本节讨论最简单和最基本的三种数据结构:表,栈和队列。
每种程序都明晰地至少使用一种这样的数据结构,而栈在程序中总要间接地用到。
内容:
1.介绍抽象数据类型(ADT)的概念;
2.阐述如何对表进行有效的操作;
3.介绍栈ADT及其在实现递归方面的应用;
4.介绍队列ADT及其在操作系统和算法设计上的与应用。
(1)抽象数据类型
程序设计的基本法则之一是:例程不应超过一页。
模块化的优点:
1)调试小程序比调试大程序容易的多;
2)多个人同时对一个模块式程序编程更加容易;
3)一个写得好的模块化程序把某些依赖关系只局限在一个例程中,这样使得修改起来更加容易。
由模块化是有益的可以推出:全局变量和副作用是有害的。
抽象数据类型(abstract data type ADT)是一些操作的集合。对诸如表、集合、图和他们的操作一起可看作是抽象数据类型。对于集合ADT,我们有诸如并,交,测定大小以及取余等操作。或者我们也可以只要两种操作:并和查找,这两种操作又在集合上定义了一种不同的ADT。
(2)表ADT
几个概念:
1)空表:大小为0的表;
2)后继元:当前元素的后一个;
3)前驱元:当前元素的前一个;
与ADT的定义有关的就是在ADT上进行操作的集合了:printList,makeEmpty,find,findKth,findPreviousinsert,delete等。
2.1表的简单数组实现:
对表的所有操作都可以使用数组来实现。虽然数组是动态指定的,但是还是需要对表的大小的最大值进行估算。这会导致有可能浪费大量的空间。数组实现使得PrintList和Find以线性时间执行,FindKth以常数时间。而插入和删除的代价昂贵。
因为插入和删除的运行时间是如此的慢以及表的大小必须事先已知,所以简单数组一般不用来实现表这种结构。
2.2链表
为了避免插入和删除的线性开销,我们允许表可以不连续存储。
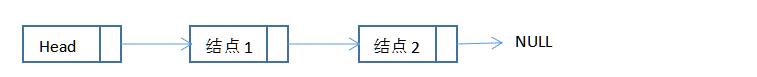
链表由一系列在不必再内存中相连的结构组成。每一个结构均包含表元素和包含指向该元素后继元的Next指针。最后一个单元的Next指针指向NULL,ANSI C规定NULL为0;
图:
一个链表:
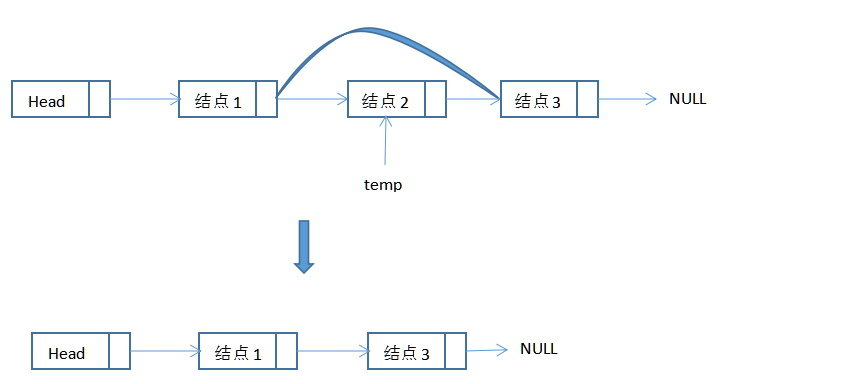
从链表中删除一个元素:
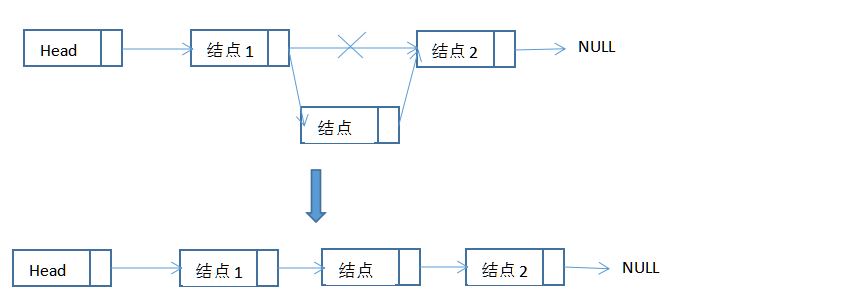
向链表中插入:
2.3程序设计细节:
可能遇到的问题:
1)不存在从所给定义出发在表的前面插入元素的真正显示的方法;
2)从表的前面实行删除是一个特殊情况,因为它改变了表的起始段,在编程中对疏忽可能导致表的丢失。
3)在一般的删除中要求我们记住被删除单元前面的表元。
为了解决这个问题,我们通常留出一个标记结点,有时我们称之为表头(header)或者哑结点(dummy node)。同时为了避免删除中的一些问题,我们需要编写例程findPrevious返回我们要删除表元的前驱元的位置。表头的使用能够使我们表达基本的指针操作而又不致使特殊情形的代码含糊不清。
在处理链表的删除操作的相关问题时,我们需要编写例程findPrevious(),它将返回我们要删除的表元的前驱元的位置。如果我们使用头节点,那么当我们删除表的第一个元素时,findPrevious()将返回表头的位置。
2.4单向链表:
单向链表的ADT的例程:
#ifndef_List_H struct Node; typedef struct Node *PtrToNode; typedef PtrToNode List;//另起一个名字 typedef PtrToNode Position; typedef int ElementType; List MakeEmpty(List L); int IsEmtpy(List L); int IsLast(Position P,List L); Position Find(ElementType X,List L); void Delete(ElementType X,List L); Position FindPrevious(ElementType X,List L); void Insert(ElementType X,List L,Position P); void DeleteList(List L); Position Header(List L); Position First(List L); ElementType Retrieve(Position P); #endif /* _List_H */ /*Node结点的声明是在.c文件中(Place in the implementation file)*/ struct Node{ ElementType Element; Position Next; }; //测试一个链表是否为空表 int IsEmtpy(List L){ return L->Next==NULL; } //测试当前位置是不是链表的尾部 int IsLast(Position P,List L){ return P->next==NULL; } //Find例程 Position Find(ElementType X,List L){ Position P; P=P->Next; while(P!=NULL&&P->Element!=X){ P=P->Next; } return P; } //链表的删除例程 void Delete(ElementType X,List L){ Position P,TmpCell; P=FindPrevious(X,L); if(!IsLast(P,L)){ //这里需要判断是否是链表的最后一个结点,如果是,则表示找的元素未在链表中 TmpCell=P->Next; P->Next=TmpCell->Next; free(TmpCell); } } //找到元素结点的前一个结点,找不到就返回链表的最后的结点 Position FindPrevious(ElementType X,List L){ Position P; P=L; while(P->Next!