习题答案目录:https://www.cnblogs.com/Mered1th/p/10485695.html
第8章 IO库
练习8.1
istream &iofunc(istream &is) {
string s;
while (is >> s) {
cout << s << endl;
}
is.clear();
return is;
}
练习8.2
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
istream &iofunc(istream &is) {
string s;
while (is >> s) {
cout << s << endl;
}
is.clear();
return is;
}
int main() {
iofunc(cin);
return 0;
}
练习8.3
badbit、failbit和eofbit任一个被置位,则检测流状态的条件会失败。
练习8.4
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int fileToVector(string fileName,vector<string> &svec){
ifstream inFile(fileName);
if (!inFile) {
return 1;
}
string s;
while (getline(inFile, s)) {
svec.push_back(s);
}
inFile.close();
if (inFile.eof()) {
return 4;
}
if (inFile.bad()) {
return 2;
}
if (inFile.fail()) {
return 3;
}
}
int main() {
vector<string> svec;
string fileName, s;
cout << "Enter fileName:" << endl;
cin >> fileName;
switch (fileToVector(fileName, svec))
{
case 1:
cout << "error: can not open file: " << fileName << endl;
return -1;
case 2:
cout << "error: system failure." << endl;
return -1;
case 3:
cout << "error: read failure." << endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "向量里面的内容:" << endl;
for (vector<string>::iterator iter = svec.begin();iter != svec.end();++iter)
cout << *iter << endl;
return 0;
}
练习8.5
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int fileToVector(string fileName, vector<string>& svec) {
ifstream inFile(fileName.c_str());
if (!inFile) {
return 1;
}
string s;
//习题8.4一次输入一行
//while (getline(inFile, s)) {
// svec.push_back(s);
//}
//习题8.5一次一个单词
while (inFile >> s) {
svec.push_back(s);
}
inFile.close();
if (inFile.eof()) {
return 4;
}
if (inFile.bad()) {
return 2;
}
if (inFile.fail()) {
return 3;
}
}
int main() {
cout << "测试下" << endl;
vector<string> svec;
string fileName, s;
cout << "Enter filename: ";
cin >> fileName;
switch (fileToVector(fileName,svec))
{
case 1:
cout << "error: can not open file: " << fileName << endl;
return -1;
case 2:
cout << "error: system failure." << endl;
return -1;
case 3:
cout << "error: read failure." << endl;
return -1;
}
cout << "向量里面的内容:" << endl;
for (vector<string>::iterator iter = svec.begin();iter != svec.end();++iter)
cout << *iter << endl;
return 0;
}
练习8.6-8.7
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
class Sales_data {
public:
Sales_data() {}
Sales_data(std::string bN, unsigned sold, double reven) :bookNo(bN), units_sold(sold), revenue(reven) {}
std::string isbn() const { return this->bookNo; }
Sales_data& combine(const Sales_data &rhs) {
units_sold += rhs.units_sold;
revenue += rhs.revenue;
return *this;
}
double avg_price() const {
if (units_sold) {
return revenue / units_sold;
}
else return 0;
}
Sales_data add(const Sales_data &lhs, const Sales_data &rhs) {
Sales_data sum = lhs;
sum.combine(rhs);
return sum;
}
public:
std::string bookNo; //书号
unsigned units_sold;
double revenue;
};
istream &read(istream &is, Sales_data &item) {
double price = 0;
