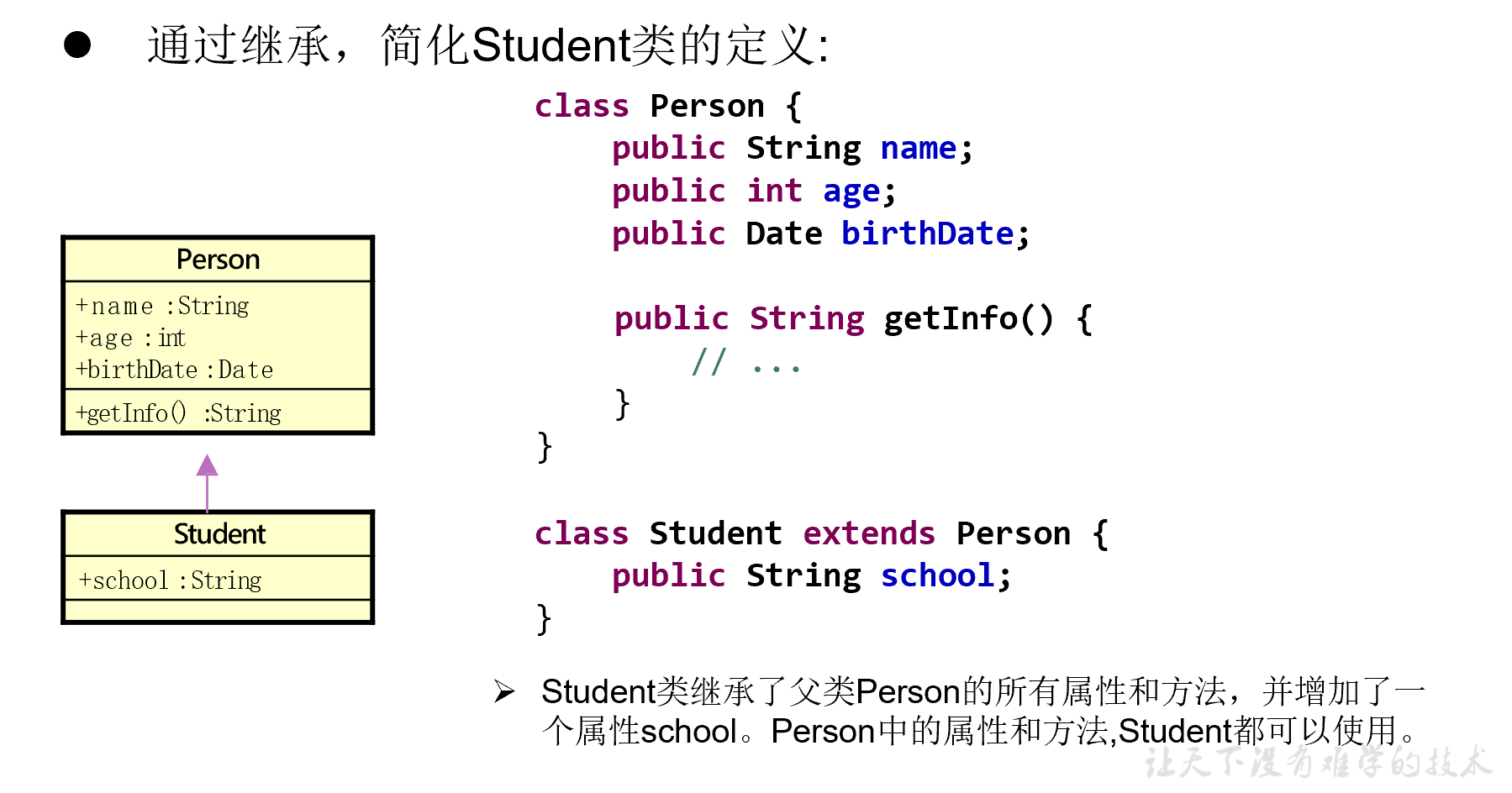
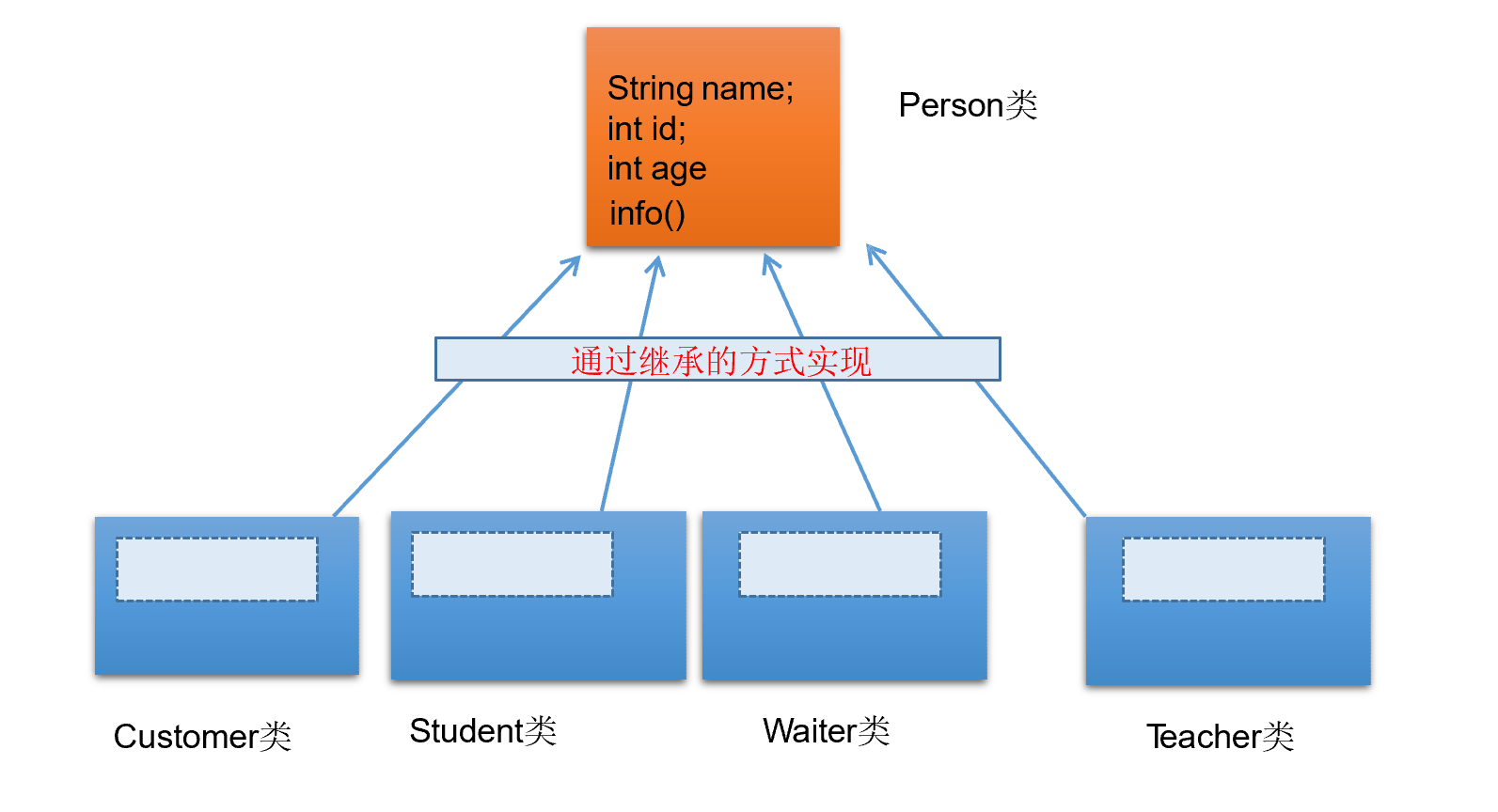
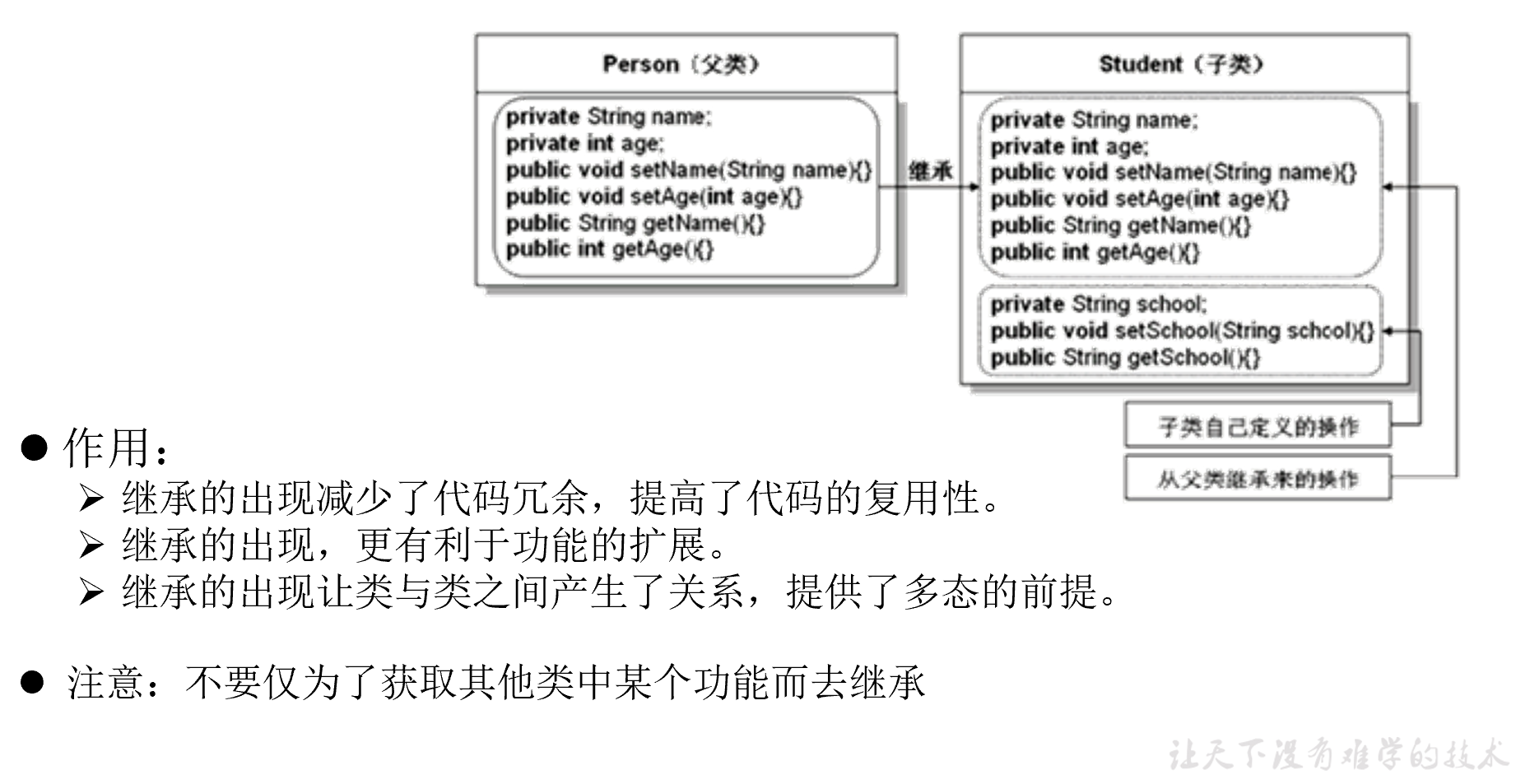
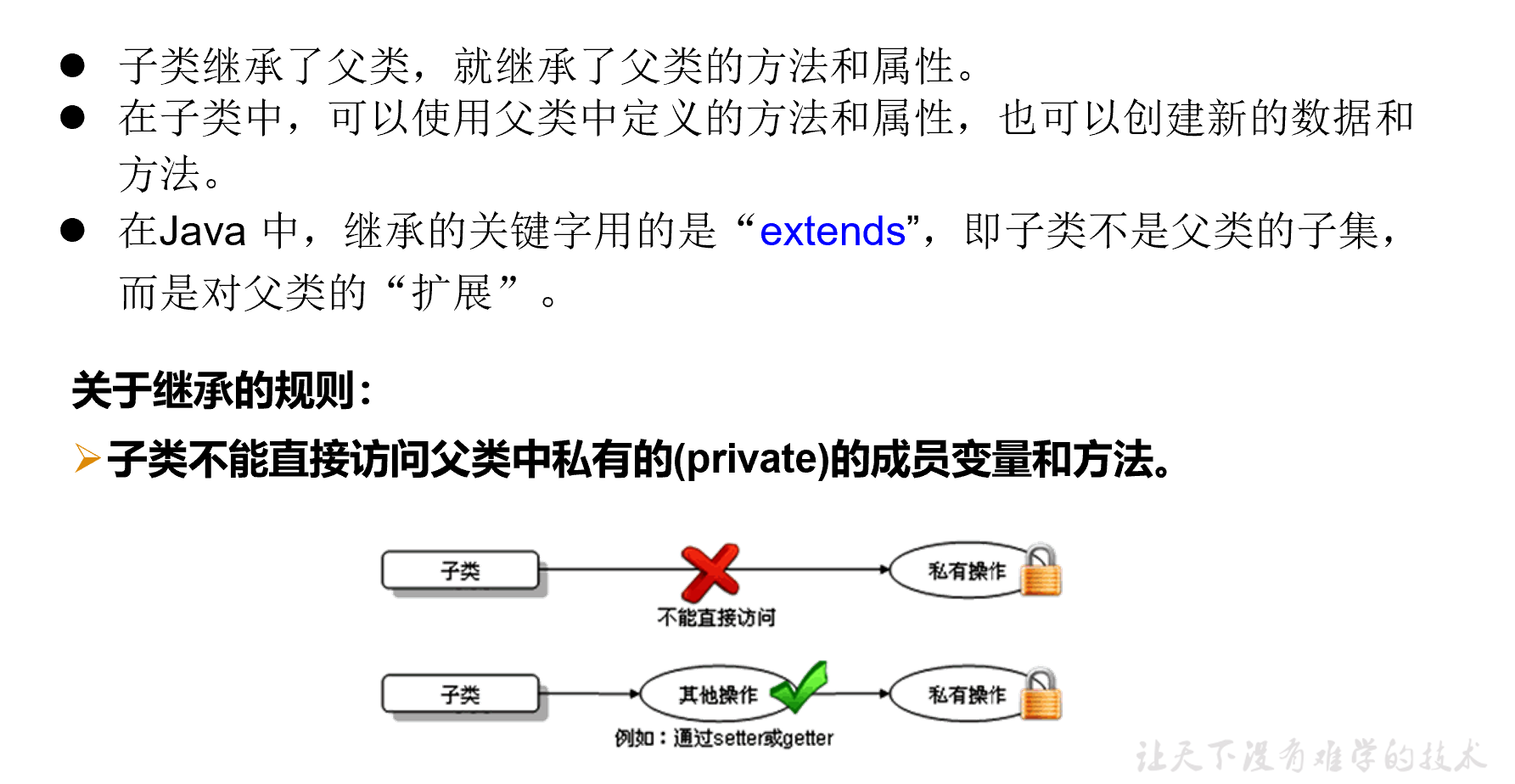
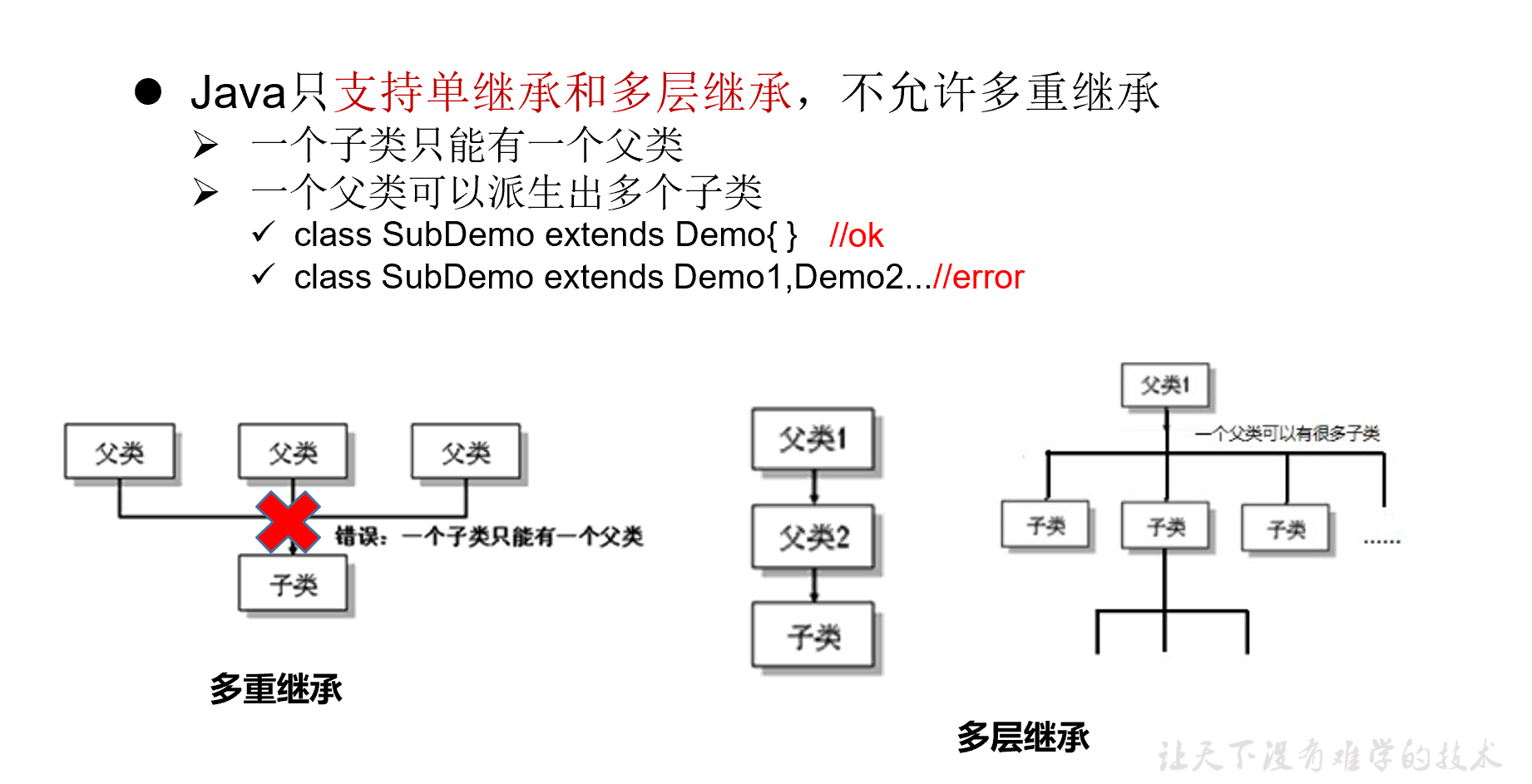
继承性

练习1:圆与圆柱
package com.atguigu.exer1;
public class Circle {
private double radius;
public Circle() {
this.radius = 1;
}
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getRadius() {
return radius;
}
public double findArea() { // 计算圆的面积
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer1;
public class Cylinder extends Circle {
private double length;
public Cylinder() {
this.length = 1;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public double findVolume() { // 计算圆柱体积
return super.findArea() * length;
}
public double findArea() { // 重写父类方法,计算圆柱表面积
return getRadius() * 2 * Math.PI * getLength() + super.findArea() * 2;
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer1;
public class CylinderTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Cylinder cylinder = new Cylinder();
cylinder.setRadius(4);
cylinder.setLength(10);