=NULL&&P->Next->Element!=X){ P=P->Next; } return P; } //链表的插入例程 void Insert(ElementType X,List L,Position P){ Position TmpCell; TmpCell=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); if(TmpCell==NULL){ printf("Error! "); }else{ TmpCell->Element=X; TmpCell->Next=P->Next; P->Next=TmpCell; } } void DeleteList(List L){ Position P,Tmp; P=L->Next; L->Next=NULL; while(P!=NULL){ Tmp=p; P=P->Next; free(Tmp); } }
在表的例程运用中的几个提醒:
1.指针变量包含伪地址,系统提醒"memory access vialation"或"segmentation violation"。例如:{free(p);p=p->Next;}
2.声明一个指向结构的指针并不创建该结构,而只是给出足够的空间容纳结构可能使用的地址。创建尚未声明过的记录的一般方法是使用malloc库函数。malloc创建一个新的结构并返回指向该结构体的指针。一些比较老的编译器需要在malloc的前面加上类型转换(type cast)。C语言提供了两种动态分配内存空间的库函数,malloc和calloc。他们都要求包含stdlib头文件。
3.free(p)的作用是:p正在指向的地址没变,但在该地址处的数据此时已经无定义了。
4.malloc(sizeof(PtrToNode))是合法的,但是它并不给结构体分配足够的内存空间,他只给指针分配内存空间。
单向链表的实例:
1)生成100个随机整数并放入一个链表中,要求链表中的元素按从小到大顺序排列:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<time.h> 4 5 struct Node{ 6 int Element; 7 struct Node *Next; 8 }; 9 typedef struct Node *List; 10 typedef struct Node *PtrToNode; 11 12 List create(){ 13 List L; 14 PtrToNode header=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 15 header->Next=NULL; 16 L=header; 17 return L; 18 } 19 20 //递归的有序的插入 21 void InsertRecursive(PtrToNode temp,List L){ 22 PtrToNode p=L; 23 if(p->Next==NULL){ 24 temp->Next=p->Next; 25 p->Next=temp; 26 } 27 else if(p->Next!=NULL){ 28 if(temp->Element<=p->Next->Element){ 29 temp->Next=p->Next; //temp指向p的指向的下一个元素 30 p->Next=temp; //p指向temp 31 }else if(temp->Element>p->Next->Element){ 32 InsertRecursive(temp,p->Next); 33 } 34 } 35 } 36 37 //非递归有序的插入 38 void InsertUnRecursive(PtrToNode temp,List L){ 39 PtrToNode p=L; 40 //一个元素也没插入时 41 if(p->Next==NULL){ 42 temp->Next=p->Next; 43 p->Next=temp; 44 return; 45 } 46 //只有一个元素时 47 if((p->Next!=NULL)&&(p->Next->Next==NULL)){ 48 if((temp->Element)<=(p->Next->Element)){ 49 temp->Next=p->Next; 50 p->Next=temp; 51 }else if(temp->Element>p->Next->Element){ 52 temp->Next=p->Next->Next; 53 p->Next->Next=temp; 54 } 55 return; 56 } 57 while(p->Next!=NULL&&p->Next->Next!=NULL){ 58 if(temp->Element<=p->Next->Element){ 59 temp->Next=p->Next; 60 p->Next=temp; 61 return; 62 }else if(temp->Element>p->Next->Element&&temp->Element<=p->Next->Next->Element){ 63 temp->Next=p->Next->Next; 64 p->Next->Next=temp; 65 return; 66 }else{ 67 p=p->Next; 68 } 69 //有两个元素,但执行p=p->Next时有可能碰到p->Next->Next==NULL; 70 if(p->Next->Next==NULL){ 71 if((temp->Element)<=(p->Next->Element)){ 72 temp->Next=p->Next; 73 p->Next=temp; 74 }else if(temp->Element>p->Next->Element){ 75 temp->Next=p->Next->Next; 76 p->Next->Next=temp; 77 } 78 return; 79 } 80 } 81 } 82 83 void printAll(List list){ 84 PtrToNode p=list; 85 int flag=1; 86 while(p->Next!