ACM比赛计算几何就比较重要了,高中只学了个凸包,今儿从圆的反演学起吧。
先来看一道需要用反演解决的题:HDU4773 Problem of Apollonius
题意:给定两个圆(x1,y1,r1)、(x2,y2,r2),它们是相离的,在这两个圆外给定一个点p(x0,y0)。求符合条件:过点p的圆且与已知的两个圆外切的所有圆的总数和它们的圆心坐标和半径。
SOL:如果不知道反演,这道题的做法显然是列出两个方程:
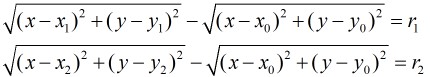
然后发现这个东西根本就没有办法搞。所以就需要用到反演来解答此题。
反演的定义:已知一圆C,圆心为O,半径为r,如果P与P’在过圆心O的直线上,且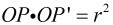 ,则称P与P'关于O互为反演点。
,则称P与P'关于O互为反演点。
几条反演的重要性质:
(1)过反演中心的圆,反形(经过反演之后的图形)为不过反演中心的直线。
(2)不过反演中心的直线,反形为过反演中心的圆。
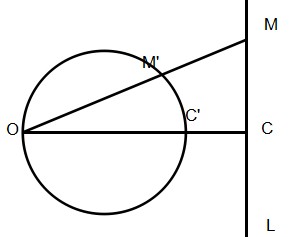
证明的话比较显然,对于上面这个图,就是证明$|OM|*|OM^{'}| = |OC|*|OC^{'}|$就好了,也就是$Delta OM^{'}C^{'} sim Delta OCM$。这个的话根据那个直角很容易得出。
(3)不过反演中心的圆,反形也为不过反演中心的圆,并且反演中心为这两个互为反形的圆的位似中心。
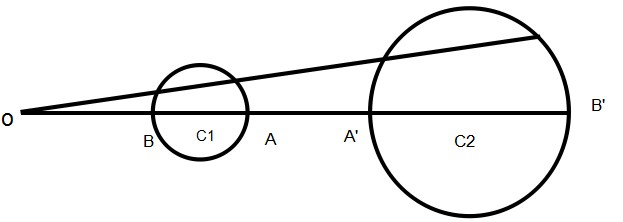
比如上图,O为反演中心,A和A'、B和B'都是互为反演点。证明从略。
这样的话显而易见的就得到了定理(4):相切两圆的反象仍相切,若切点恰是反演中心,则其反象为两平行线。
另外可以推出,相离的两圆反演(反演中心不在圆上)后仍然相离;两圆相切,若反演中心在某圆上,则为反形为相切的直线与圆。
有了这个定理,我们就可以这样解这个题:
首先我们把给定的p点看做反演中心,然后自定义反演半径的大小(为保证精度,不宜过小),接着,求出题目给出的两个圆c1,c2各自的反形c1’,c2’。然后,作出c1’和c2’的外公切线,再将公切线反演回去就得到答案所需的圆了。
为什么这样做是对的呢?我们倒着考虑,最终的图形为3个圆,答案圆与另外两圆外切,如果将这三个圆反演回去,答案圆因为过反演中心,所以反形是一条直线,另外两个题目给出的圆因为没有过反演中心,所以反形是两个圆,由于相切性不变,这条直线与这两个反形圆均相切,即为公切线。
然而我们不能随意求公切线,不仅要求的是公切线,为了防止出现内切的情况,我们要求的是“外公切线”,并且要使得P点和反形圆的圆心在外公切线的同一侧。
(这里可以这样想,反演之前如果圆A在圆B左侧,反演之后圆A就会在在圆B右侧,对反演成直线的圆也是同理的。)
所以接下来的问题就是要求圆和直线的反形以及两个圆的公切线了。
先说如何求圆的反形。对于上面那个图,我们先列出式子:
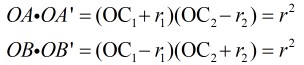
$r_1$和$OC_1$是已知的,然后消去$OC_2$,得到:$r_2 = frac{r_1*r^{2}}{OC_1^2-r_1^2}$。
然后对于反演圆的圆心,我们这样求:
设O的坐标为(x0,y0),C1的坐标为(x1,y1),C2的坐标为(x2,y2),然后就有:
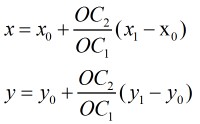
至于$OC_2$的长度,我们可以直接根据反演的定义求出$OA^{'}$的长度,然后加上r2即可。
好了,我们完成了求一个圆的反形。那么直线的反形呢?
