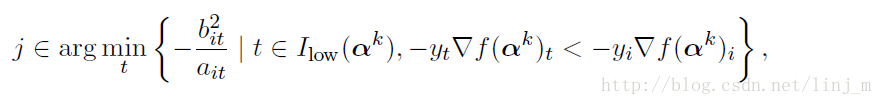如果你看完了上篇博文的伪代码,那么我们就可以开始谈谈它的源代码了。
下面先贴出它的类定义,一些成员函数的具体实现先忽略。
- // An SMO algorithm in Fan et al., JMLR 6(2005), p. 1889--1918
- // Solves:
- // min 0.5(alpha^T Q alpha) + p^T alpha
- //
- // y^T alpha = delta
- // y_i = +1 or -1
- // 0 <= alpha_i <= Cp for y_i = 1
- // 0 <= alpha_i <= Cn for y_i = -1
- //
- // Given:
- // Q, p, y, Cp, Cn, and an initial feasible point alpha
- // l is the size of vectors and matrices
- // eps is the stopping tolerance
- // solution will be put in alpha, objective value will be put in obj
- //
- class Solver {
- public:
- Solver() {};
- virtual ~Solver() {};//用虚析构函数的原因是:保证根据实际运行适当的析构函数
- struct SolutionInfo {
- double obj;
- double rho;
- double upper_bound_p;
- double upper_bound_n;
- double r; // for Solver_NU
- };
- void Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double *p_, const schar *y_,
- double *alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps,
- SolutionInfo* si, int shrinking);
- protected:
- int active_size;//计算时实际参加运算的样本数目,经过shrink处理后,该数目小于全部样本数
- schar *y; //样本所属类别,该值只能取-1或+1。
- double *G; // gradient of objective function = (Q alpha + p)
- enum { LOWER_BOUND, UPPER_BOUND, FREE };
- char *alpha_status; // LOWER_BOUND, UPPER_BOUND, FREE
- double *alpha; //
- const QMatrix *Q;
- const double *QD;
- double eps; //误差限
- double Cp,Cn;
- double *p;
- int *active_set;
- double *G_bar; // gradient, if we treat free variables as 0
- int l;
- bool unshrink; // XXX
- //返回对应于样本的C。设置不同的Cp和Cn是为了处理数据的不平衡
- double get_C(int i)
- {
- return (y[i] > 0)? Cp : Cn;
- }
- void update_alpha_status(int i)
- {
- if(alpha[i] >= get_C(i))
- alpha_status[i] = UPPER_BOUND;
- else if(alpha[i] <= 0)
- alpha_status[i] = LOWER_BOUND;
- else alpha_status[i] = FREE;
- }
- bool is_upper_bound(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == UPPER_BOUND; }
- bool is_lower_bound(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == LOWER_BOUND; }
- bool is_free(int i) { return alpha_status[i] == FREE; }
- void swap_index(int i, int j);//交换样本i和j的内容,包括申请的内存的地址
- void reconstruct_gradient(); //重新计算梯度。
- virtual int select_working_set(int &i, int &j);//选择工作集
- virtual double calculate_rho();
- virtual void do_shrinking();//对样本集做缩减。
- private:
- bool be_shrunk(int i, double Gmax1, double Gmax2);
- };
下面我们来看看SMO如何选择工作集(working set B),选择的约束如下:
- // return i,j such that
- // i: maximizes -y_i * grad(f)_i, i in I_up(alpha)
- // j: minimizes the decrease of obj value
- // (if quadratic coefficeint <= 0, replace it with tau)
- // -y_j*grad(f)_j < -y_i*grad(f)_i, j in I_low(alpha)
论文中的公式如下:
- int Solver::select_working_set(int &out_i, int &out_j)
- {
- // return i,j such that
- // i: maximizes -y_i * grad(f)_i, i in I_up(alpha)
- // j: minimizes the decrease of obj value
- // (if quadratic coefficeint <= 0, replace it with tau)
- // -y_j*grad(f)_j < -y_i*grad(f)_i, j in I_low(alpha)
- //select i
- double Gmax = -INF;
- double Gmax2 = -INF;
- int Gmax_idx = -1;
- int Gmin_idx = -1;
- double obj_diff_min = INF;
- for(int t=0;t<active_size;t++)
- if(y[t]==+1) //若类别为1
- {
- if(!is_upper_bound(t))//若alpha<C
- if(-G[t] >= Gmax)
- {
- Gmax = -G[t];// -y[t]*G[t]=-1*G[t]