=NULL){ 87 printf("a[%2d]=%3d ",flag,p->Next->Element); 88 p=p->Next; 89 if(flag%10==0){ 90 printf(" "); 91 } 92 flag++; 93 } 94 } 95 96 int main(){ 97 srand(time(NULL)); 98 List list=create(); 99 int i,x; 100 PtrToNode p; 101 //InsertRecursive与InsertUnRecursive函数具有一样的功能: 102 for(i=0;i<50;i++){ 103 x=rand()%1000; 104 p=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 105 p->Element=x; 106 InsertRecursive(p,list); 107 } 108 for(i=0;i<50;i++){ 109 x=rand()%1000; 110 p=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 111 p->Element=x; 112 InsertUnRecursive(p,list); 113 } 114 //输出插入的结果 115 printAll(list); 116 }
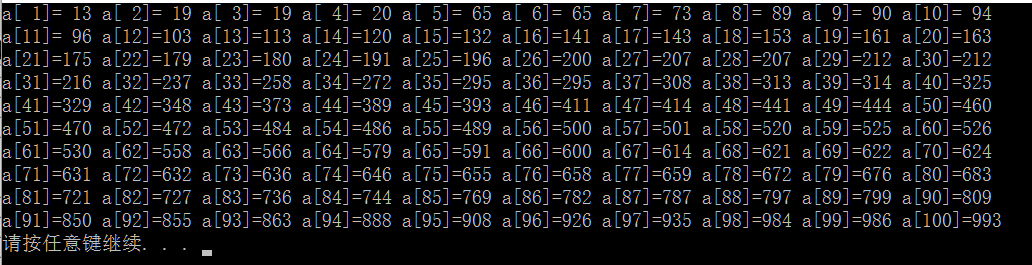
2)将两个从小到大排列的链表合并为一个新链表,要求:
(1)原来的两个链表不保存(合并时,无需生成新的空间来存放每个结点,直接将所有结点合并为新链表)
(2)原来的两个链表不作改变(合并时,对每一个结点需要复制并产生新链表)
(3)对以上两小题,若链表中遇到有相同的元素,则在合并时去掉重复元素。(当然,你也可以在链表合并完以后再扫描整个链表去掉重复元素,但这需要额外的运行时间,因此并不是一个好的办法)
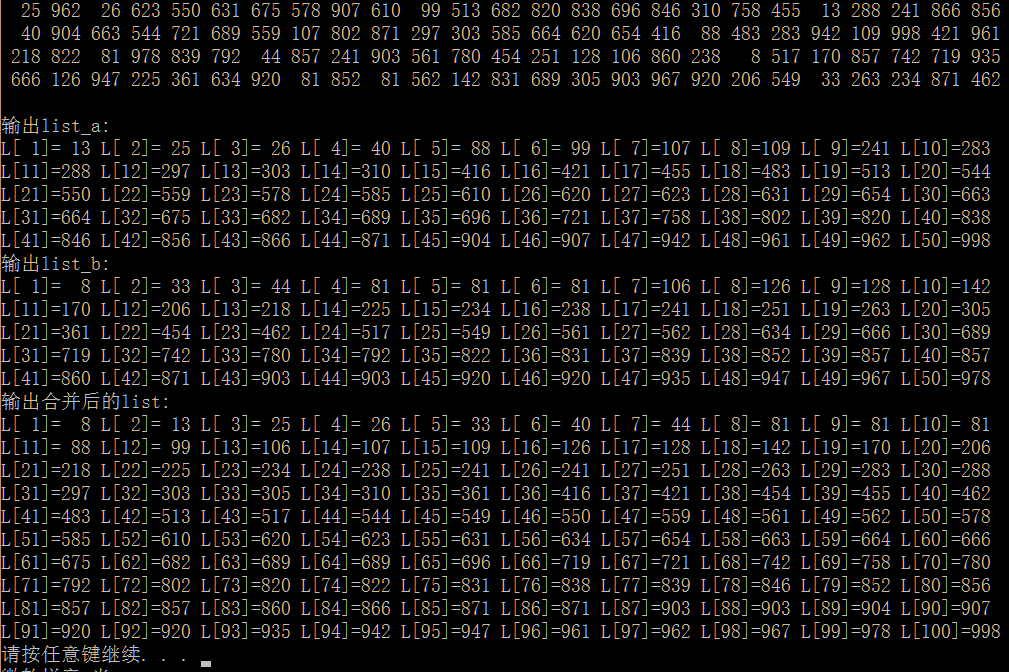
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<time.h> 4 5 struct Node{ 6 int Element; 7 int flag; //用来不重复插入相同数据,做个标记 8 struct Node *Next; 9 }; 10 11 typedef struct Node *List; 12 typedef struct Node *PtrToNode; 13 typedef PtrToNode Position; 14 15 //创建具有头节点的链表 16 List create(){ 17 List L; 18 PtrToNode header=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 19 header->Next=NULL; 20 L=header; 21 return L; 22 } 23 //执行插入操作,参数表示,element将插入到posi所指向的元素的后面 24 void Insert(int element,List list,Position posi){ 25 PtrToNode p=list;//用作循环遍历链表,找到地址与posi相同的结点 26 PtrToNode temp;//用来新建结点 27 while(p!=posi){ 28 p=p->Next; 29 }//找到posi所在位置 30 if(p==list){//a1.当位置在头节点 31 if(p->Next==NULL){//a1.b1在头节点,当头结点的下一个为空时,直接插入 32 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 33 temp->Element=element; 34 temp->flag=1; 35 temp->Next=p->Next; 36 p->Next=temp; 37 }else{//a1.b2在头节点,当头结点的下一个不为空时 38 if(element==p->Next->Element){//a1.b2.c1当要插入的元素与位置指向的下一个元素相同时,不用重复插入 39 p->Next->flag++; 40 }else{//a1.b2.c2不同时,肯定小于,所以插入 41 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 42 temp->Element=element; 43 temp->flag=1; 44 temp->Next=p->Next; 45 p->Next=temp; 46 } 47 } 48 //a2.当位置不在头节点 49 }else if(p!=list){ 50 if(element==posi->Element){//a2.b1当要插入元素与当前位置元素相同时,不插入 51 posi->flag++; 52 return; 53 }else{//a2.b2当不同时,肯定大于当前元素 54 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 55 temp->Element=element; 56 temp->flag=1; 57 temp->Next=p->Next; 58 p->Next=temp; 59 } 60 } 61 } 62 63 //一下这部分的功能是找到要插入的位置 64 Position FindInsertPosition(List list,int element){ 65 PtrToNode p=list; 66 Position position; 67 while(p!