// 重写前
// System.out.println("圆面积: " + cylinder.findArea()); //圆面积
// 重写后
System.out.println("圆柱表面积: " + cylinder.findArea());// 圆柱表面积
System.out.println("圆柱体积: " + cylinder.findVolume()); // 圆柱体积
}
}
方法的重写

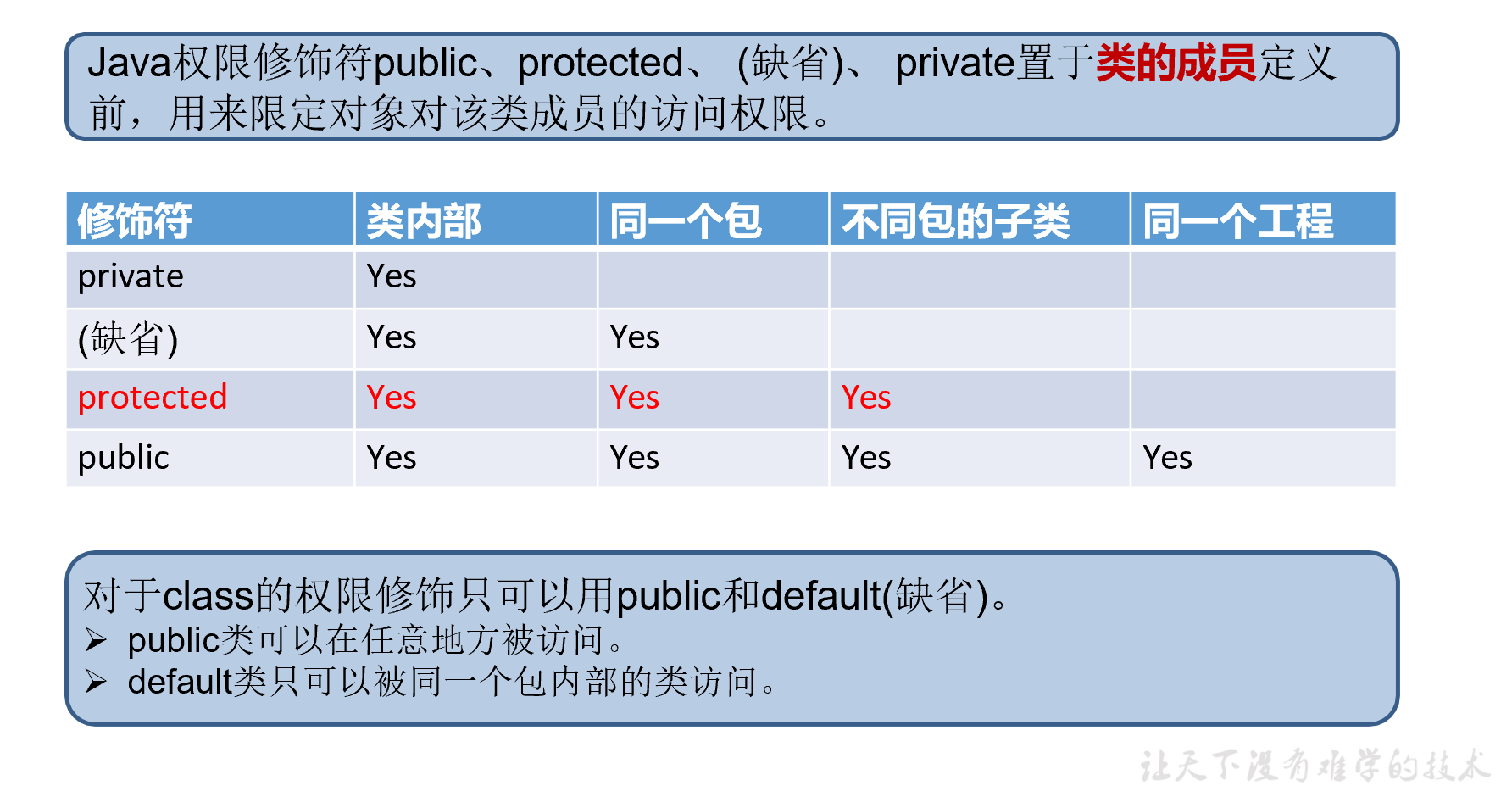
四种访问权限修饰符
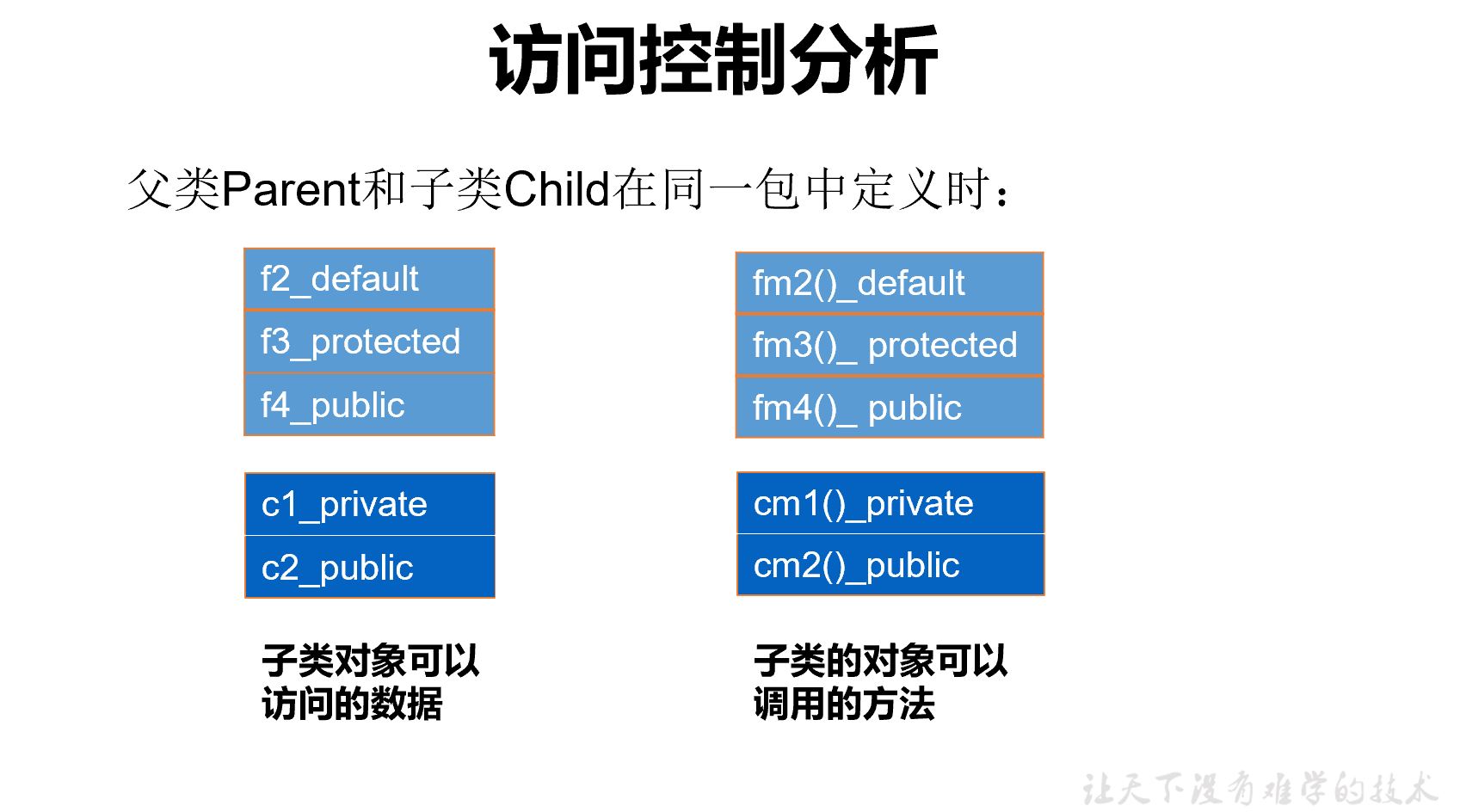
练习1:体会权限调用
package com.atguigu.exer2;
public class Parent {
private int f1 = 1;
int f2 = 2;
protected int f3 = 3;
public int f4 = 4;
private void fm1() { //The method fm1() from the type Parent is never used locally
System.out.println("in fm1() f1=" + f1);
}
void fm2() {
System.out.println("in fm2() f2=" + f2);
}
protected void fm3() {
System.out.println("in fm3() f3=" + f3);
}
public void fm4() {
System.out.println("in fm4() f4=" + f4);
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer2;
class Child extends Parent {
private int c1 = 21;
public int c2 = 22;
private void cm1() {
System.out.println("in cm1() c1=" + c1);
}
public void cm2() {
System.out.println("in cm2() c2=" + c2);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parent p = new Parent();
