一,SpringApplicationRunListeners
1》SpringApplicationRunListeners负责在SpringBoot启动的不同阶段,广播出不同的消息, 传递给ApplicationListener监听器实现类。它的实例化和调用都在SpringApplication.run方法中。
2》我们看源码:在304行这里有一个SpringApplicationRunListeners的创建
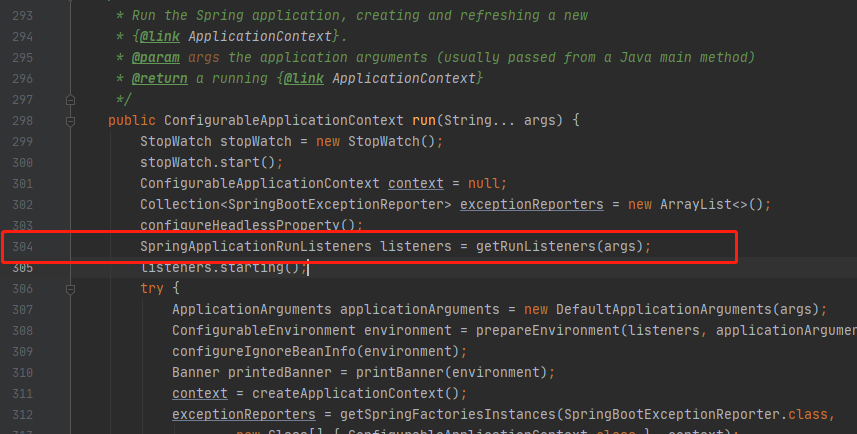
3》我们看看getRunListeners方法是怎么实现的,如下图
PS:他去加载了两个class
1,com.nl.springapprunlistener.SpringApplicationRunListenerDemo(这个我是在META-INF/spring.factories自定定义的SpringApplicationRunListener)
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener=com.nl.springapprunlistener.SpringApplicationRunListenerDemo
2,org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener(而这个是系统默认加载的,这个跟GenericApplicationListener有关系,待会下面解释)
# Run Listeners org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener= org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
在spring-boot-2.3.6.RELEASE.jar 的 META-INF/spring.factories中能找到
4》这个时候我们拿到所有的监听器 ,那该怎么执行么,我们看回run方法
我们可以看到整一个listeners的执行周期,
5》我们看下SpringApplicationRunListeners的listeners的实现方法
/* * Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.util.ReflectionUtils; /** * A collection of {@link SpringApplicationRunListener}. * * @author Phillip Webb */ class SpringApplicationRunListeners { private final Log log; private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners; SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners) { this.log = log; this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners); } void starting() { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.starting(); } } void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.environmentPrepared(environment); } } void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.contextPrepared(context); } } void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.contextLoaded(context); } } void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.started(context); } } void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { listener.running(context); } } void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) { callFailedListener(listener, context, exception); } } private void callFailedListener(SpringApplicationRunListener listener, ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { try { listener.failed(context, exception); } catch (Throwable ex) { if (exception == null) { ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(ex); } if (this.log.isDebugEnabled()) { this.log.error("Error handling failed", ex); } else { String message = ex.getMessage(); message = (message != null) ? message : "no error message"; this.log.warn("Error handling failed (" + message + ")"); } } } }
ps:看源码的,这里就是将自己定义的SpringApplicationRunListenerDemo等等和系统定义的EventPublishingRunListener循环遍历实现他的方法,这样就知道他的周期和自定义的逻辑了,实现广播的模式
二,GenericApplicationListener这个又是怎么实现的呢?