=NULL){ 68 if(p->Next==NULL){//a1如果下一个元素为空,则一定是这个位置 69 position=p; 70 break; 71 }else if(p->Next!=NULL){//a2如果下一个不为空 72 if(element<=p->Next->Element){//a2.b1要插入元素小于或等于下一个元素,都可以插在p和p指向的下一个元素之间 73 position=p; 74 break; 75 }else if(element>p->Next->Element){//a2.b2当要插入元素还大于p指向的下一个元素时,肯定插入点在下一个元素的后面,只需循环遍历 76 p=p->Next; 77 } 78 } 79 } 80 return position; 81 } 82 83 void InsertWithNode(PtrToNode temp,List list,Position posi){ 84 PtrToNode p=list;//用作循环遍历链表,找到地址与posi相同的结点 85 int element=temp->Element; 86 while(p!=posi){ 87 p=p->Next; 88 }//找到posi所在位置 89 if(p==list){//a1.当位置在头节点 90 if(p->Next==NULL){//a1.b1在头节点,当头结点的下一个为空时,直接插入 91 temp->Next=p->Next; 92 p->Next=temp; 93 }else{//a1.b2在头节点,当头结点的下一个不为空时 94 if(element==p->Next->Element){//a1.b2.c1当要插入的元素与位置指向的下一个元素相同时,不用重复插入 95 p->Next->flag+=temp->flag; 96 free(temp); 97 }else{//a1.b2.c2不同时,肯定小于,所以插入 98 temp->Next=p->Next; 99 p->Next=temp; 100 } 101 } 102 //a2.当位置不在头节点 103 }else if(p!=list){ 104 if(element==posi->Element){//a2.b1当要插入元素与当前位置元素相同时,不插入 105 posi->flag+=temp->flag; 106 free(temp); 107 return; 108 }else{//a2.b2当不同时,肯定大于当前元素 109 temp->Next=p->Next; 110 p->Next=temp; 111 } 112 } 113 } 114 List UnitTwoList(List list1,List list2){ 115 //让将要返回的链表先指向第一个,然后将第二个链表的每个元素依次插入 116 List list=list1; 117 PtrToNode ptr=list2->Next; 118 Position position; 119 PtrToNode ptrD=ptr; 120 while(ptr!=NULL){ 121 //对于链表2中的每个元素都要依次找出其在链表1中需要插入的位置 122 position=FindInsertPosition(list,ptr->Element); 123 //Insert(ptr->Element,list,position); 124 //ptr=ptr->Next; 125 ptrD=ptr->Next; 126 InsertWithNode(ptr,list,position); 127 ptr=ptrD; 128 } 129 return list; 130 } 131 132 void printListWithFlag(List list){ 133 PtrToNode p=list->Next; 134 int i,t=1; 135 while(p!=NULL){ 136 for(i=1;i<=p->flag;i++){ 137 printf("L[%2d]=%3d ",t,p->Element); 138 if(t%10==0){ 139 printf(" "); 140 } 141 t++; 142 } 143 p=p->Next; 144 } 145 } 146 147 void initList(List list){ 148 int x,i; 149 Position position; 150 for(i=0;i<50;i++){ 151 x=rand()%1000; 152 printf("%4d",x); 153 if((i+1)%25==0){ 154 printf(" "); 155 } 156 position=FindInsertPosition(list,x); 157 Insert(x,list,position); 158 } 159 } 160 int main(){ 161 srand(time(NULL)); 162 List list_a=create(); 163 List list_b=create(); 164 //初始化第一个链表 165 initList(list_a); 166 //初始化第二个链表 167 initList(list_b); 168 printf(" "); 169 printf("输出list_a: "); 170 printListWithFlag(list_a); 171 printf("输出list_b: "); 172 printListWithFlag(list_b); 173 List list=UnitTwoList(list_a,list_b); 174 printf("输出合并后的list: "); 175 printListWithFlag(list); 176 return 0; 177 }
2.5双向链表:
双向链表用来倒序扫描链表很方便,而且简化了删除操作,不再迫使使用一个指向前驱元的指针来访问一个关键字。
