| 项目 | 内容 |
|---|---|
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | 2020春季计算机学院软件工程(罗杰 任健) |
| 这个作业的要求在哪里 | 作业要求 |
| 教学班级 | 006 |
| 项目地址 | https://github.com/MountVoom/IntersectProject.git |
一.PSP表格
| PSP2.1 | Personal Software Process Stages | 预估耗时(分钟) | 实际耗时(分钟) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Planning | 计划 | 10 | 10 |
| · Estimate | · 估计这个任务需要多少时间 | 480 | 600 |
| Development | 开发 | ||
| · Analysis | · 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) | 30 | 60 |
| · Design Spec | · 生成设计文档 | 10 | 10 |
| · Design Review | · 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) | ||
| · Coding Standard | · 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) | ||
| · Design | · 具体设计 | 10 | 10 |
| · Coding | · 具体编码 | 120 | 120 |
| · Code Review | · 代码复审 | 15 | 15 |
| · Test | · 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) | 60 | 60 |
| Reporting | 报告 | ||
| · Test Report | · 测试报告 | 20 | 20 |
| · Size Measurement | · 计算工作量 | 10 | 10 |
| · Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan | · 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 | 30 | 30 |
| 合计 | 795 | 945 |
二.思路描述
看到题目后,发现当n <= 1000时 n^2log(n)的做法很显然,是计算几何模板题目,直接两两枚举几何对象然后求出他们的交点,最后再排序去重即可。
参考资料:算法竞赛入门经典
三.设计实现过程
- 总体结构
根据个人习惯,类都用struct来实现。
头文件IntersectProject.h中定义了点类Point,直线类Line,圆类Circle,和许多相关的函数,并在源文件IntersectProject.cpp中实现,最终把所有的交点放入一个集合,集合的大小即为答案。
-
三个类
- 点类Point