// System.out.println(p.f1);//The field Parent.f1 is not visible
System.out.println(p.f2);
System.out.println(p.f3);
System.out.println(p.f4);
// p.fm1();//The method fm1() from the type Parent is not visible
p.fm2();
p.fm3();
p.fm4();
Child c = new Child();
System.out.println(c.f2);
System.out.println(c.f3);
System.out.println(c.f4);
System.out.println(c.c1);
System.out.println(c.c2);
c.cm1();
c.cm2();
c.fm2();
c.fm3();
c.fm4();
}
}
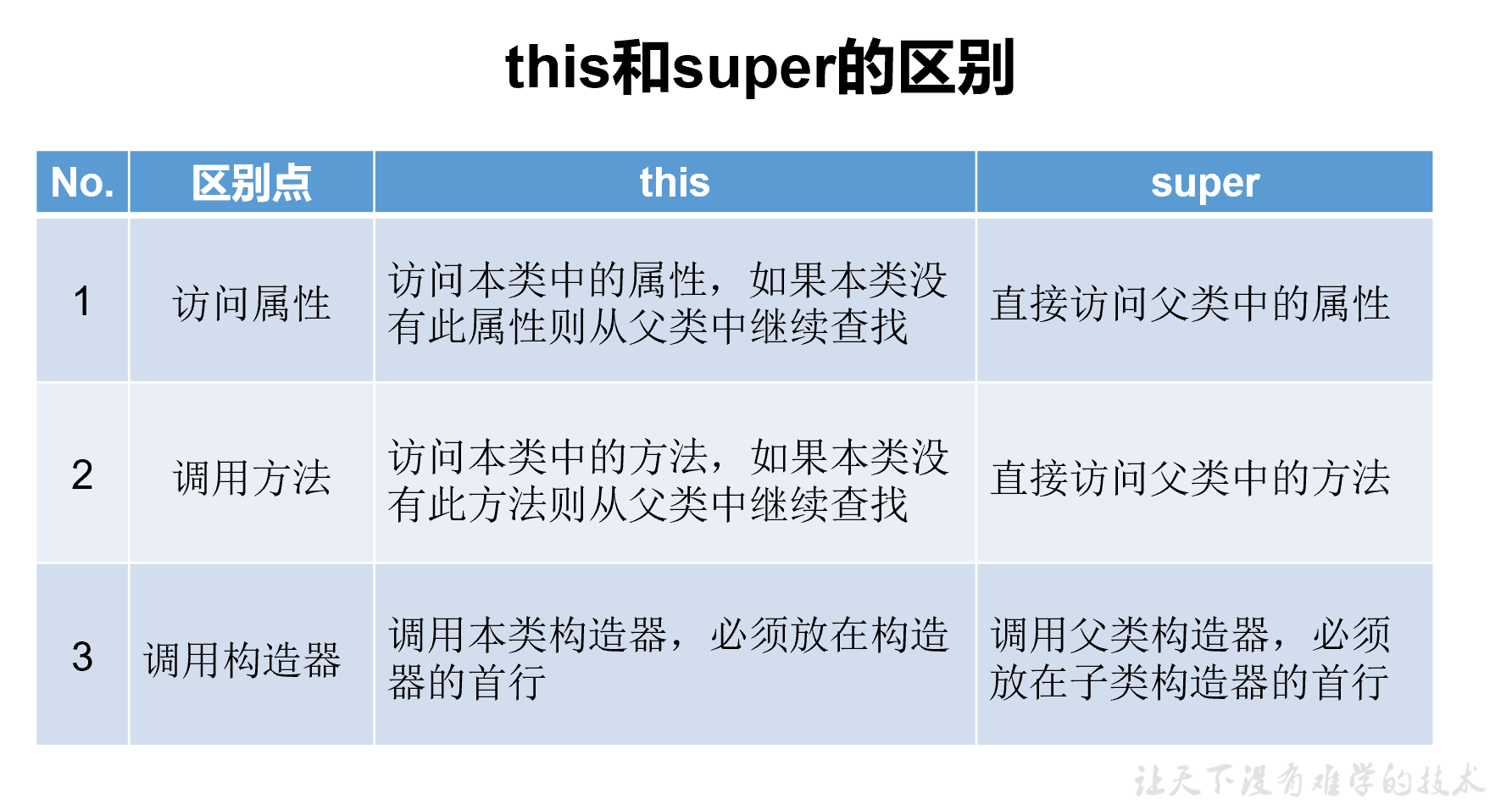
super关键字


练习1:super调用
package com.atguigu.exer3;
import java.sql.Date;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Date birthDate;
public Person(String name, int age, Date d) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthDate = d;
}
public Person(String name, int age) {
this(name, age, null);
}
public Person(String name, Date d) {
this(name, 30, d);
}
public Person(String name) {
this(name, 30);
}
}
package com.atguigu.exer3;
public class Student extends Person {
private String school;
public Student(String name, int age, String s) {
super(name, age);
