郑重声明:小编理解甚浅,如有错误还请及时指正。
一、构造函数
c++ 构造函数详解_C/C++_若尘的博客-CSDN博客
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Clock{
private:int h,m,s;///数据成员
public:///对外接口
///默认构造函数
Clock():h(0),m(0),s(0){
// h=0,m=0,s=0;
}
///有参构造函数
Clock(int hh,int mm,int ss):h(hh),m(mm),s(ss){
}
///函数重载的理解
Clock(int mm,int ss):h(5),m(mm),s(ss){
}
///拷贝构造函数
Clock(const Clock& x){
h=x.h;m=x.m;s=x.s;
}
void showtime(){
cout<<"("<<h<<":"<<m<<":"<<s<<")"<<endl;
}
void settime(int hh,int mm,int ss){
h=hh,m=mm,s=ss;
}
};
int main(){
///默认构造函数
Clock a;
a.showtime();
///有参构造函数
Clock b(1,2,3);
b.showtime();
///函数重载
Clock c(2,3);
c.showtime();
///拷贝函数
Clock d(c);
d.showtime();
return 0;
}
二、析构函数
我们都知道,C语言里的局部变量在使用完毕后要释放内存空间,而模块使用后也要把申请的资源释放掉,这一步调用该过程的析构函数释放。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Clock{
private:int h,m,s;///数据成员
public:///对外接口
///默认构造函数
Clock():h(0),m(0),s(0){
// h=0,m=0,s=0;
}
///有参构造函数
Clock(int hh,int mm,int ss):h(hh),m(mm),s(ss){
cout<<"有参构造函数"<<endl;
}
///函数重载的理解
Clock(int mm,int ss):h(5),m(mm),s(ss){
}
///拷贝构造函数
Clock(const Clock& x){
cout<<"拷贝构造函数开始"<<endl;
h=x.h;m=x.m;s=x.s;
cout<<"拷贝构造函数结束"<<endl;
}
~Clock(){
cout<<"析构函数结束"<<endl;
}
void showtime(){
cout<<"("<<h<<":"<<m<<":"<<s<<")"<<endl;
}
void settime(int hh,int mm,int ss){
h=hh,m=mm,s=ss;
}
};
void outputClock(Clock c){
cout<<"outputClock"<<endl;
c.showtime();
}
int main(){
Clock c(2,3,4);
outputClock(c);
return 0;
}
三、类模块在函数参数传递中的通用理解
先来回想一下函数调用的过程:1.记录返回地址 2.为被调函数的执行分配资源,创造运行条件3.将控制交给被调函数执行。
函数在进行参数传递时,有两种方式,传值调用和传引用调用,这两种方式的区别就在于第二步资源的分配。前者会为实参数据在被调函数内部生成数据副本,后者是直接操作主调函数被的原始数据。
也就是说,对于类模块的参数传递中的传值方式,将会把主调函数中的实参转化为被调函数空间里的形参。
对于普通的变量(相当于C语言中的局部变量),这一过程仅仅是申请空间后进行赋值,执行完毕后系统会释放其内存,这也就保证了他的作用域。
而对于有自己的元素组成和构造方式的模块来说,仅仅是单纯的申请空间是无法生成新的模块的,这就需要用拷贝构造函数用实参生成形参。在执行完毕后,也不能单纯的释放空间来达到限制模块的作用域的目的,这就需要析构函数把模块申请的资源释放掉。
对于参数传引用的方式,仅仅是对同一个数据模块,在主调函数里是一个名字,在被调函数里是一个名字,相当于一个人的大名和小名~在这种方式下,无论是简单的变量,还是复杂的类对象,处理和理解都是一样的。
以下代码为了更好的体现这两个代码的执行过程,使用了this指针,this指针是C++自带的可以输出当前操作对象地址的东西(好高大上啊 %%)
这是传值调用代码~
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Clock{
private:int h,m,s;///数据成员
public:///对外接口
///默认构造函数
Clock():h(0),m(0),s(0){
// h=0,m=0,s=0;
}
///有参构造函数
Clock(int hh,int mm,int ss):h(hh),m(mm),s(ss){
cout<<"有参构造函数"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
///函数重载的理解
Clock(int mm,int ss):h(5),m(mm),s(ss){
}
///拷贝构造函数
Clock(const Clock& x){
cout<<"拷贝构造函数开始"<<" "<<this<<endl;
h=x.h;m=x.m;s=x.s;
