图1 新建-数据存储
1,基本特性
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据键(Key)而直接访问在内存存储位置的数据结构。
①以键值对的形式进行存储;
②不允许存在相同的key值,保证唯一映射,再次存入相同key数据,相当于更新数据;
③无序存储、无序输出【原理导致,详见3、底层实现部分】;
④可以存储为null的键和值;
注意--hashMap与hashTable的区别
2,Java使用实例
样例1:

package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo1; import java.util.HashMap; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hm=new HashMap<>(50); hm.put(1,1); hm.put(1,2);//相当于把数据更新 hm.put(null,3); hm.put(2,null); hm.forEach((k,v)->{ System.out.println("key:"+k+",value:"+v); }); } }
样例1输出:
key:null,value:3 key:1,value:2 key:2,value:null
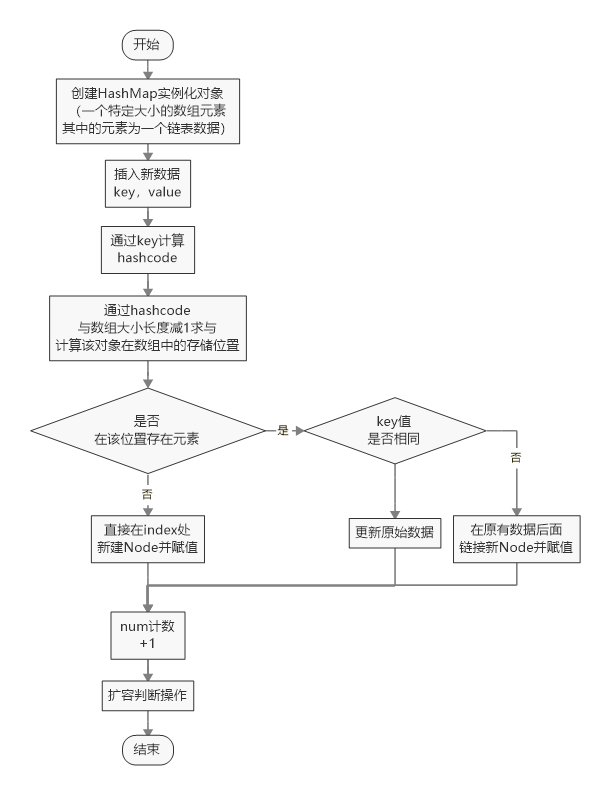
3,底层实现逻辑
3.1基本实现流程
①HashMap本质上是在内存中开辟一个固定大小的数组空间,②然后根据key计算的hashcode来定位将value存储在数组空间中的哪里【浪费空间很多,完美的情况是每个key对应的数组空间地址都不相同并且都刚好把空间填满!】,③但是在通过key计算hash值的时候总会出现所得结果相同的情况【除非开辟的原始空间特别大、hash算法特别好】,这个就是hash冲突。
通过上面三个基本步骤可以知道HashMap中两个关键的技术点:①hash算法;②hash冲突;
注意:①hashcode值相同但是有可能不是同一个对象,有可能是hash冲突;②同一个对象的hashcode值一定相同;
现在命名为Node,以前命名为Entry

static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> { final K key; V value; Entry<K,V> next; int hash; Entry(int h, K k, V v, Entry<K,V> n) { value = v; next = n; key = k; hash = h; } public final K getKey() { return key; } public final V getValue() { return value; } public final V setValue(V newValue) { V oldValue = value; value = newValue; return oldValue; } public final boolean equals(Object o) { if (!(o instanceof Map.Entry)) return false; Map.Entry e = (Map.Entry)o; Object k1 = getKey(); Object k2 = e.getKey(); if (k1 == k2 || (k1 != null && k1.equals(k2))) { Object v1 = getValue(); Object v2 = e.getValue(); if (v1 == v2 || (v1 != null && v1.equals(v2))) return true; } return false; } public final int hashCode() { return Objects.hashCode(getKey()) ^ Objects.hashCode(getValue()); } public final String toString() { return getKey() + "=" + getValue(); } }
4,注意事项
4.1 hashCode实现
hashcode实现:
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo2; public class hmcode extends Object{ @Override public int hashCode() { return super.hashCode(); }//public native int hashCode();??? public static int hashcode2(String str){ int code=0,len=str.length(); char[] strs=str.toCharArray(); for(int i=0;i<len;i++){ code = 31 * code + (Integer.valueOf(strs[i]) & 0xff); } return code; } } class Client{ public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println((new hmcode()).hashCode()); System.out.println(hmcode.hashcode2("123")); System.out.println("123".hashCode()); } }
输出【原生的hashCode调用的是C++的方法,已经被编译成了DLL文件了】:
1854778591 48690 48690
其中hashcode越分散,在hashmap应用中性能越好!