实例:编写程序,从键盘输入10个整数并放入一个循环双向链表中(不排序),然后按输入顺序输出这些整数和逆序输出这些整数。
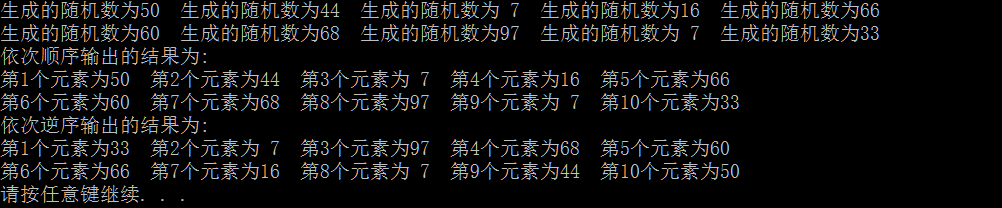
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<time.h> 4 5 struct Node{ 6 struct Node *Pre; 7 int Element; 8 struct Node *Next; 9 }; 10 typedef struct Node *List; 11 typedef struct Node *PtrToNode; 12 13 List create(){ 14 List list; 15 PtrToNode header,tailer; 16 header=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 17 tailer=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 18 list=header; 19 header->Pre=tailer; 20 header->Next=tailer; 21 tailer->Pre=header; 22 tailer->Next=header; 23 return list; 24 } 25 void Insert(List list,int x){ 26 PtrToNode temp; 27 PtrToNode p=list; 28 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); 29 temp->Element=x; 30 31 while(p->Next!=list){ 32 p=p->Next;//找到尾节点 33 } 34 temp->Next=p; 35 temp->Pre=p->Pre; 36 p->Pre->Next=temp; 37 p->Pre=temp; 38 39 } 40 void PrintTwoDListOrder(List list){ 41 printf("依次顺序输出的结果为: "); 42 PtrToNode p=list; 43 int i=1; 44 while(p->Next!=list){ 45 if(p->Next!=list->Pre){ 46 printf("第%d个元素为%2d ",i,p->Next->Element); 47 p=p->Next; 48 if(i%5==0){ 49 printf(" "); 50 } 51 i++; 52 continue; 53 } 54 break; 55 } 56 } 57 void PrintTwoDListNOrder(List list){ 58 printf("依次逆序输出的结果为: "); 59 PtrToNode p=list->Pre; 60 int i=1; 61 while(p->Pre!=list->Pre){ 62 if(p->Pre!=list){ 63 printf("第%d个元素为%2d ",i,p->Pre->Element); 64 p=p->Pre; 65 if(i%5==0){ 66 printf(" "); 67 } 68 i++; 69 continue; 70 } 71 break; 72 } 73 } 74 int main(){ 75 //创建一个有头有尾的双向链表 76 srand(time(NULL)); 77 List list=create(); 78 int i,x; 79 for(i=0;i<10;i++){ 80 x=rand()%100; 81 printf("生成的随机数为%2d ",x); 82 if((i+1)%5==0){ 83 printf(" "); 84 } 85 Insert(list,x); 86 } 87 PrintTwoDListOrder(list); 88 PrintTwoDListNOrder(list); 89 return 0; 90 }
双向链表的另一个特例是循环链表,即让最后的单元反过来指向第一个单元。循环链表也可以不是双向链表。这种结构在某些应用程序中很流行。
2.6十字链表
主链表上的每个结点都是支链表的头结点:
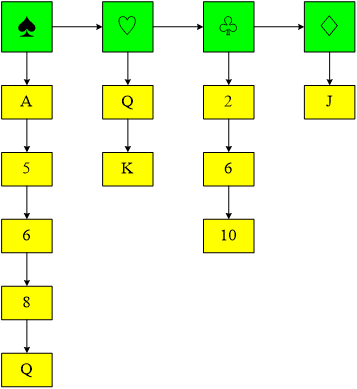
实例:随机抽取20张扑克牌(扑克牌有两项数据,一为花色,二为大小),花色按黑桃、红桃、梅花、方块次序排列,要求建立链表来存放这些扑克牌,最后输出。
(1)先按花色,再按大小排列
(2)先按大小,再按花色排列
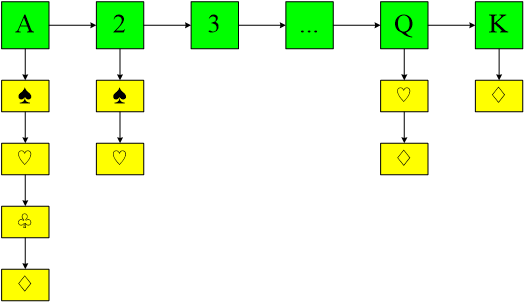
注:一副牌共有52张,每张不能重复,请考虑如何随机产生不重复的牌。
先按花色排序,后按大小:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<time.h> 4 5 struct Poker{ 6 int Element; 7 int Color; 8 int Num; 9 struct Poker *mainNext; 10 struct Poker *BranchNext; 11 }; 12 typedef struct Poker *List; 13 typedef struct Poker *PtrToNode; 14 15 void InitNode(PtrToNode p){ 16 if(p->Element%13==0){ 17 p->Num=13; 18 p->Color=p->Element/13-1; 19 }else{ 20 p->Num=p->Element%13; 21 p->Color=p->Element/13; 22 } 23 } 24 //用数组辅助产生不重复的52以内的无序的整数20个包含52 25 void InitDisOrder(int a[]){ 26 int s[52]; 27 int i,x; 28 