school = s;
}
public Student(String name, String s) {
super(name);
school = s;
}
// 编译出错: no super(),系统将调用父类无参数的构造器。
// public Student(String s) { //Implicit super constructor Person() is
// undefined. Must explicitly invoke another constructor
// school = s;
// }
}
练习2:综合练习
Account
package com.atguigu.java;
public class Account {
private int id;
private double balance;
private double annualInterestRate;
public Account(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate) {
this.id = id;
this.balance = balance;
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public double getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public double getAnnualInterestRate() {
return annualInterestRate;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setBalance(double balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
public void setAnnualInterestRate(double annualInterestRate) {
this.annualInterestRate = annualInterestRate;
}
public double getMonthlyInterest() {
return annualInterestRate / 12;
}
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount <= balance) {
balance -= amount;
} else {
System.out.println("余额不足!");
}
}
public void deposit(double amount) {
balance += amount;
}
}
CheckAccount
package com.atguigu.java;
/*
创建 Account 类的一个子类 CheckAccount 代表可透支的账户,该账户中定义一个属性
overdraft 代表可透支限额。在 CheckAccount 类中重写 withdraw 方法,
*/
public class CheckAccount extends Account {
private double overdraft;
public CheckAccount(int id, double balance, double annualInterestRate, double overdraft) {
super(id, balance, annualInterestRate);
this.overdraft = overdraft;
}
@Override
public void withdraw(double amount) {
if (amount <= getBalance()) { // 余额满足扣除金额
super.withdraw(amount);
} else if (amount <= (getBalance() + overdraft)) { // 余额加透支额度满足扣除金额
overdraft = overdraft - (amount - getBalance());
super.withdraw(getBalance());
} else {
System.out.println("超过可透支额的限额");
}
}
public double getOverdraft() {
return overdraft;
}
}
AccountTest
package com.atguigu.java;
public class AccountTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试Account功能
/*
* 写一个用户程序测试 Account 类。在用户程序中,创建一个账号为 1122、余额为 20000、 年利率 4.5%的 Account
