LeetCode题目练习记录 _栈、队列01 _20211012
84. 柱状图中最大的矩形
难度困难1581
给定 n 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
示例 1:
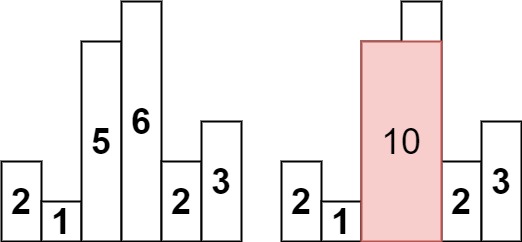
输入:heights = [2,1,5,6,2,3]
输出:10
解释:最大的矩形为图中红色区域,面积为 10
示例 2:
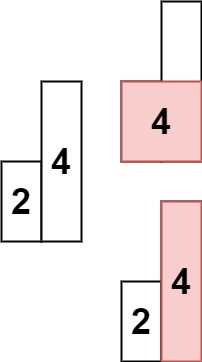
输入: heights = [2,4]
输出: 4
提示:
1 <= heights.length <=1050 <= heights[i] <= 104
方法一:单调栈
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int n = heights.length;
int[] left = new int[n];
int[] right = new int[n];
Deque<Integer> mono_stack = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while(!mono_stack.isEmpty() && heights[mono_stack.peek()] >= heights[i]) {
mono_stack.pop();
}
left[i] = (mono_stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : mono_stack.peek());
mono_stack.push(i);
}
mono_stack.clear();
for(int i=n-1; i >=0; i--) {
while (!mono_stack.isEmpty() && heights[mono_stack.peek()] >= heights[i]) {
mono_stack.pop();
}
right[i] = (mono_stack.isEmpty() ? n : mono_stack.peek());
mono_stack.push(i);
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
ans = Math.max(ans,(right[i] - left[i] - 1) * heights[i]);
}
return ans;
}
}
func largestRectangleArea(heights []int) int {
n := len(heights)
left, right := make([]int, n), make([]int, n)
mono_stack := []int{}
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
for len(mono_stack) > 0 && heights[mono_stack[len(mono_stack)-1]] >= heights[i] {
mono_stack = mono_stack[:len(mono_stack)-1]
}
if len(mono_stack) == 0 {
left[i] = -1
}else{
left[i] = mono_stack[len(mono_stack)-1]
}
mono_stack = append(mono_stack, i)
}
mono_stack = []int{}
for i := n -1; i >= 0; i-- {
for len(mono_stack) > 0 && heights[mono_stack[len(mono_stack) -1]] >= heights[i] {
mono_stack = mono_stack[:len(mono_stack) -1]
}
if len(mono_stack) == 0 {
right[i] = n
}else {
right[i] = mono_stack[len(mono_stack) -1]
}
mono_stack = append(mono_stack, i)
}
ans := 0
for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
ans = max(ans, (right[i] - left[i] -1) * heights[i])
}
return ans
}
func max(x,y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
239. 滑动窗口最大值
难度困难1215
给你一个整数数组 nums,有一个大小为 k 的滑动窗口从数组的最左侧移动到数组的最右侧。你只可以看到在滑动窗口内的 k 个数字。滑动窗口每次只向右移动一位。
返回滑动窗口中的最大值。
示例 1:
输入:nums = [1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7], k = 3
输出:[3,3,5,5,6,7]
解释:
滑动窗口的位置 最大值
--------------- -----
[1 3 -1] -3 5 3 6 7 3
1 [3 -1 -3] 5 3 6 7 3
1 3 [-1 -3 5] 3 6 7 5
1 3 -1 [-3 5 3] 6 7 5
1 3 -1 -3 [5 3 6] 7 6
1 3 -1 -3 5 [3 6 7] 7
示例 2:
输入:nums = [1], k = 1
输出:[1]
示例 3:
输入:nums = [1,-1], k = 1
输出:[1,-1]
示例 4:
输入:nums = [9,11], k = 2
输出:[11]
示例 5:
输入:nums = [4,-2], k = 2
输出:[4]
提示:
1 <= nums.length <= 105-104 <= nums[i] <= 1041 <= k <= nums.length
方法一:优先队列
class Solution {
// Java 方法一:优先队列
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<int[]>(new Comparator<int[]>(){
public int compare(int[] pair1,int[] pair2){
return pair1[0] != pair2[0] ? pair2[0] - pair1[0] : pair2[1] - pair1[1];
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
pq.offer(new int[]{nums[i],i});
}
int[] ans = new int[n - k + 1];
ans[0] = pq.peek()[0];
for (int i = k; i < n; i++) {
pq.offer(new int[]{nums[i], i});
while (pq.peek()[1] <= i -k) {
pq.poll();
}
ans[i - k +1] = pq.peek()[0];
}
return ans;
}
}
// Go 方法一:优先队列
var a []int
type hp struct{ sort.IntSlice }
func (h hp)Less(i, j int)bool {
return a[h.IntSlice[i]] > a[h.IntSlice[j]]
}
func (h *hp) Push(v interface{}) {
h.IntSlice = append(h.IntSlice, v.(int))
}
func (h *hp) Pop() interface{} {
a := h.IntSlice
v := a[len(a)-1]
h.IntSlice = a[:len(a)-1]
return v
}
func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
a = nums
q := &hp{make([]int,k)}
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
q.IntSlice[i] = i
}
heap.Init(q)
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int, 1, n-k+1)
ans[0] = nums[q.IntSlice[0]]
for i := k; i < n; i++ {
heap.Push(q, i)
for q.IntSlice[0] <= i-k {
heap.Pop(q)
}
ans = append(ans,nums[q.IntSlice[0]])