先求出p到直线的距离,这样根据定义就求出了反形圆的半径。至于圆心很烦,但在本题可以通过与已知圆圆心与切点的向量的像似向量求出,详见代码。
好了,最后我们只剩下求两个圆的公切线了,转化成求切点。
方法就是求出先求出两圆圆心连线的倾角,在求出与切线垂直的半径与两圆圆心连线的夹角,这样就求出了切点与圆心连线与x轴的夹角,再用向量解决之。
好了,很烦人啊,下面给出代码:

1 #include <cmath> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 const int LEN = 1e3 + 5; 8 const double zero = 1e-8; 9 int i, j, k, n, m, s, t, tot; 10 double R; 11 struct node { 12 double x, y; 13 void in() { 14 scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y); 15 } 16 } p; 17 node operator + (const node &x, const node &y) { 18 return (node){x.x + y.x, x.y + y.y}; 19 } 20 node operator - (const node &x, const node &y) { 21 return (node){x.x - y.x, x.y - y.y}; 22 } 23 node operator * (const node &x, const double &t) { 24 return (node){x.x * t, x.y * t}; 25 } 26 struct circle { 27 node o; 28 double r; 29 void in() { 30 o.in(); 31 scanf("%lf", &r); 32 } 33 void out() { 34 printf("%.8f %.8f %.8f ", o.x, o.y, r); 35 } 36 } a, b, ans[LEN]; 37 double sqr(double x) { 38 return x * x; 39 } 40 double dist(const node &x, const node &y) { 41 return sqrt(sqr(x.x - y.x) + sqr(x.y - y.y)); 42 } 43 circle inversion(const circle &a) { 44 circle res; 45 double d1 = dist(p, a.o); 46 res.r = a.r / (sqr(d1) - sqr(a.r)) * R * R; 47 double d2 = R * R / (d1 - a.r) -res.r; 48 res.o = p + (a.o - p) * (d2 / d1); 49 return res; 50 } 51 node moveit(const node &x, const double &a, const double &d) { 52 return (node){x.x + d * cos(a), x.y + d * sin(a)}; 53 } 54 double cross(const node &x, const node &y) { 55 return y.y * x.x - y.x * x.y; 56 } 57 int sign(double x) { 58 if (fabs(x) < zero) { 59 return 0; 60 } else if (x > 0) { 61 return 1; 62 } else { 63 return -1; 64 } 65 } 66 void addans(const node &x, const node &y) { 67 tot++; 68 double d = fabs(cross(y - p, x - p)) / dist(x, y); 69 ans[tot].r = sqr(R) / (2.0 * d); 70 ans[tot].o = p + (x - a.o) * (ans[tot].r / a.r); 71 } 72 void solve() { 73 a = inversion(a); 74 b = inversion(b); 75 if (a.r < b.r) { 76 swap(a, b); 77 } 78 node c = b.o - a.o; 79 double a1 = atan2(c.y, c.x); 80 double a2 = acos((a.r - b.r) / dist(a.o, b.o)); 81 node t1 = moveit(a.o, a1 + a2, a.r); 82 node t2 = moveit(b.o, a1 + a2, b.r); 83 if (sign(cross(t2 - t1, a.o - t1)) == sign(cross(t2 - t1, p - t1))) { 84 addans(t1, t2); 85 } 86 t1 = moveit(a.o, a1 - a2, a.r); 87 t2 = moveit(b.o, a1 - a2, b.r); 88 if (sign(cross(t2 - t1, a.o - t1)) == sign(cross(t2 - t1, p - t1))) { 89 addans(t1, t2); 90 } 91 } 92 int main() { 93 R = 15.0; 94 int T; 95 scanf("%d", &T); 96 while (T--) { 97 tot = 0; 98 a.in(), b.in(); 99 p.in(); 100 solve(); 101 printf("%d ", tot); 102 for (int i = 1; i <= tot; i++) { 103 ans[i].out(); 104 } 105 } 106 return 0; 107 }
以上内容有部分搬自https://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/16966369#comments,如涉及版权问题,请联系2265755689@qq.com,本人将及时删除。
花了九牛二虎之力AC了反演的第一题,再来看看这一题:HDU6097Mindis
题意:有一个圆心在原点的圆,给定圆的半径,给定P、Q两点坐标(PO=QO,P、Q不在圆外),取圆上一点D,求PD+QD的最小值。
SOL:做P点关于圆的反演点P',$Delta OPD sim Delta ODP'$,相似比是|OP| : r,Q点同理。
极小化PD+QD可以转化为极小化P'D+Q'D。
当P'Q'与圆有交点时,答案为两点距离,否则最优值在中垂线上取到。
时间复杂度 O(1)。
这个题就比较简单了,比较坑的地方是两个点重叠和P,Q为原点的情况。
code:

1 #include <cmath> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 int i, j, k, n, m, s, t; 8 const double zero = 1e-8; 9 double R; 10 struct node { 11 double x, y; 12 void in() { 13 scanf("%lf %lf", &x, &y); 14 } 15 } a, b; 16 double sqr(const double &x) { 17 return x * x; 18 } 19 double dist(const node &x, const node &y) { 20 return sqrt(sqr(x.x - y.x) + sqr(x.y - y.y)); 21 } 22 node moveit(const node &p, const double &a, const double &d) { 23 return (node){p.x + d * cos(a), p.y + d * sin(a)}; 24 } 25 node inversion(const node &x) { 26 double d = sqr(R) / dist((node){0, 0}, x); 27 double a = atan2(x.y, x.x); 28 return moveit((node){0, 0}, a, d); 29 } 30 double cross(const node &x, const node &y) { 31 return y.y * x.x - x.y * y.x; 32 } 33 int sign(const double &x) { 34 if (fabs(x) < zero) { 35 return 0; 36 } else if (x > 0) { 37 return 1; 38 } else { 39 return -1; 40 } 41 } 42 double getdist(const node &x, const node &y) { 43 double L = dist(x, y); 44 if (fabs(L) == 0) { 45 return 2.0 * (dist((node){0, 0}, x) - R); 46 } 47 double d = fabs(cross(x, y)) / L; 48 if (sign(R - d) != -1) { 49 return L; 50 } else { 51 return 2.0 * sqrt(sqr(L / 2) + sqr(d - R)); 52 } 53 } 54 int main() { 55 