is >> item.bookNo >> item.units_sold >> price;
item.revenue = item.units_sold * price;
return is;
}
ostream &print(ostream &os, const Sales_data &item) {
os << item.isbn() << " " << item.units_sold << " " << item.revenue << " " << item.avg_price()<<"
";
return os;
}
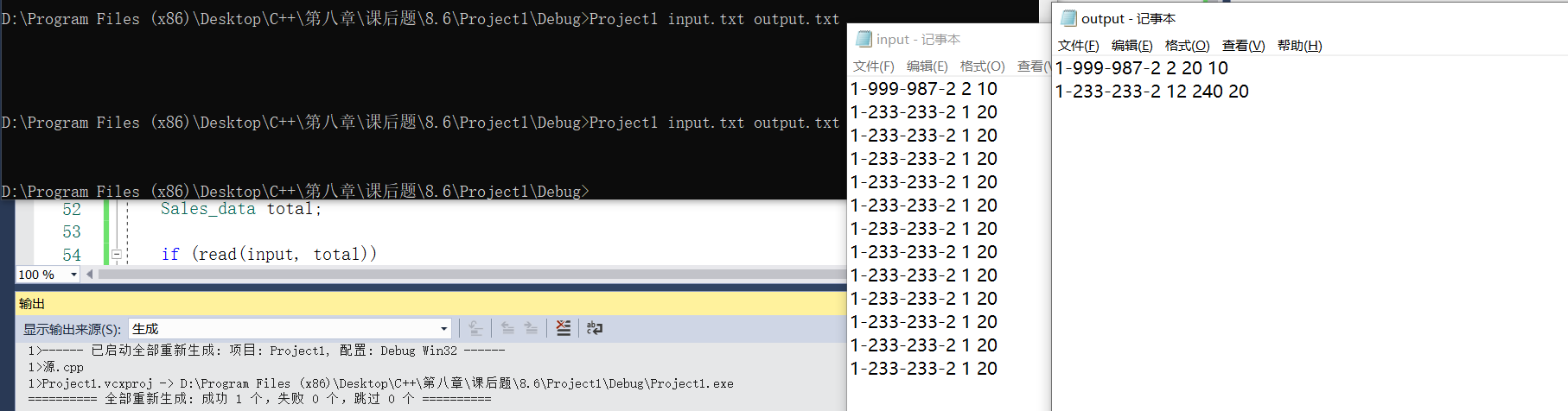
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
ifstream input(argv[1]);
ofstream output(argv[2]);
Sales_data total;
if (read(input, total))
{
Sales_data trans;
while (read(input, trans))
{
if (total.isbn() == trans.isbn())
{
total.combine(trans);
}
else
{
print(output, total);
cout << endl;
total = trans;
}
}
print(output, total);
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
else
{
cerr << "No data?!" << std::endl;
return -1; // indicate failure
}
}
练习8.8
ofstream output(argv[2],ofstream::app);

练习8.9
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<fstream>
#include<sstream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
istream &iofunc(istream &is) {
string s;
while (is >> s) {
cout << s << endl;
}
is.clear();
return is;
}
int main() {
string sss;
cin >> sss;
istringstream iss(sss);
iofunc(iss);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习8.10
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string infile = "test.txt";
vector<string> svec;
ifstream in(infile);
if (in) {
string buf;
while (getline(in, buf)) {
svec.push_back(buf);
}
}
else {
cerr << "can not open the file:" << infile << endl;
}
for (auto s : svec) {
istringstream iss(s);
string word;
while (iss >> word) {
cout << word << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习8.11
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct PersonInfo {
string name;
vector<string> phones;
};
int main() {
string line, word;
vector<PersonInfo> people;
istringstream record;
while (getline(cin, line)) {
record.str(line);
PersonInfo info;
record >> info.name;
while (record >> word) {
info.phones.push_back(word);
}
record.clear();
people.push_back(info);
}
for (const auto &entry : people) {
cout << entry.name << " ";
for (const auto &ph : entry.phones) {
cout << ph << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
练习8.12
vector和string在定义后自动初始化。
练习8.13
#include<iostream>
#include<sstream>
#include<fstream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
struct PersonInfo {
string name;
vector<string> phones;
};
int main() {
cout << "Please input the fileName:" << endl;
string infile;
cin >> infile;
ifstream in(infile);
if (!in) {
cerr << "can not open the file: " << infile << endl;
return 0;
}
string line, word;
vector<PersonInfo> people;
istringstream record;
while (getline(in, line)) {
record.str(line);
PersonInfo info;
record >> info.name;
while (record >> word) {
info.phones.push_back(word);
}
record.clear();
people.push_back(info);
}
for (const auto &entry : people) {
cout << entry.name << " ";
for (const auto &ph : entry.phones) {
cout << ph << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
练习8.14
无需修改所以用const,另外引用传值更快。