hashcode优化路线:①普通的映射函数-h(x);②二次映射-a*h(x)+a^2*h(x);/③多函数组合法-a*h1(x)+b*h2(x);【再次验证正确可以这样解决稀疏问题】
4.2 hash冲突解决
当两个key值不同的数据返回的hash值相同的时候,可以采用拉链法来将新数据连接到之前数据的最后【链表型数据】,并且当这个hashMap的容量超过限定的容量DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR时,就需要对容量进行扩充(一般情况下是进行2倍扩充),并且还要将原始数据转移到新的hashMap中【这个过程相当于查询、存储数据,有些耗时】,原始的数据变成了垃圾空间。
应该注意到链表的插入是以头插法方式进行的,例如上面的 <K3,V3> 不是插在 <K2,V2> 后面,而是插入在链表头部。下面的先put K2,V2后put K3,V3。
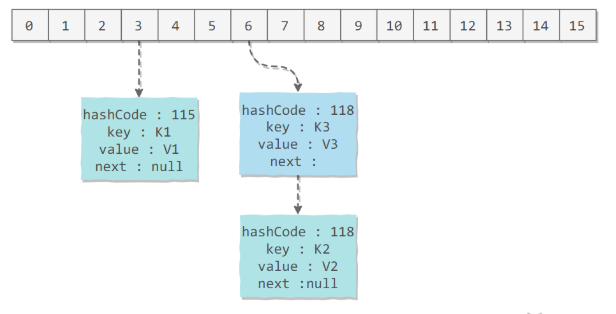
查找需要分成两步进行:
- 计算键值对所在的桶;
- 在链表上顺序查找,时间复杂度显然和链表的长度成正比。
5,手动实现HashMap
hashMap扩容:
①HashMap是先遍历旧table,再遍历旧table中每个元素的单向链表,取得Entry以后,重新计算hash值,然后存放到新table的对应位置。
②LinkedHashMap是遍历的双向链表,取得每一个Entry,然后重新计算hash值,然后存放到新table的对应位置。
从遍历的效率来说,遍历双向链表的效率要高于遍历table,因为遍历双向链表是N次(N为元素个数);而遍历table是N+table的空余个数(N为元素个数)。
hMap函数代码:
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo0; import java.util.HashMap; class hMap<K,V> { static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30;//hm最大开辟空间 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f;//最大容量,超过这个容量就需要进行内存的扩充 private int initialCapacity=13; private float loadFactor= 0.75f; private int num=0; transient Node<K,V>[] table;//不可序列化 /* 第一步:构建数据存储结构,特定长度数组、每个里面是一个Node链表型数据<K,V> 三个构造函数【方法重载】 */ public hMap(){ table=new Node[initialCapacity]; } public hMap(int initialCapacity){ if(initialCapacity>MAXIMUM_CAPACITY){ this.initialCapacity=MAXIMUM_CAPACITY; }else { this.initialCapacity=initialCapacity; } table=new Node[initialCapacity]; } public hMap(int initialCapacity,float loadFactor){ this(initialCapacity); if(loadFactor<=0||loadFactor>DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR){ this.loadFactor=DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR; }else { this.loadFactor=loadFactor; } table=new Node[initialCapacity]; } /* 第二步:通过key计算hashcode */ private int hashcode(Object key){ int h; return (key==null?0:((h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16))); } /* 第三步:数据存、读、删、扩容 */ public void put(K k, V v){//数据存储 if(num>(int) initialCapacity*loadFactor){//需要进行容量扩充了 int newCap=initialCapacity<<1;//默认不超过最大容量,这里需要注意最大容量问题 hMap<K,V> preTable=new hMap<>(newCap); System.out.println("当前size="+num+",数据内存进行扩容"+",以前大小为:"+initialCapacity+",现在大小为:"+newCap); //重新进行旧数据到新数据的转移 //①遍历;②计算存储 for(int i=0;i<initialCapacity;i++){//对原始数据进行遍历整合到新的数据中 if(table[i]!