* 对象。使用 withdraw 方法提款 30000 元,并打印余额。 再使用 withdraw 方法提款 2500 元,使用
* deposit 方法存款 3000 元,然后打印余额和月利 率
*/
Account account = new Account(1122, 20000, 0.045);
account.withdraw(30000);
System.out.println("您的账户余额为: " + account.getBalance());
account.withdraw(2500);
account.deposit(3000);
System.out.println("您的账户余额为: " + account.getBalance());
System.out.println("月利率为: " + (account.getMonthlyInterest() * 100) + "%");
System.out.println("**********************");
// 测试CheckAccount功能
/*
* 写一个用户程序测试 CheckAccount 类。在用户程序中,创建一个账号为 1122、余 额为 20000、年利率
* 4.5%,可透支限额为 5000 元的 CheckAccount 对象。 使用 withdraw 方法提款 5000
* 元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。 再使用 withdraw 方法提款 18000 元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。 再使用 withdraw
* 方法提款 3000 元,并打印账户余额和可透支额。
*/
// 第一次测试
CheckAccount checkAccount = new CheckAccount(1122, 20000, 0.045, 5000);
checkAccount.withdraw(5000);
System.out.println("您的账户余额: " + checkAccount.getBalance());
System.out.println("您的可透支额: " + checkAccount.getOverdraft());
System.out.println();
// 第二次测试