}
return ans
}
方法二:单调队列
class Solution {
// Java 方法二:单调队列
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
Deque<Integer> deque = new LinkedList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] >= nums[deque.peekLast()]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
}
int[] ans = new int[n - k + 1];
ans[0] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
for (int i=k; i < n; i++) {
while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[i] >= nums[deque.peekLast()]) {
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(i);
while (deque.peekFirst() <= i -k) {
deque.pollFirst();
}
ans[i - k + 1] = nums[deque.peekFirst()];
}
return ans;
}
}
func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
// Go 方法二:单调队列
q := []int{}
push := func(i int) {
for len(q) > 0 && nums[i] >= nums[q[len(q) -1]] {
q = q[:len(q)-1]
}
q = append(q,i)
}
for i := 0; i < k; i++ {
push(i)
}
n := len(nums)
ans := make([]int,1,n-k+1)
ans[0] = nums[q[0]]
for i := k; i < n; i++ {
push(i)
for q[0] <= i-k {
q = q[1:]
}
ans = append(ans, nums[q[0]])
}
return ans
}
方法三:分块 + 预处理
class Solution {
// Java 方法三:分块 + 预处理 —— 最速解
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] prefixMax = new int[n];
int[] suffixMax = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i % k == 0) {
prefixMax[i] = nums[i];
}else {
prefixMax[i] = Math.max(prefixMax[i-1],nums[i]);
}
}
for (int i = n-1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (i == n-1 || (i+1)%k == 0) {
suffixMax[i] = nums[i];
}else{
suffixMax[i] = Math.max(suffixMax[i + 1],nums[i]);
}
}
int[] ans = new int [n - k + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n -k; ++i) {
ans[i] = Math.max(suffixMax[i], prefixMax[i + k -1]);
}
return ans;
}
}
func maxSlidingWindow(nums []int, k int) []int {
// Go 方法三:分块 + 预处理
n := len(nums)
prefixMax := make([]int, n)
suffixMax := make([]int, n)
for i, v := range nums {
if i % k == 0 {
prefixMax[i] = v
}else {
prefixMax[i] = max(prefixMax[i-1], v)
}
}
for i := n - 1; i >=0; i-- {
if i == n-1 || (i+1)%k == 0 {
suffixMax[i] = nums[i]
} else {
suffixMax[i] = max(suffixMax[i+1], nums[i])
}
}
ans := make([]int, n-k+1)
for i := range ans {
ans[i] = max(suffixMax[i],prefixMax[i+k-1])
}
return ans
}
func max(a,b int) int {
if a > b {
return a
}
return b
}
641. 设计循环双端队列
难度中等98
设计实现双端队列。
你的实现需要支持以下操作:
- MyCircularDeque(k):构造函数,双端队列的大小为k。
- insertFront():将一个元素添加到双端队列头部。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- insertLast():将一个元素添加到双端队列尾部。如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteFront():从双端队列头部删除一个元素。 如果操作成功返回 true。
- deleteLast():从双端队列尾部删除一个元素。如果操作成功返回 true。
- getFront():从双端队列头部获得一个元素。如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- getRear():获得双端队列的最后一个元素。 如果双端队列为空,返回 -1。
- isEmpty():检查双端队列是否为空。
- isFull():检查双端队列是否满了。
示例:
MyCircularDeque circularDeque = new MycircularDeque(3); // 设置容量大小为3
circularDeque.insertLast(1); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertLast(2); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(3); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 已经满了,返回 false
circularDeque.getRear(); // 返回 2
circularDeque.isFull(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.deleteLast(); // 返回 true
circularDeque.insertFront(4); // 返回 true
circularDeque.getFront(); // 返回 4
提示:
- 所有值的范围为 [1, 1000]
- 操作次数的范围为 [1, 1000]
- 请不要使用内置的双端队列库。
// Java 双向链表实现,一个节点包含前后两个指针
class MyCircularDeque {
int capacity;
int curContain = 0;
class ListNode {
int val;
ListNode next;
ListNode prev;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
ListNode start;
ListNode end;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
this.capacity = k;
start = new ListNode(0);
end = start;
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(value);
newNode.next = start.next;
if (newNode.next != null) {
newNode.next.prev = newNode;
}else{
end = newNode;
}
newNode.prev = start;
start.next = newNode;
curContain += 1;