int T; 56 scanf("%d", &T); 57 while (T--) { 58 scanf("%lf", &R); 59 a.in(), b.in(); 60 double t = dist((node){0, 0}, a); 61 if (sign(t) != 1) { 62 printf("%.8f ", 2.0 * R); 63 continue; 64 } 65 t = dist((node){0, 0}, a) / R; 66 a = inversion(a); 67 b = inversion(b); 68 printf("%.8f ", getdist(a, b) * t); 69 } 70 return 0; 71 }
接下来又是一个练习题:HDU6158The Designer
题意:
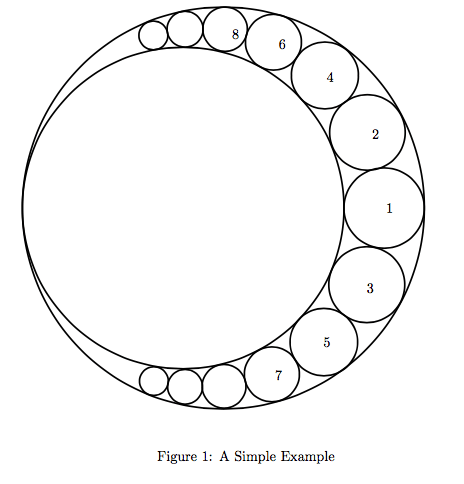
给出最大的两个圆,求带标号的那些小圆的前N个圆的面积和。
SOL:
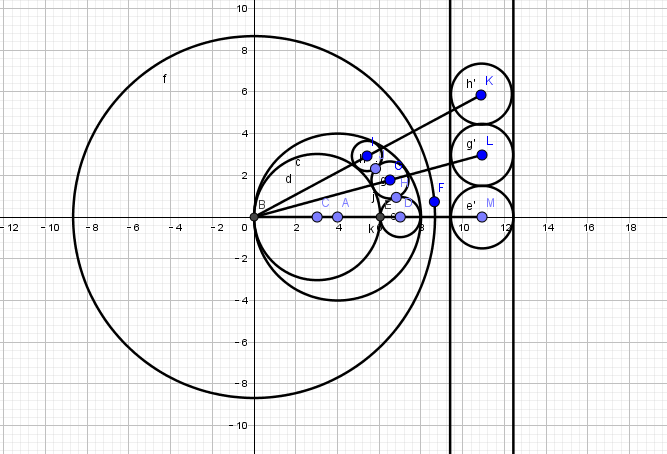
将两个大圆的切点作为反演中心反演两个大圆成两条直线,根据反演前后相切性不变的道理,直接将两直线间夹着的那些圆反演回去求个面积就好了。
另外此题N很大,所以当一定时候面积很小时可以直接忽略。

1 #include <cmath> 2 #include <cstdio> 3 #include <cstring> 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <algorithm> 6 using namespace std; 7 const double pi = acos(-1); 8 const double zero = 1e-14; 9 int i, j, k, n, m, s, t; 10 double r1, r2, R, x1, x2, ans, r; 11 struct node { 12 double x, y; 13 } p; 14 struct circle { 15 node o; 16 double r; 17 } now; 18 double sqr(const double &x) { 19 return x * x; 20 } 21 int sign(const double &x) { 22 if (fabs(x) < zero) { 23 return 0; 24 } else if (x > 0) { 25 return 1; 26 } else { 27 return -1; 28 } 29 } 30 double dist(const node &x, const node &y) { 31 return sqrt(sqr(x.x - y.x) + sqr(x.y - y.y)); 32 } 33 circle inversion(const node &p, const double &r) { 34 circle res; 35 res.r = r / (sqr(dist(p, (node){0, 0})) - sqr(r)) * sqr(R); 36 res.o = (node){0, 0}; 37 return res; 38 } 39 int main() { 40 R = 20.0; 41 int T; 42 scanf("%d", &T); 43 while (T--) { 44 scanf("%lf %lf", &r1, &r2); 45 if (r1 < r2) { 46 swap(r1, r2); 47 } 48 scanf("%d", &n); 49 x1 = sqr(R) / (2.0 * r1); 50 x2 = sqr(R) / (2.0 * r2); 51 r = (x2 - x1) / 2.0; 52 p = (node){(x1 + x2) / 2.0 , 0}; 53 now = inversion(p, r); 54 ans = pi * sqr(now.r); 55 for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { 56 if ((i & 1) == 0) { 57 p.y += 2.0 * r; 58 now = inversion(p, r); 59 } 60 ans += pi * sqr(now.r); 61 if (sign(pi * sqr(now.r)) != 1) { 62 break; 63 } 64 } 65 printf("%.5f ", ans); 66 } 67 return 0; 68 }
图片来自https://blog.csdn.net/coder__yang/article/details/77489327,如有侵权请联系2265755689@qq.com,本人将及时删除。
好了,大概反演就是这样子了。以后等遇到题目是在多练练吧。