- Gmax_idx = t;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(!is_lower_bound(t))
- if(G[t] >= Gmax)
- {
- Gmax = G[t];
- Gmax_idx = t;
- }
- }
- int i = Gmax_idx;
- const Qfloat *Q_i = NULL;
- if(i != -1) // NULL Q_i not accessed: Gmax=-INF if i=-1
- Q_i = Q->get_Q(i,active_size);
- //select j
- for(int j=0;j<active_size;j++)
- {
- if(y[j]==+1)
- {
- if (!is_lower_bound(j))
- {
- double grad_diff=Gmax+G[j];
- if (G[j] >= Gmax2)
- Gmax2 = G[j];
- if (grad_diff > 0)
- {
- double obj_diff;
- double quad_coef = QD[i]+QD[j]-2.0*y[i]*Q_i[j];
- if (quad_coef > 0)
- obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff)/quad_coef;
- else
- obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff)/TAU;
- if (obj_diff <= obj_diff_min)
- {
- Gmin_idx=j;
- obj_diff_min = obj_diff;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if (!is_upper_bound(j))
- {
- double grad_diff= Gmax-G[j];
- if (-G[j] >= Gmax2)
- Gmax2 = -G[j];
- if (grad_diff > 0)
- {
- double obj_diff;
- double quad_coef = QD[i]+QD[j]+2.0*y[i]*Q_i[j];
- if (quad_coef > 0)
- obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff)/quad_coef;
- else
- obj_diff = -(grad_diff*grad_diff)/TAU;
- if (obj_diff <= obj_diff_min)
- {
- Gmin_idx=j;
- obj_diff_min = obj_diff;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- }
- if(Gmax+Gmax2 < eps)
- return 1;
- out_i = Gmax_idx;
- out_j = Gmin_idx;
- return 0;
- }
配合上面几个公式看,这段代码还是很清晰了。
下面来看看它的构造函数,这个构造函数是solver类的核心。这个算法也结合上一篇博文的algorithm2来看。其中要注意的是get_Q是获取核函数。
- void Solver::Solve(int l, const QMatrix& Q, const double *p_, const schar *y_,
- double *alpha_, double Cp, double Cn, double eps,
- SolutionInfo* si, int shrinking)
- {
- this->l = l;
- this->Q = &Q;
- QD=Q.get_QD();//这个是获取核函数(如果分类的话在SVC_Q中定义)
- clone(p, p_,l);
- clone(y, y_,l);
- clone(alpha,alpha_,l);
- this->Cp = Cp;
- this->Cn = Cn;
- this->eps = eps;
- unshrink = false;
- // initialize alpha_status
- {
- alpha_status = new char[l];
- for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
- update_alpha_status(i);
- }
- // initialize active set (for shrinking)
- {
- active_set = new int[l];
- for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
- active_set[i] = i;
- active_size = l;
- }
- // initialize gradient
- {
- G = new double[l];
- G_bar = new double[l];
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<l;i++)
- {
- G[i] = p[i];
- G_bar[i] = 0;
- }
- for(i=0;i<l;i++)
- if(!is_lower_bound(i))
- {
- const Qfloat *Q_i = Q.get_Q(i,l);
- double alpha_i = alpha[i];
- int j;
- for(j=0;j<l;j++)
- G[j] += alpha_i*Q_i[j];
- if(is_upper_bound(i))
- for(j=0;j<l;j++)
- G_bar[j] += get_C(i) * Q_i[j]; //这里见文献LIBSVM: A Library for SVM公式(33)
- }
- }
- // optimization step
- int iter = 0;
- int max_iter = max(10000000, l>INT_MAX/100 ? INT_MAX : 100*l);
- int counter = min(l,1000)+1;
- while(iter < max_iter)
- {
- // show progress and do shrinking
- if(--counter == 0)
- {
- counter = min(l,1000);
- if(shrinking) do_shrinking();
- info(".");
- }
- int i,j;
- if(select_working_set(i,j)!=0)
- {
- // reconstruct the whole gradient
- reconstruct_gradient();
- // reset active set size and check
- active_size = l;
- info("*");
- if(select_working_set(i,j)!=0)
- break;
- else
- counter = 1; // do shrinking next iteration