=null){ Node pre=table[i]; while (pre!=null){ preTable.put((K)pre.getK(),(V)pre.getV()); pre=pre.getNext(); } } } table=preTable.getTable(); num=preTable.getNum(); initialCapacity=newCap; preTable=null;//成为垃圾 // System.gc();//手动GC } int hash=hashcode(k); hash=hash&(initialCapacity-1);//计算出应该存储的位置 if(table[hash]==null){ table[hash]=new Node<>(k,v); num++;//计数+1 }else {//在那个位置存在一个数据,可能为【hash冲突】,也可能是数据更新 Node pre=table[hash]; while (pre!=null){ if(pre.getK()==k){ pre.setV(v); break; } pre=pre.getNext(); } if(pre==null){ pre=new Node(k,v); } } } public V getValue(K k){//数据读取 int hash=hashcode(k); hash=hash&(initialCapacity-1);//计算出应该存储的位置 Node pre=table[hash]; V v = null; while (pre!=null){ if(pre.getK().equals(k)){ v= (V) pre.getV(); break; } pre=pre.getNext(); } return v; } public void remove(K k){//数据删除 int hash=hashcode(k); hash=hash&(initialCapacity-1);//计算出应该存储的位置 Node pre=table[hash]; if(pre==null){//空数据 return; }else {//存在数据 --num;//计数自减 while (pre!=null){ if(pre.getK().equals(k)){//找到数据位置 pre=pre.getNext(); break; } } } } public int size(){//获取数据大小 return num; } public void removeAll(){//清楚所有数据 num=0; table=new Node[initialCapacity]; } private Node<K,V>[] getTable(){ return this.table; } private int getNum(){ return this.num; } }
自编写的hashMap测试:
package com.cnblogs.mufasa.demo0; public class Client { public static void main(String[] args) { //测试自己写的hashMap数据结构 hMap<Integer,Integer> hm=new hMap<>(4,0.5f); hm.put(null,1); hm.put(null,2); hm.put(1,10); hm.put(2,20); hm.put(3,30); for(int i=4;i<=50;i++){ hm.put(i,i*10); } System.out.println(hm.size()); } }
输出【经验证正确】:
当前size=3,数据内存进行扩容,以前大小为:4,现在大小为:8 当前size=5,数据内存进行扩容,以前大小为:8,现在大小为:16 当前size=9,数据内存进行扩容,以前大小为:16,现在大小为:32 当前size=17,数据内存进行扩容,以前大小为:32,现在大小为:64 当前size=33,数据内存进行扩容,以前大小为:64,现在大小为:128 51
其中hashcode使用的是Object类中的方法!!!
参考链接
https://www.cnblogs.com/java-jun-world2099/p/9258605.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/tag6254/p/9416946.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenssy/p/3521565.html
https://blog.csdn.net/liji_xc/article/details/79698223
https://www.cnblogs.com/zhchoutai/p/8676351.html
https://blog.csdn.net/cjf1002361126/article/details/52750528
