package xiaochengxu; public class pet { protected String name; protected int sex; protected int age; protected int happy; protected int healthy; protected int hungry; public pet(){}//不加在子类中会报错 public pet(String name,int sex){ this.name=name; this.sex =sex; this.age=1; this.happy=80; this.healthy=100; this.hungry=80; }//构造playgame方法 public void playGame(){ if(!Check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起玩"); this.happy+=10; this.healthy-=5; this.hungry+=5; } public void est(){ if(!Check()){ System.out.println("各项属性值不能为负"); return; } System.out.println("与"+this.name+"一起吃饭"); this.hungry-=20; //this.happy-=5; this.healthy+=5; }//判断各个值是否为负 public boolean Check(){ if(this.happy>0&&this.healthy>0&&this.hungry>0){ return true; } if(this.happy<0){ happy=0; } if(this.healthy<0){ healthy=0; } if(this.hungry<0){ hungry=0; } return false; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getSex() { return sex; } public void setSex(int sex) { this.sex = sex; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public int getHappy() { return happy; } public void setHappy(int happy) { this.happy = happy; } public int getHealthy() { return healthy; } public void setHealthy(int healthy) { this.healthy = healthy; } public int getHungry() { return hungry; } public void setHungry(int hungry) { this.hungry = hungry; } }
//子类
package xiaochengxu; public class cat extends pet { public cat(){} public cat(String catName,int catSex){ super(catName,catSex); } public void showInfo(){ System.out.println("宠物名称:"+this.name); System.out.println("宠物性别:"+this.sex); System.out.println("宠物年龄:"+this.age); System.out.println("开心值:"+this.happy); System.out.println("健康值:"+this.healthy); System.out.println("饥饿值:"+this.hungry); } }
//调用测试
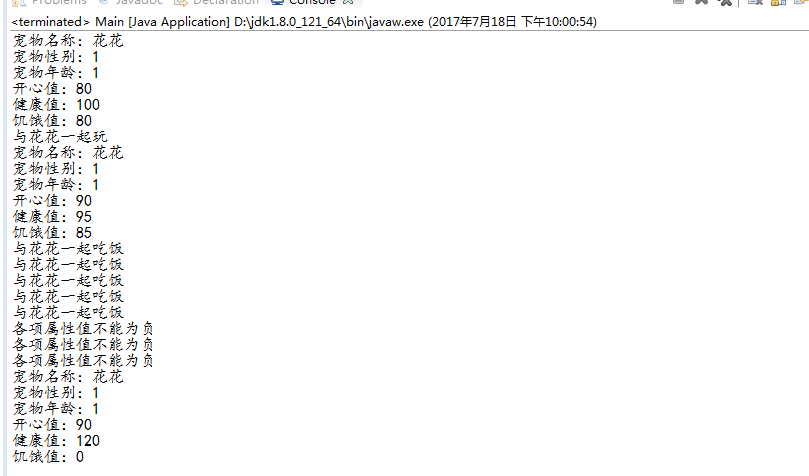
package xiaochengxu; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { cat s=new cat("花花",1); s.showInfo(); s.playGame(); s.showInfo(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.est(); s.showInfo(); } }
计算圆的面积
package shipin; public class TextCirle { public static void main(String[] args) { Circle c1=new Circle(); c1.radius=2.3; double area= c1.fingArea() ; c1.setRadius(4.5); System.out.println(c1.fingArea()); } } class Circle{ public double radius=1.0; public double fingArea(){ return radius*3.14*radius; } public void setRadius(double r){ radius=r; } public double getRadius(){ return radius; } }
1、extends继承:student extends person学生类继承人员类
2、super关键字,表示对父类对象的引用
3、 当子类继承父类的时候, 子类中的构造方法必须调用一下父类的构造方法, 调用哪个都行
如果在子类没有去调用, 子类会默认调用父类的空参构造方法, 这个时候父类中如果没有空参的构造方法程序会报错
4、this,当前对象的使用
5、static静态,不管你实例化多少个,都只共享一个
访问权限:private(私有的)只能在当前类使用,即使是他的子类也不行,public(公用的),
default(默认的,就是不定义权限的时候,eclipse自动默认的)不在一个包中不能访问;子类也不能访问;
protected(受保护的)不在一个包内不能使用
6、final修饰的是常量eg:final int a=10;不能在给a赋值定义;修饰类不能被继承;用final修饰的方法不能被重写
分析:
开始感觉构造方法,成员方法,弄不懂,也不会写,现在也不懂不过起码现在有些可以自己写出来,首先要定义变量,然后构造方法,调用,现在学到的就是继承类,用extends来链接父类,还有在子类中super方法,调用父类资源。用的最多的就是this,代表当前对象的使用,避免重复。