cout<<"拷贝构造函数结束"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
~Clock(){
cout<<"析构函数结束"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
void showtime(){
cout<<"("<<h<<":"<<m<<":"<<s<<")"<<endl;
}
void settime(int hh,int mm,int ss){
h=hh,m=mm,s=ss;
}
};
void outputClock(Clock c){
cout<<"outputClock"<<endl;
c.showtime();
}
int main(){
Clock c(2,3,4);
outputClock(c);
return 0;
}
根据运行结果可以知道,主函数里的c和outputClock中的c的地址不同。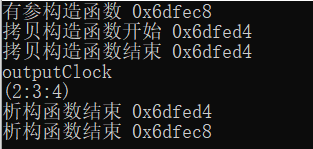
稍微一改就是传引用调用了
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Clock{
private:int h,m,s;///数据成员
public:///对外接口
///默认构造函数
Clock():h(0),m(0),s(0){
// h=0,m=0,s=0;
}
///有参构造函数
Clock(int hh,int mm,int ss):h(hh),m(mm),s(ss){
cout<<"有参构造函数"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
///函数重载的理解
Clock(int mm,int ss):h(5),m(mm),s(ss){
}
///拷贝构造函数
Clock(const Clock& x){
cout<<"拷贝构造函数开始"<<" "<<this<<endl;
h=x.h;m=x.m;s=x.s;
cout<<"拷贝构造函数结束"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
~Clock(){
cout<<"析构函数结束"<<" "<<this<<endl;
}
void showtime(){
cout<<"("<<h<<":"<<m<<":"<<s<<")"<<endl;
}
void settime(int hh,int mm,int ss){
h=hh,m=mm,s=ss;
}
};
void outputClock(Clock& c){
cout<<"outputClock"<<endl;
c.showtime();
}
int main(){
Clock c(2,3,4);
outputClock(c);
return 0;
}
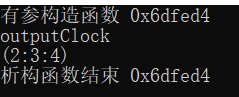
运行结果~
四,过程分析(其实是作业)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Point{///定义一个类对象相当于一个模块
private:
int x,y;///类对象的数据成员,对外不可见
public:///类对象的对外接口
///构造函数:与类同名,初始化对象的数据成员,使得小模块形成完整模块
Point(int px,int py):x(px),y(py){
cout<<"普通构造函数生成"<<this<<endl;;
ShowPoint();
}
///拷贝构造函数:完成完整模块之间的复制
Point(Point& p):x(p.x),y(p.y){
cout<<"拷贝构造函数生成"<<this<<endl;
ShowPoint();
}
///显示函数
void ShowPoint(){ cout<<"("<<x<<","<<y<<")"<<this<<endl;}
///析构函数:在类前面加~,释放模块申请的资源
~Point(){cout<<"析构函数调用"<<this<<endl;}
};
///void ShowPointInfo(Point p) 传值调用:为实参数据在被调函数内部生成数据副本
///void ShowPointInfo(Point& p) 传引用调用:直接操作主调函数被的原始数据
void ShowPointInfo(Point p){
cout<<"ShowPointInfo begin"<<endl;
p.ShowPoint() ;
cout<<"ShowPointInfo end"<<endl;
}
///传值调用需要用拷贝构造函数用实参生成形参,在执行完毕后,需要析构函数把模块申请的资源释放掉
int main(){
Point pa(3,4);
ShowPointInfo(pa);
cout<<endl;
return 0;
}
/**以下结合this指针分析程序执行过程
运行结果:
普通构造函数生成0x6dfed0
(3,4)0x6dfed0
拷贝构造函数生成0x6dfed8
(3,4)0x6dfed8
ShowPointInfo begin
(3,4)0x6dfed8
ShowPointInfo end
析构函数调用0x6dfed8
析构函数调用0x6dfed0
过程分析:
首先调用构造函数对类对象的数据成员进行初始化,构造出类对象A
然后在函数传值调用时调用拷贝构造函数将主调函数里的实参转为被调函数里的形参
这一过程是生成了一个新的类对象B
被调函数执行完毕后,类对象B被析构,返回主调函数
主调函数执行完毕,类对象A被析构,程序结束
**/
完结撒花~