- }
- ++iter;
- // update alpha[i] and alpha[j], handle bounds carefully
- const Qfloat *Q_i = Q.get_Q(i,active_size);
- const Qfloat *Q_j = Q.get_Q(j,active_size);
- double C_i = get_C(i);
- double C_j = get_C(j);
- double old_alpha_i = alpha[i];
- double old_alpha_j = alpha[j];
- if(y[i]!=y[j])
- {
- double quad_coef = QD[i]+QD[j]+2*Q_i[j];
- if (quad_coef <= 0)
- quad_coef = TAU;
- double delta = (-G[i]-G[j])/quad_coef;
- double diff = alpha[i] - alpha[j];
- alpha[i] += delta;
- alpha[j] += delta;
- if(diff > 0)
- {
- if(alpha[j] < 0)
- {
- alpha[j] = 0;
- alpha[i] = diff;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(alpha[i] < 0)
- {
- alpha[i] = 0;
- alpha[j] = -diff;
- }
- }
- if(diff > C_i - C_j)
- {
- if(alpha[i] > C_i)
- {
- alpha[i] = C_i;
- alpha[j] = C_i - diff;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(alpha[j] > C_j)
- {
- alpha[j] = C_j;
- alpha[i] = C_j + diff;
- }
- }
- }
- else
- {
- double quad_coef = QD[i]+QD[j]-2*Q_i[j];
- if (quad_coef <= 0)
- quad_coef = TAU;
- double delta = (G[i]-G[j])/quad_coef;
- double sum = alpha[i] + alpha[j];
- alpha[i] -= delta;
- alpha[j] += delta;
- if(sum > C_i)
- {
- if(alpha[i] > C_i)
- {
- alpha[i] = C_i;
- alpha[j] = sum - C_i;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(alpha[j] < 0)
- {
- alpha[j] = 0;
- alpha[i] = sum;
- }
- }
- if(sum > C_j)
- {
- if(alpha[j] > C_j)
- {
- alpha[j] = C_j;
- alpha[i] = sum - C_j;
- }
- }
- else
- {
- if(alpha[i] < 0)
- {
- alpha[i] = 0;
- alpha[j] = sum;
- }
- }
- }
- // update G
- double delta_alpha_i = alpha[i] - old_alpha_i;
- double delta_alpha_j = alpha[j] - old_alpha_j;
- for(int k=0;k<active_size;k++)
- {
- G[k] += Q_i[k]*delta_alpha_i + Q_j[k]*delta_alpha_j;
- }
- // update alpha_status and G_bar
- {
- bool ui = is_upper_bound(i);
- bool uj = is_upper_bound(j);
- update_alpha_status(i);
- update_alpha_status(j);
- int k;
- if(ui != is_upper_bound(i))
- {
- Q_i = Q.get_Q(i,l);
- if(ui)
- for(k=0;k<l;k++)
- G_bar[k] -= C_i * Q_i[k];
- else
- for(k=0;k<l;k++)
- G_bar[k] += C_i * Q_i[k];
- }
- if(uj != is_upper_bound(j))
- {
- Q_j = Q.get_Q(j,l);
- if(uj)
- for(k=0;k<l;k++)
- G_bar[k] -= C_j * Q_j[k];
- else
- for(k=0;k<l;k++)
- G_bar[k] += C_j * Q_j[k];
- }
- }
- }
- if(iter >= max_iter)
- {
- if(active_size < l)
- {
- // reconstruct the whole gradient to calculate objective value
- reconstruct_gradient();
- active_size = l;
- info("*");
- }
- fprintf(stderr," WARNING: reaching max number of iterations ");
- }
- // calculate rho
- si->rho = calculate_rho();
- // calculate objective value
- {
- double v = 0;
- int i;
- for(i=0;i<l;i++)
- v += alpha[i] * (G[i] + p[i]);
- si->obj = v/2;
- }
- // put back the solution
- {
- for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
- alpha_[active_set[i]] = alpha[i];
- }
- // juggle everything back
- /*{
- for(int i=0;i<l;i++)
- while(active_set[i] != i)
- swap_index(i,active_set[i]);
- // or Q.swap_index(i,active_set[i]);
- }*/
- si->upper_bound_p = Cp;
- si->upper_bound_n = Cn;
- info(" optimization finished, #iter = %d ",iter);
- delete[] p;
- delete[] y;
- delete[] alpha;
- delete[] alpha_status;
- delete[] active_set;
- delete[] G;
- delete[] G_bar;
- }