struct Point { double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0) : x(x), y(y) {} bool operator < (const Point& B) const { return dcmp(x - B.x) < 0 || (!dcmp(x - B.x) && dcmp(y - B.y) < 0); } };- 直线类Line
struct Line { Point u; Vector v; Line() {} Line(Point u, Vector v) :u(u), v(v) {} Point point(double t) const { return u + v * t; } };对于直线的存储,采取存直线上一点和方向向量的方式。
- 圆类Circle
struct Circle { Point c; double r; Circle() { c = Point(0, 0); r = 0; } Circle(Point c, double r) :c(c), r(r) {} Point point(double a) const { return Point(c.x + cos(a) * r, c.y + sin(a) * r); } };对于圆的存储,采取存圆心和半径的方式。
-
单元测试的设计
主要针对三个求交点的函数进行了测试。
分别测试了直线平行,直线相交,直线和圆交点个数为0,1,2,圆和圆相交、内切、外切等。并测试了交点的值,结果均符合预期。
因为代码较长所以只贴出一部分。
TEST_METHOD(line_circle)
{
Line L = Line(Point(0, 0), Vector(1, 1));
Circle C;
s.clear();
C = Circle(Point(4, 2), 1);
lineIntersectionWithCircle(L, C);
Assert::AreEqual((int)s.size(), (int)0);
s.clear();
C = Circle(Point(3, 1), sqrt(2.));
lineIntersectionWithCircle(L, C);
Assert::AreEqual((int)s.size(), (int)1);
s.insert(Point(2, 2));
Assert::AreEqual((int)s.size(), (int)1);
s.clear();
C = Circle(Point(3, 3), sqrt(2.));
lineIntersectionWithCircle(L, C);
Assert::AreEqual((int)s.size(), (int)2);
s.insert(Point(2, 2)); s.insert(Point(4, 4));
Assert::AreEqual((int)s.size(), (int)2);
}
四.改进程序性能
使用了test文件夹中的data7.in进行测试。
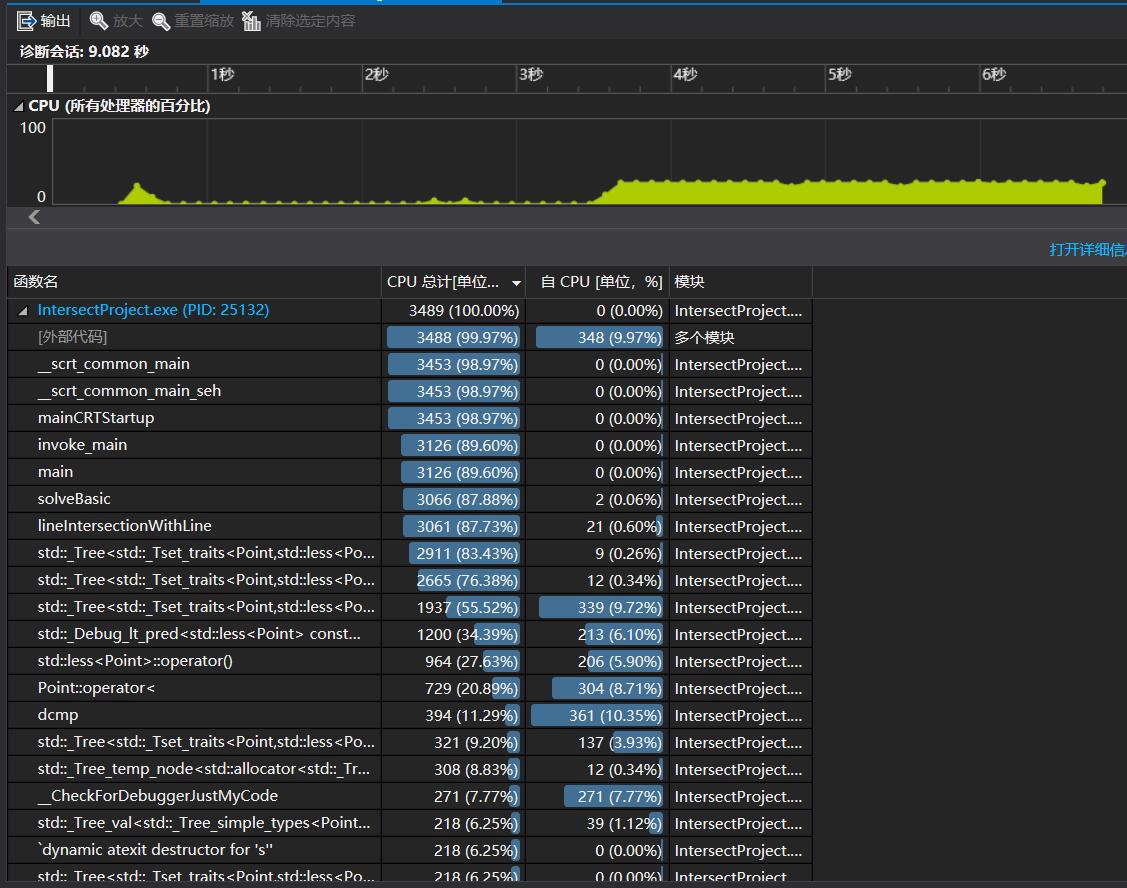
可以看出,主要是在求交点和set的操作上花费了很多时间。
set的各项操作很慢,于是考虑把交点全部放到vector中最后排序去重。
修改后再用同一组数据进行性能测试。
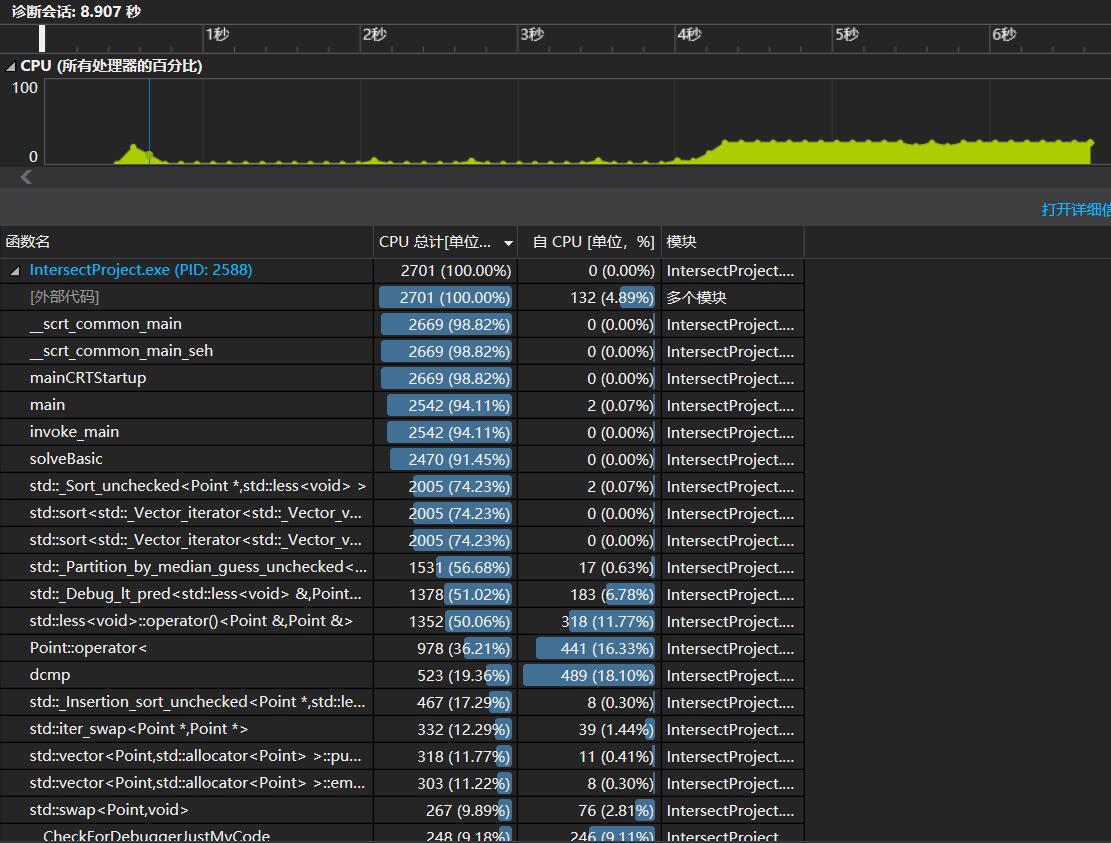