return true;
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(value);
end.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = end;
end = end.next;
curContain += 1;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
ListNode nextNode = start.next.next;
start.next.next = null;
start.next.prev = null;
start.next = nextNode;
if (start.next != null) {
start.next.prev = start;
}else{
end = start;
}
curContain -= 1;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
ListNode preNode = end.prev;
end.prev = null;
preNode.next = null;
end = preNode;
curContain -= 1;
return true;
}
public int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return start.next.val;
}
public int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return end.val;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return start == end;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return capacity == curContain;
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/
// Java 数组实现
class MyCircularDeque {
int size = 0;
int tail = -1;
int[] queue;
public MyCircularDeque(int k) {
size = k;
queue = new int[k];
}
public boolean insertFront(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = tail; i >= 0; i--) {
queue[i + 1] = queue[i];
}
queue[0] = value;
tail++;
return true;
}
public boolean insertLast(int value) {
if (isFull()) {
return false;
}
tail++;
queue[tail] = value;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
for (int i=1; i <= tail; i++) {
queue[i-1] = queue[i];
}
queue[tail] = 0;
tail--;
return true;
}
public boolean deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
queue[tail] = 0;
tail--;
return true;
}
public int getFront() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return queue[0];
}
public int getRear() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return -1;
}
return queue[tail];
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return tail == -1;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return tail == (size - 1);
}
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyCircularDeque obj = new MyCircularDeque(k);
* boolean param_1 = obj.insertFront(value);
* boolean param_2 = obj.insertLast(value);
* boolean param_3 = obj.deleteFront();
* boolean param_4 = obj.deleteLast();
* int param_5 = obj.getFront();
* int param_6 = obj.getRear();
* boolean param_7 = obj.isEmpty();
* boolean param_8 = obj.isFull();
*/
// Go 数组实现
type MyCircularDeque struct {
queue []int
head int
tail int
}
/** Initialize your data structure here. Set the size of the deque to be k. */
func Constructor(k int) MyCircularDeque {
return MyCircularDeque{
queue: make([]int, k + 1),
head: 0,
tail: 0,
}
}
/** Adds an item at the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) InsertFront(value int) bool {
if this.IsFull(){
return false
}
this.head = (this.head - 1 + len(this.queue)) % len(this.queue)
this.queue[this.head] = value
return true
}
/** Adds an item at the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) InsertLast(value int) bool {
if this.IsFull() {
return false
}
this.queue[this.tail] = value
this.tail = (this.tail + 1) % len(this.queue)
return true
}
/** Deletes an item from the front of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) DeleteFront() bool {
if this.IsEmpty() {
return false
}
this.head = (this.head + 1) % len(this.queue)
return true
}
/** Deletes an item from the rear of Deque. Return true if the operation is successful. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) DeleteLast() bool {
if this.IsEmpty() {
return false
}
this.tail = (this.tail - 1 + len(this.queue)) % len(this.queue)
return true
}
/** Get the front item from the deque. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) GetFront() int {
if this.IsEmpty() {
return -1
}
return this.queue[this.head]
}
/** Get the last item from the deque. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) GetRear() int {
if this.IsEmpty() {
