题目链接
题解
插头(dp)
特点:范围小,网格图,连通性
轮廓线:已决策点和未决策点的分界线
插头:存在于网格之间,表示着网格建的信息,此题中表示两个网格间是否连边
状态表示:当前点((i,j))和轮廓线上(m + 1)个插头的状态
状态转移:
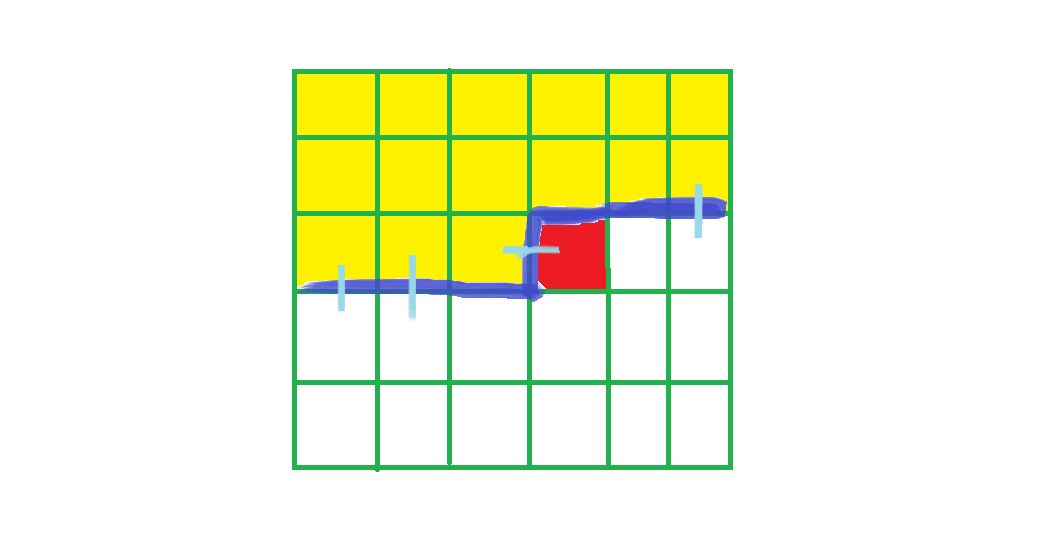
我们用(f[i][j][s])表示如上的状态,最后一次决策点为((i,j)),轮廓线上插头状态为(s)的方案数
比如上图(s = 1101001)
之后我们扩展新的点,枚举它插头的状态进行转移
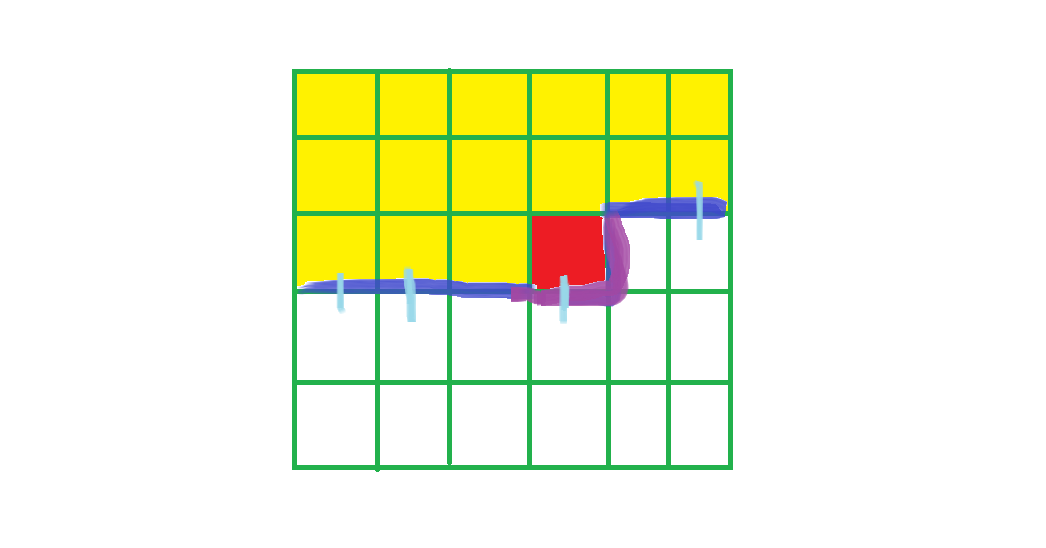
在本题中,要使最终形成若干回路,每个点度数必须为(2),所以我们扩展点的时候记录它已有的插头数,然后剩余的插头数就可以唯一确定
然后就可以(O(nm2^m))过了这道插头(dp)入门题
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<map>
#define Redge(u) for (int k = h[u],to; k; k = ed[k].nxt)
#define REP(i,n) for (int i = 1; i <= (n); i++)
#define mp(a,b) make_pair<int,int>(a,b)
#define cls(s) memset(s,0,sizeof(s))
#define cp pair<int,int>
#define LL long long int
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 12,maxm = 100005,INF = 1000000000;
inline int read(){
int out = 0,flag = 1; char c = getchar();
while (c < 48 || c > 57){if (c == '-') flag = -1; c = getchar();}
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57){out = (out << 3) + (out << 1) + c - 48; c = getchar();}
return out * flag;
}
int n,m,S[maxn][maxn];
LL f[maxn][maxn][1 << maxn];
void work(int C){
cls(f);
if (!S[1][1]) f[1][1][0] = 1;
else {
if (S[1][2] == 0 || S[2][1] == 0){
printf("Case %d: There are 0 ways to eat the trees.
",C);
return;
}
f[1][1][3] = 1;
}
int maxv = (1 << m + 1) - 1,cnt,e,t;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++){