1》事件触发机制,基于观察者模式
2》我们源码剖析下,如上SpringApplicationRunListeners 中执行了每个listeners的方法,listeners的类型是SpringApplicationRunListener是一个接口,我们看看源码
/* * Copyright 2012-2019 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader; /** * Listener for the {@link SpringApplication} {@code run} method. * {@link SpringApplicationRunListener}s are loaded via the {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} * and should declare a public constructor that accepts a {@link SpringApplication} * instance and a {@code String[]} of arguments. A new * {@link SpringApplicationRunListener} instance will be created for each run. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Dave Syer * @author Andy Wilkinson * @since 1.0.0 */ public interface SpringApplicationRunListener { /** * Called immediately when the run method has first started. Can be used for very * early initialization. */ default void starting() { } /** * Called once the environment has been prepared, but before the * {@link ApplicationContext} has been created. * @param environment the environment */ default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { } /** * Called once the {@link ApplicationContext} has been created and prepared, but * before sources have been loaded. * @param context the application context */ default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * Called once the application context has been loaded but before it has been * refreshed. * @param context the application context */ default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * The context has been refreshed and the application has started but * {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and {@link ApplicationRunner * ApplicationRunners} have not been called. * @param context the application context. * @since 2.0.0 */ default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * Called immediately before the run method finishes, when the application context has * been refreshed and all {@link CommandLineRunner CommandLineRunners} and * {@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners} have been called. * @param context the application context. * @since 2.0.0 */ default void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { } /** * Called when a failure occurs when running the application. * @param context the application context or {@code null} if a failure occurred before * the context was created * @param exception the failure * @since 2.0.0 */ default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { } }
2》我们看看SpringApplicationRunListener接口的实现,发现EventPublishingRunListener也是实现这个接口,我们看看EventPublishingRunListener的源码
/* * Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors. * * Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); * you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. * You may obtain a copy of the License at * * https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 * * Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software * distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, * WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. * See the License for the specific language governing permissions and * limitations under the License. */ package org.springframework.boot.context.event; import org.apache.commons.logging.Log; import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener; import org.springframework.boot.availability.AvailabilityChangeEvent; import org.springframework.boot.availability.LivenessState; import org.springframework.boot.availability.ReadinessState; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener; import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.event.ApplicationEventMulticaster; import org.springframework.context.event.SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster; import org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext; import org.springframework.core.Ordered; import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment; import org.springframework.util.ErrorHandler; /** * {@link SpringApplicationRunListener} to publish {@link SpringApplicationEvent}s. * <p> * Uses an internal {@link ApplicationEventMulticaster} for the events that are fired * before the context is actually refreshed. * * @author Phillip Webb * @author Stephane Nicoll * @author Andy Wilkinson * @author Artsiom Yudovin * @author Brian Clozel * @since 1.0.0 */ public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered { private final SpringApplication application; private final String[] args; private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster; public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) { this.application = application; this.args = args; this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } } @Override public int getOrder() { return 0; } @Override public void starting() { this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args)); } @Override public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment)); } @Override public void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { this.initialMulticaster .multicastEvent(new ApplicationContextInitializedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) { if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) { ((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context); } context.addApplicationListener(listener); } this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); } @Override public void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationStartedEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, LivenessState.CORRECT); } @Override public void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) { context.publishEvent(new ApplicationReadyEvent(this.application, this.args, context)); AvailabilityChangeEvent.publish(context, ReadinessState.ACCEPTING_TRAFFIC); } @Override public void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) { ApplicationFailedEvent event = new ApplicationFailedEvent(this.application, this.args, context, exception); if (context != null && context.isActive()) { // Listeners have been registered to the application context so we should // use it at this point if we can context.publishEvent(event); } else { // An inactive context may not have a multicaster so we use our multicaster to // call all of the context's listeners instead if (context instanceof AbstractApplicationContext) { for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : ((AbstractApplicationContext) context) .getApplicationListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } } this.initialMulticaster.setErrorHandler(new LoggingErrorHandler()); this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(event); } } private static class LoggingErrorHandler implements ErrorHandler { private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(EventPublishingRunListener.class); @Override public void handleError(Throwable throwable) { logger.warn("Error calling ApplicationEventListener", throwable); } } }
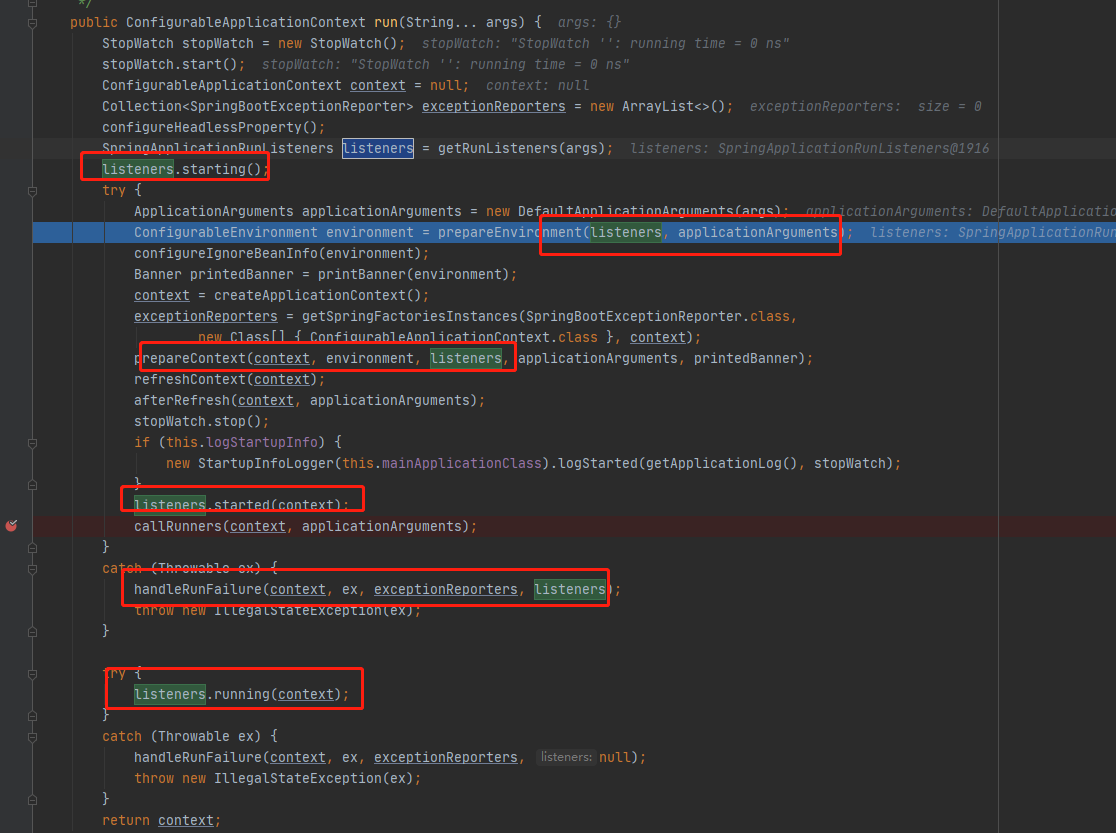
3》看到EventPublishingRunListener这个源码我们明白了,是在EventPublishingRunListener执行所有的ApplicationListener,而每一个GenericApplicationListener就是ApplicationListener,但是我们又有疑惑,EventPublishingRunListener的构造获取所有的ApplicationListener是什么时候初始化进去的呢?
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) { this.application = application; this.args = args; this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster(); for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) { this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener); } }
如下图,原来在run的方法的时候就已经初始化了所有的ApplicationListener(事件)

5》最终我们屡屡整个流程和关系
1,SpringApplicationRunListener
1)SpringApplicationRunListener执行的逻辑是在run获取所有的SpringApplicationRunListener类型,
2)然后遍历执行时生命周期的方法(包含了starting,environmentPrepared,contextPrepared,contextLoaded,started,running和failed)
2,GenericApplicationListener
1)GenericApplicationListener是继承ApplicationListener
2)ApplicationListener所有的执行是在EventPublishingRunListener(EventPublishingRunListener是SpringApplicationRunListener,这个是springboot框架自己初始化)
3)EventPublishingRunListener在自己的包含了starting,environmentPrepared,contextPrepared,contextLoaded,started,running和failed分别执行了ApplicationListener,
4)所以这是典型的观察者模式(GenericApplicationListener是使用SpringApplicationRunListener来实现事件的执行)