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 29 s[i]=1; 30 } 31 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 32 L: x=rand()%52;//产生1到52的随机数 33 if(s[x]==0){ 34 goto L; 35 }else{ 36 a[i]=x+1; 37 s[x]=0; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 //用数组辅助产生不重复的有序的整数20个包括52 42 void InitOrder(int a[]){ 43 int s[52]; 44 int i,j,x; 45 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 46 s[i]=1; 47 } 48 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 49 L: x=rand()%52; 50 if(s[x]==0){ 51 goto L; 52 }else 53 s[x]=0; 54 } 55 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 56 if(s[i]==0){ 57 a[j]=i+1; 58 j++; 59 }else 60 continue; 61 } 62 } 63 PtrToNode InsertBranch(List list,int x){ 64 PtrToNode p1,p2,temp; 65 p1=p2=list; 66 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 67 temp->Element=x; 68 temp->mainNext=NULL; 69 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 70 InitNode(temp); 71 while(p1!=NULL){ 72 if(temp->Num<p1->Num){ 73 temp->BranchNext=p1; 74 if(p2==list&&p1==p2){ 75 list=temp; 76 return list; 77 }else 78 p2->BranchNext=temp; 79 return list; 80 } 81 else if(temp->Num>p1->Num){ 82 p2=p1; 83 p1=p1->BranchNext; 84 //当p1==NULL,下一步会跳出while循环,也可以放在while后 85 if(p1==NULL){ 86 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 87 p2->BranchNext=temp; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 return list; 92 } 93 List InsertMain(List list,int x){ //(x/13代表花色,x%13代表大小) 94 PtrToNode p1,p2,temp; 95 p1=p2=list; 96 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 97 temp->Element=x; 98 InitNode(temp); 99 temp->mainNext=NULL; 100 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 101 //printf(" %d=%d,%d",temp->Element,temp->Color,temp->Num); 102 if(list==NULL){ 103 list=temp; 104 } 105 else 106 while(p1!=NULL){ 107 if(temp->Color<p1->Color){ 108 if(p2==list&&p1==p2){ 109 temp->mainNext=p1; 110 list=temp; 111 }else{ 112 temp->mainNext=p1; 113 p2->mainNext=temp; 114 } 115 return list; 116 }else if(temp->Color==p1->Color){ 117 PtrToNode p3=p1->mainNext; 118 PtrToNode p4=p1; 119 PtrToNode p=InsertBranch(p1,x); 120 p->mainNext=p3; 121 if(p2==list&&p2==p4){ 122 list=p; 123 }else{ 124 p2->mainNext=p; 125 } 126 return list; 127 }else{ 128 p2=p1; 129 p1=p1->mainNext; 130 if(p1==NULL){ 131 temp->mainNext=NULL; 132 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 133 p2->mainNext=temp; 134 } 135 } 136 }//while结束 137 return list; 138 } 139 void printSingleList(List list){ 140 PtrToNode p1; 141 p1=list; 142 while(p1!