可以看出性能提高了不少。
五.代码说明
- dcmp函数,此函数用于控制精度,eps为设置的极小值。
int dcmp(double x) {
return (x > eps) - (x < -eps);
}
- 直线与直线求交
int lineIntersectionWithLine(const Line& L1, const Line& L2) {
if (!dcmp(L1.v ^ L2.v)) return 0; //平行
Vector u = L1.u - L2.u;
double t = (L2.v ^ u) / (L1.v ^ L2.v);
globalIntersection = L1.u + L1.v * t;
s.insert(globalIntersection);
return 1;
}
- 直线与圆求交
void lineIntersectionWithCircle(const Line& L, const Circle& C) {
double t1, t2;
double a = L.v.x, b = L.u.x - C.c.x, c = L.v.y, d = L.u.y - C.c.y;
double e = a * a + c * c, f = 2 * (a * b + c * d), g = b * b + d * d - C.r * C.r;
double delta = f * f - 4 * e * g;
if (dcmp(delta) < 0) return; //没有交点
if (dcmp(delta) == 0) {//有一个交点
s.insert(L.point(-f / (2 * e)));
}
else {//有两个交点
t1 = (-f - sqrt(delta)) / (2 * e); s.insert(L.point(t1));
t2 = (-f + sqrt(delta)) / (2 * e); s.insert(L.point(t2));
}
}
- 圆与圆求交
void circleIntersectionWithCircle(const Circle& C1, const Circle& C2) {
double d = calLength(C1.c - C2.c);
if (dcmp(d) == 0) return; //圆心重合
if (dcmp(C1.r + C2.r - d) < 0) return;//相离
if (dcmp(fabs(C1.r - C2.r) - d) > 0) return;//内含
double a = angle(C2.c - C1.c);
double da = acos((C1.r * C1.r + d * d - C2.r * C2.r) / (2 * C1.r * d));
Point p1 = C1.point(a - da), p2 = C1.point(a + da);
s.insert(p1);
if (p1 == p2) return; //相切
s.insert(p2);//相交
}
六.截图
- 单元测试

- 消除警告

七、感想
-
这次作业给我感觉和软工几乎不搭边,希望下次能有改善。
-
学了个扫描线最后发现学假了,浪费了不少时间,说明写之前还是应该多想想。
-
VS的性能测试用起来感觉还不错。