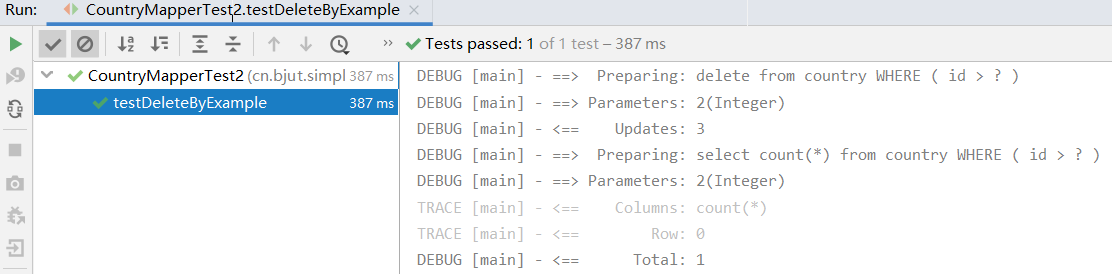
通过上面几个例子,相信大家对 Example 应该已经有所了解,使用 Example 查询能解决大部分复杂的单表操作,从一定程度上能减少工作量。
但是建议在条件很多并且判断很多的情况下,避免使用 Example 查询。这种情况下,使用 XML 方式会更有效。
===================================================================================================================
end