=NULL){ 143 switch(p1->Color){ 144 case 0:printf("黑桃");break; 145 case 1:printf("红桃");break; 146 case 2:printf("梅花");break; 147 case 3:printf("方块");break; 148 } 149 printf("%2d ",p1->Num); 150 p1=p1->BranchNext; 151 } 152 } 153 void printDoubleList(List list){ 154 PtrToNode p=list; 155 while(p!=NULL){ 156 switch(p->Color){ 157 case 0:printf(" 下面输出黑桃的数字排序: ");break; 158 case 1:printf(" 下面输出红桃的数字排序: ");break; 159 case 2:printf(" 下面输出梅花的数字排序: ");break; 160 case 3:printf(" 下面输出方块的数字排序: ");break; 161 default:printf("没有这个花色: ");exit(0); 162 } 163 printSingleList(p); 164 p=p->mainNext; 165 } 166 } 167 void Warn(){ 168 printf("本程序的规定: "); 169 printf(" 1到13代表黑桃 14到26代表红桃 27到39代表梅花 40到52代表方块。 " ); 170 } 171 int main(){ 172 Warn(); 173 PtrToNode temp; 174 int i; 175 srand(time(NULL)); 176 int select[20]; 177 InitDisOrder(select); 178 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 179 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 180 temp->Element=select[i]; 181 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 182 InitNode(temp); 183 printSingleList(temp); 184 if((i+1)%10==0){ 185 printf(" "); 186 } 187 } 188 List list=NULL; 189 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 190 list=InsertMain(list,select[i]); 191 } 192 printDoubleList(list); 193 printf(" "); 194 return 0; 195 }

再先按大小后按花色排序:
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<time.h> 4 5 struct Poker{ 6 int Element; 7 int Color; 8 int Num; 9 struct Poker *mainNext; 10 struct Poker *BranchNext; 11 }; 12 typedef struct Poker *List; 13 typedef struct Poker *PtrToNode; 14 15 void InitNode(PtrToNode p){ 16 if(p->Element%13==0){ 17 p->Num=13; 18 p->Color=p->Element/13-1; 19 }else{ 20 p->Num=p->Element%13; 21 p->Color=p->Element/13; 22 } 23 } 24 //用数组辅助产生不重复的52以内的无序的整数20个包含52 25 void InitDisOrder(int a[]){ 26 int s[52]; 27 int i,x; 28 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 29 s[i]=1; 30 } 31 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 32 L: x=rand()%52;//产生1到52的随机数 33 if(s[x]==0){ 34 goto L; 35 }else{ 36 a[i]=x+1; 37 s[x]=0; 38 } 39 } 40 } 41 //用数组辅助产生不重复的有序的整数20个包括52 42 void InitOrder(int a[]){ 43 int s[52]; 44 int i,j,x; 45 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 46 s[i]=1; 47 } 48 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 49 L: x=rand()%52; 50 if(s[x]==0){ 51 goto L; 52 }else 53 s[x]=0; 54 } 55 for(i=0;i<52;i++){ 56 if(s[i]==0){ 57 a[j]=i+1; 58 j++; 59 }else 60 continue; 61 } 62 } 63 PtrToNode InsertBranch(List list,int x){ 64 PtrToNode p1,p2,temp; 65 p1=p2=list; 66 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 67 temp->Element=x; 68 temp->mainNext=NULL; 69 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 70 InitNode(temp); 71 while(p1!