return -1
}
n := (this.tail - 1 + len(this.queue)) % len(this.queue)
return this.queue[n]
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is empty or not. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) IsEmpty() bool {
return this.head == this.tail
}
/** Checks whether the circular deque is full or not. */
func (this *MyCircularDeque) IsFull() bool {
return (this.tail + 1) % len(this.queue) == this.head
}
/**
* Your MyCircularDeque object will be instantiated and called as such:
* obj := Constructor(k);
* param_1 := obj.InsertFront(value);
* param_2 := obj.InsertLast(value);
* param_3 := obj.DeleteFront();
* param_4 := obj.DeleteLast();
* param_5 := obj.GetFront();
* param_6 := obj.GetRear();
* param_7 := obj.IsEmpty();
* param_8 := obj.IsFull();
*/
42. 接雨水
难度困难2756
给定 n 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
示例 1:

输入:height = [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1]
输出:6
解释:上面是由数组 [0,1,0,2,1,0,1,3,2,1,2,1] 表示的高度图,在这种情况下,可以接 6 个单位的雨水(蓝色部分表示雨水)。
示例 2:
输入:height = [4,2,0,3,2,5]
输出:9
提示:
n == height.length1 <= n <= 2 * 1040 <= height[i] <= 105
class Solution {
// Java 方法 1:暴力
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans = 0;
int size = height.length;
for (int i = 1; i < size - 1; i++) {
int max_left = 0;
int max_right = 0;
for (int j = i; j >=0 ; j--) {
max_left = Math.max(max_left,height[j]);
}
for (int j = i; j < size; j++) {
max_right = Math.max(max_right, height[j]);
}
ans += Math.min(max_left,max_right) - height[i];
}
return ans;
}
}
// G 方法 1:暴力
func trap(height []int) int {
ans := 0
size := len(height)
for i := 1; i < size; i++ {
max_left := 0
max_right := 0
for j := i; j >= 0; j-- {
max_left = max(max_left,height[j])
}
for j := i ; j < size ; j++ {
max_right = max(max_right,height[j])
}
ans += min(max_left,max_right) - height[i]
}
return ans
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}
func min(x, y int) int {
if x < y {
return x
}
return y
}
方法二:单调栈
class Solution {
// Java 方法二:单调栈
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<Integer>();
int n = height.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (!stack.isEmpty() && height[i] > height[stack.peek()]) {
int top = stack.pop();
if (stack.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
int left = stack.peek();
int currWidth = i - left - 1;
int currHeight = Math.min(height[left], height[i]) - height[top];
ans += currWidth * currHeight;
}
stack.push(i);
}
return ans;
}
}
// Go 方法二:单调栈
// 指明返回的是ans 就可以直接return 不用带参数
func trap(height []int) (ans int) {
stack := []int{}
for i, h := range height {
for len(stack) > 0 && h > height[stack[len(stack) - 1]] {
top := stack[len(stack) - 1]
stack = stack[:len(stack) - 1]
if len(stack) == 0 {
break
}
left := stack[len(stack) - 1]
curWidth := i - left -1
curHeight := min(height[left],h) - height[top]
ans += curWidth * curHeight
}
stack = append(stack,i)
}
return
}
func min(x, y int) int {
if x < y {
return x
}
return y
}
class Solution {
// Java 方法三:双指针
public int trap(int[] height) {
int ans = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = height.length - 1;
int leftMax = 0;
int rightMax = 0;
while (left < right) {
leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, height[left]);
rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, height[right]);
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
ans += leftMax - height[left];
left ++;
} else {
ans += rightMax - height[right];
right --;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
// Go 方法三:双指针
// 声明返回的是ans 就可以直接return 不用带参数
func trap(height []int) (ans int) {
left := 0
right := len(height) -1
leftMax := 0
rightMax := 0
for left < right {
leftMax = max(leftMax,height[left])
rightMax = max(rightMax,height[right])
if (height[left] < height[right]) {
ans += leftMax - height[left]
left++
} else {
ans += rightMax - height[right]
right--
}
}
return
}
func max(x, y int) int {
if x > y {
return x
}
return y
}