checkAccount.withdraw(18000);
System.out.println("您的账户余额: " + checkAccount.getBalance());
System.out.println("您的可透支额: " + checkAccount.getOverdraft());
System.out.println();
// 第三次测试
checkAccount.withdraw(3000);
System.out.println("您的账户余额: " + checkAccount.getBalance());
System.out.println("您的可透支额: " + checkAccount.getOverdraft());
System.out.println();
}
}
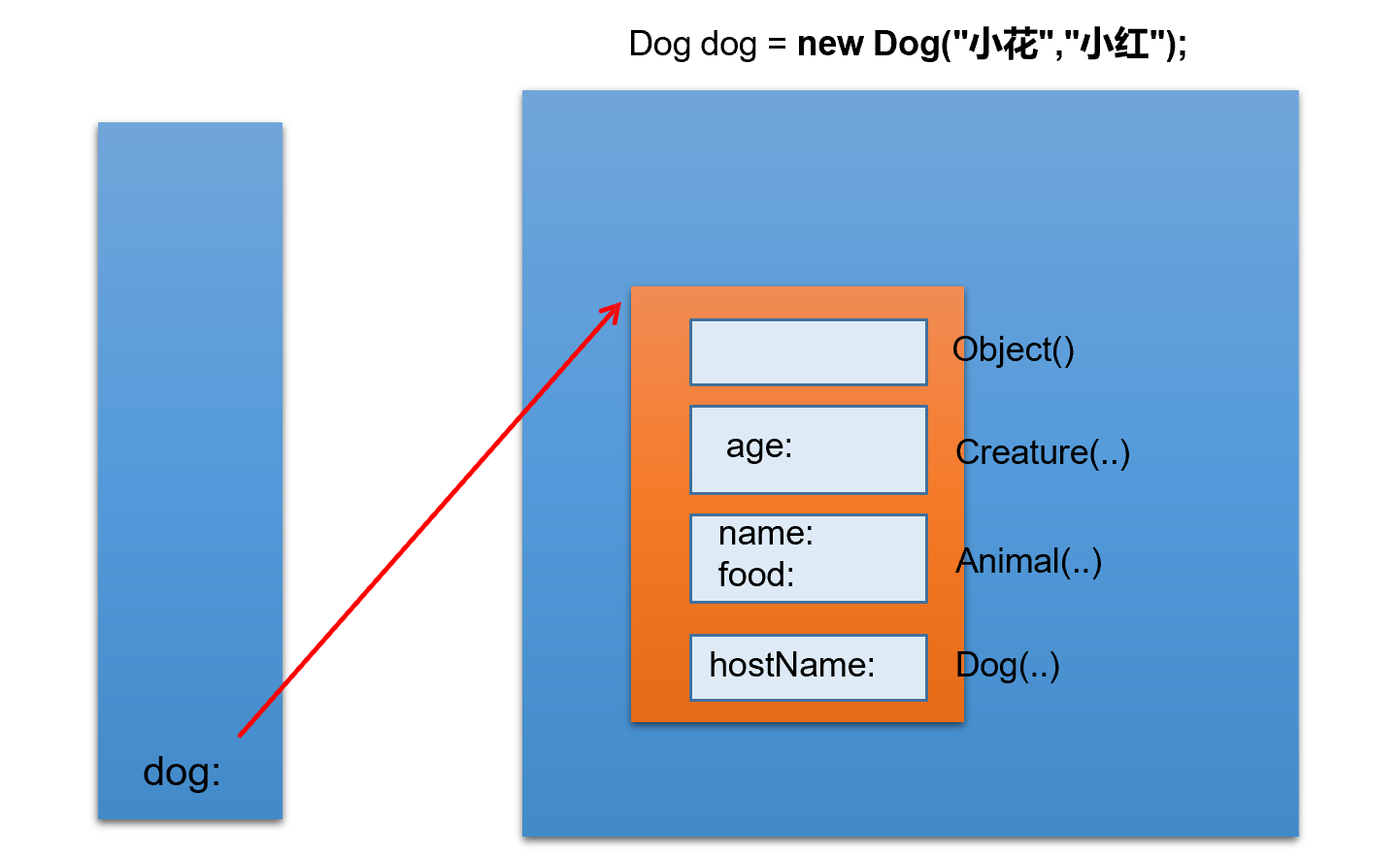
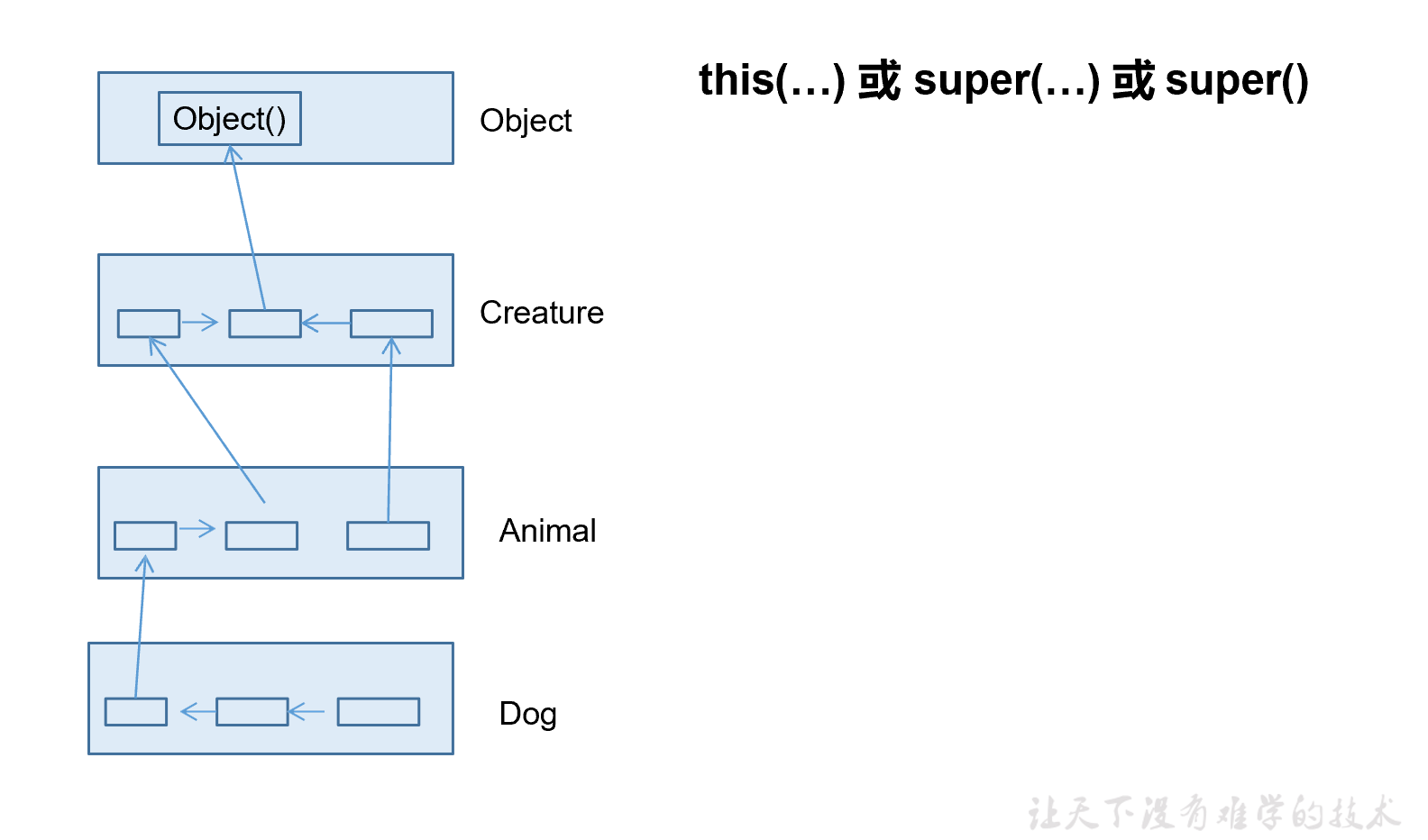
多态性





练习1:多态是运行时行为
package com.atguigu.exer4;
import java.util.Random;
//面试题:多态是编译时行为还是运行时行为?
//证明如下:
class Animal {
protected void eat() {
System.out.println("animal eat food");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
protected void eat() {
System.out.println("cat eat fish");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Dog eat bone");
}
}
class Sheep extends Animal {
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Sheep eat grass");
}
}
public class InterviewTest {
public static Animal getInstance(int key) {
switch (key) {
case 0:
return new Cat();
case 1:
return new Dog();
default:
return new Sheep();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int key = new Random().nextInt(3);
System.out.println(key);
Animal animal = getInstance(key);
animal.eat();
}
}
练习2:多态性的练习
package com.atguigu.exer4;
//考查多态的笔试题目:
public class InterviewTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Base base = new Sub();
base.add(1, 2, 3);
/*
* 父类引用指向子类对象,当子类add(int a, int[] arr)注释时,调用add方法使用的是父类的add,
* 而不使用子类add(int a, int b, int c)的原因是不满足重写条件,子类add(int a, int[] arr)构成重写
*/
Sub s = (Sub) base;
s.add(1, 2, 3);
}
}
class Base {
public void add(int a, int... arr) {
System.out.println("base");
}
}
class Sub extends Base {
// public void add(int a, int[] arr) {
// System.out.println("sub_1");
// }
public void add(int a, int b, int c) {
System.out.println("sub_2");
}
}

重载(overload)和重写(overried)的区别
方法的重写Overriding和重载Overloading是Java多态性的不同表现。重写Overriding是父类与子类之间多态性的一种表现,重载Overloading是一个类中多态性的一种表现。如果在子类中定义某方法与其父类有相同的名称和参数,我们说该方法被重写 (Overriding)。子类的对象使用这个方法时,将调用子类中的定义,对它而言,父类中的定义如同被"屏蔽"了。如果在一个类中定义了多个同名的方法,它们或有不同的参数个数或有不同的参数类型,则称为方法的重载(Overloading)。
