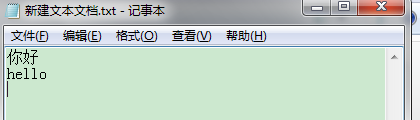
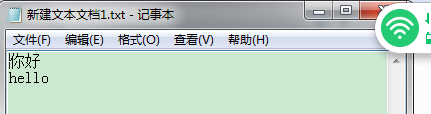
bw.write(s);//如果不用nextLine可以bw.write(s+"/n"); bw.newLine();//换行 bw.flush();//刷新
while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(s); bw.write(s); bw.newLine();//换行 bw.flush(); }
读写只用一个while就可以
类名和方法名不能相同
package keshang; import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.BufferedWriter; import java.io.File; import java.io.FileNotFoundException; import java.io.FileReader; import java.io.FileWriter; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.Reader; import java.io.Writer; //边读边写缓冲流 public class BufferRW { public static void main(String[] args) { File file1=new File("E://新建文本文档1.txt"); File file=new File("E://新建文本文档.txt"); Reader reader=null; Writer writer=null; try { reader = new FileReader(file); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } try { writer= new FileWriter(file1); } catch (IOException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(writer); BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(reader); String s=null; try { while((s=br.readLine())!=null){ System.out.println(s); bw.write(s); bw.newLine();//换行 bw.flush(); } } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); }try { br.close(); bw.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } }
1, 线程的概念
一个程序中的方法有几条执行路径, 就有几个线程
2, 线程的创建:
两种方式:
1, 继承Thread类
class TestThread extends Thread {......}
2, 实现Runnable接口, 然后作为参数传入到Thread类的构造方法中
class TestThread implements Runnable {......}
线程的启动:
调用线程类中的start()方法, 不能直接调用run()方法, 直接调用run()方法那叫方法调用, 不是启动线程
3, 线程常用方法
isAlive()
判断线程是否还活着, 调用start()之前和终止之后都是死的, 其他的都是活的
interrupt()
停止线程
getPriority()
setPriority()
设置优先级, 优先级的概念: 谁的优先级高, 谁执行的时间就多
Thread里面的默认优先级:
Thread.MIN_PRIORITY = 1
Thread.MAX_PRIORITY = 10
Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5
Thread.sleep(long millions)
将程序暂停一会
join()
合并线程
yield()---礼让
让出CPU执行其他线程
wait()---简单了解
notify()---简单了解
notifyAll()---简单了解
4, 线程同步
synchronized
package com.hanqi.xiancheng; //当两个人同时从一张卡上取钱 public class Bank { public int money=3000; public void getMoney(String name,int mon){ synchronized(this){ if(money>mon&&money>0){ try { Thread.sleep(1); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } money-=mon; System.out.println(name+"你好"); System.out.println("取款"+mon); System.out.println("余额剩余:"+money); }else{ System.out.println(name+"你好"); System.out.println("取款"+mon); System.out.println("余额不足"); } } } }
package com.hanqi.xiancheng; public class TextThread { public static void main(String[] args) { MyThread mt=new MyThread(); Thread t1=new Thread(mt); Thread t2=new Thread(mt); t1.setName("超人"); t2.setName("神奇女侠"); t1.start(); t2.start(); } } class MyThread implements Runnable{ public Bank bank=new Bank(); @Override public void run() { bank.getMoney(Thread.currentThread().getName(),2000); } }
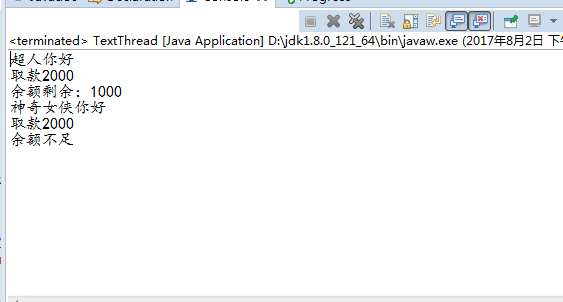
启动线程用start()
不能直接调用run方法,
currentThread()当前线程
synchronized(this){}或者写在public与class之间:锁住当前对象
class MyThread implements Runnable{ public Bank bank=new Bank(); @Override public void run() { bank.getMoney(Thread.currentThread().getName(),2000); } } 必须要重写run方法
同时锁住两个对象容易造成死锁