if (i == n && j == m) break;
for (int s = 0; s <= maxv; s++){
if (!f[i][j][s]) continue;
if (j == m){
if (s & 1){
if (i + 2 <= n && S[i + 2][1])
f[i + 1][1][(s >> 1) << 2 | 1] += f[i][j][s];
if (S[i + 1][2])
f[i + 1][1][(s >> 1) << 2 | 2] += f[i][j][s];
}
else {
if (!S[i + 1][1]) f[i + 1][1][(s >> 1) << 2] += f[i][j][s];
else {
if (i + 2 > n || !S[i + 2][1] || !S[i + 1][2]) continue;
f[i + 1][1][(s >> 1) << 2 | 3] += f[i][j][s];
}
}
}
else {
cnt = ((s >> j) & 1) + ((s >> j + 1) & 1);
t = (s >> j) & 3; e = s ^ (t << j);
if (cnt && !S[i][j + 1]) continue;
if (cnt == 2) f[i][j + 1][e] += f[i][j][s];
else if (cnt == 1){
if (i + 1 <= n && S[i + 1][j + 1])
f[i][j + 1][e | (1 << j)] += f[i][j][s];
if (j + 2 <= m && S[i][j + 2])
f[i][j + 1][e | (1 << j + 1)] += f[i][j][s];
}
else {
if (!S[i][j + 1]) f[i][j + 1][e] += f[i][j][s];
else {
if (i + 1 > n || j + 2 > m || !S[i + 1][j + 1] || !S[i][j + 2])
continue;
f[i][j + 1][e | (3 << j)] += f[i][j][s];
}
}
}
}
}
}
LL ans = 0;
for (int s = 0; s <= maxv; s++)
ans += f[n][m][s];
printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.
",C,ans);
}
int main(){
int T = read();
REP(t,T){
n = read(); m = read();
REP(i,n) REP(j,m) S[i][j] = read();
if (n == 1 || m == 1){
if (!S[n][m]) printf("Case %d: There are 1 ways to eat the trees.
",t);
else printf("Case %d: There are 0 ways to eat the trees.
",t);
continue;
}
work(t);
}
return 0;
}