=NULL){ 72 if(temp->Color<p1->Color){ 73 temp->BranchNext=p1; 74 if(p2==list&&p1==p2){ 75 list=temp; 76 return list; 77 }else 78 p2->BranchNext=temp; 79 return list; 80 } 81 else if(temp->Color>p1->Color){ 82 p2=p1; 83 p1=p1->BranchNext; 84 //当p1==NULL,下一步会跳出while循环,也可以放在while后 85 if(p1==NULL){ 86 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 87 p2->BranchNext=temp; 88 } 89 } 90 } 91 return list; 92 } 93 List InsertMain(List list,int x){ //(x/13代表花色,x%13代表大小) 94 PtrToNode p1,p2,temp; 95 p1=p2=list; 96 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 97 temp->Element=x; 98 InitNode(temp); 99 temp->mainNext=NULL; 100 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 101 //printf(" %d=%d,%d",temp->Element,temp->Color,temp->Num); 102 if(list==NULL){ 103 list=temp; 104 } 105 else 106 while(p1!=NULL){ 107 if(temp->Num<p1->Num){ 108 if(p2==list&&p1==p2){ 109 temp->mainNext=p1; 110 list=temp; 111 }else{ 112 temp->mainNext=p1; 113 p2->mainNext=temp; 114 } 115 return list; 116 }else if(temp->Num==p1->Num){ 117 PtrToNode p3=p1->mainNext; 118 PtrToNode p4=p1; 119 PtrToNode p=InsertBranch(p1,x); 120 p->mainNext=p3; 121 if(p2==list&&p2==p4){ 122 list=p; 123 }else{ 124 p2->mainNext=p; 125 } 126 return list; 127 }else{ 128 p2=p1; 129 p1=p1->mainNext; 130 if(p1==NULL){ 131 temp->mainNext=NULL; 132 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 133 p2->mainNext=temp; 134 } 135 } 136 }//while结束 137 return list; 138 } 139 void printSingleList(List list){ 140 PtrToNode p1; 141 p1=list; 142 while(p1!=NULL){ 143 switch(p1->Color){ 144 case 0:printf("黑桃");break; 145 case 1:printf("红桃");break; 146 case 2:printf("梅花");break; 147 case 3:printf("方块");break; 148 } 149 printf("%2d ",p1->Num); 150 p1=p1->BranchNext; 151 } 152 } 153 void printDoubleList(List list){ 154 PtrToNode p=list; 155 while(p!=NULL){ 156 printf(" 数字%d: ",p->Num); 157 printSingleList(p); 158 p=p->mainNext; 159 } 160 } 161 void Warn(){ 162 printf("本程序的规定: "); 163 printf(" 1到13代表黑桃 14到26代表红桃 27到39代表梅花 40到52代表方块。 " ); 164 } 165 166 int main(){ 167 Warn(); 168 int i; 169 srand(time(NULL)); 170 int select[20]; 171 PtrToNode temp; 172 InitDisOrder(select); 173 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 174 printf("%3d=",select[i]); 175 temp=malloc(sizeof(struct Poker)); 176 temp->Element=select[i]; 177 temp->BranchNext=NULL; 178 InitNode(temp); 179 printSingleList(temp); 180 if((i+1)%10==0){ 181 printf(" "); 182 } 183 } 184 List list=NULL; 185 for(i=0;i<20;i++){ 186 list=InsertMain(list,select[i]); 187 } 188 printDoubleList(list); 189 return 0; 190 }

其实第二个程序只是第一个程序在条件上,顺序改了改,在做第一个时我考虑到了扩展性的问题,于是第二个程序只用了5分钟就完成了。而第一个程序用了几个小时。