前言
update 2021.2.16 加上了目录,修复了部分 (markdown)。
大佬博客
这是一篇质量还行的博客
前排放大佬的博客用来(orz)
前置芝士
据说(
equire{enclose}enclose{horizontalstrike}{ ext{Treap}})也可以,但蒟蒻作者不会
树链剖分(如果你学过的话可以更好理解,没学过也没有关系)
定义
又到了喜闻乐见的百度百科自学时间
真·定义:
动态树,( ext{Link-Cut Tree}),简称( ext{LCT})
其中的( ext{Link})指加边,( ext{Cut})指删边
类似于树链剖分,但是线段树变成了(Splay)(大概是这样的)
我们就可以在树上自由地删边、连边了,当然也可以搞其它的
作用
-
查询、修改链上的信息(最值,总和等)
-
换根
-
动态连边、删边
-
合并两棵树、分离一棵树
-
动态维护连通性
-
敬请期待更多操作
讲解
令人窒息的百度百科(反正我再也不会看了)
如果你一头雾水地回来了,那么我又双叒叕成功了
( ext{LCT})是由很多( ext{Splay})维护的一个数据结构
其中最重要的当然就是( equire{enclose}enclose{horizontalstrike}{ ext{Splay}})
零、大概的实现
如果有一棵树,我们将每个点选一个儿子为偏爱儿子(类似于树链剖分的重儿子,但是这是我们自己定的)
然后偏爱儿子与父亲的边为实边,其余的为虚边
每一个实边相连的部分为一棵( ext{Splay})
我们将每一个实边相连的部分(一条链)叫做偏爱路径((Preferred Path))
组成的( ext{Splay})叫做辅助树((Auxiliary Tree))
学专业术语就是出去装A_C用的
假设我们可以构造这么一棵树,长这样:(红色为实边,绿色为虚边)
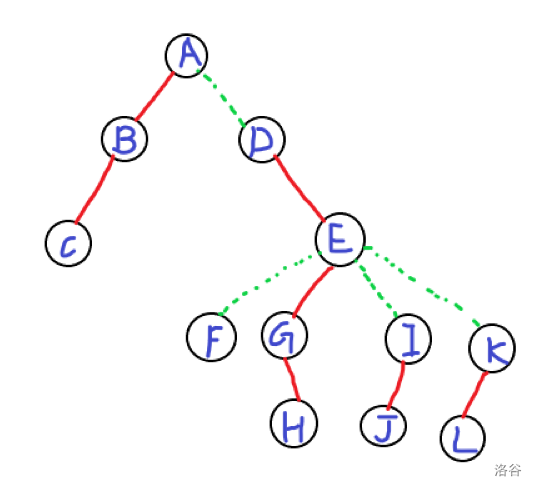
其中框出来的部分就是一棵( ext{Splay})
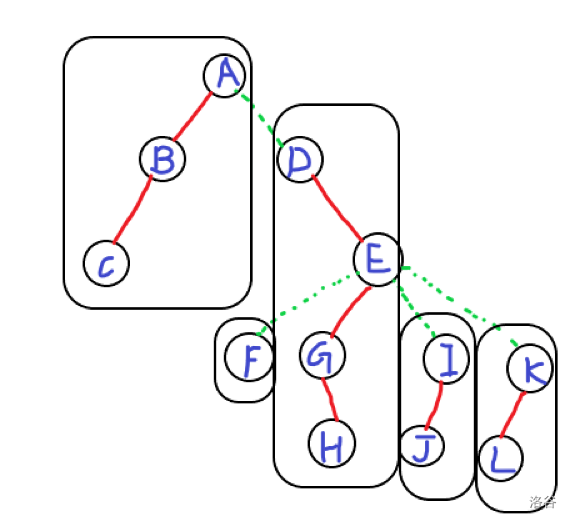
图好丑啊啊啊啊啊!!!
注意不要把( ext{F})给忘了
对于每一棵( ext{Splay}),我们按深度的从小到大排序
排序完了之后当然就是:前面(左边)的是祖先,后面(右边)的是后代
( ext{LCT})不画了,(lazy),但是( ext{LCT})要满足上面的规则
其中:
虚边认父不认子(如只记录(F)的父亲是(E),但不记录(E)的儿子是(F))
实边都要认(两边都要存)
这些东西是为了保证我们接下来的操作
一、( ext{access})
核心操作!!!
如果你英语好,或者知道这个东西
你就可以知道这个单词的意思是访问
具体的,它用来实现把节点(x)与树根连接起来(搞到一棵( ext{Splay})里)
跟访问有什么关系呢?
我们举个栗子,把上面的树搬下来:

假设我们要( ext{access(L)}),就要把(A)到(L)路径上的所有边全部变为实边
怎么实现呢?
1.首先我么要把(L)转为自己所在的( ext{Splay})的根
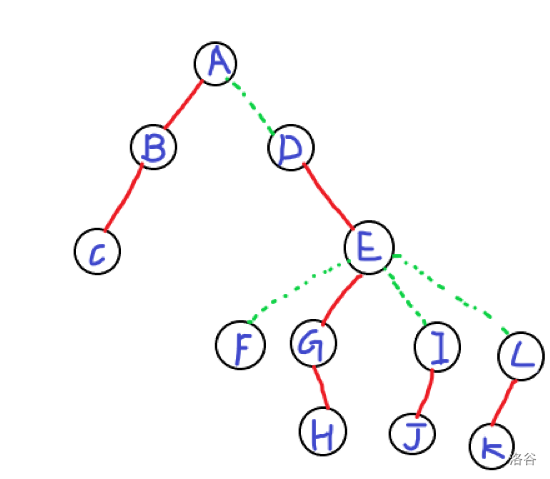
注意我画的图不是按照排序规律画的(因为懒)
现在(K)在(L)的左边
2.然后,由于我们马上就要把(L)与(E)连成实边了,所以我们要把(L)的右儿子赋为空(认父不认子),尽管它并没有右儿子
3.接着,我们更新一下(L)的信息(由下到上)
4.最后,我们走向(L)的父亲(E)(通过虚边走向父亲)
现在我们在(E)
把(E)转到根
把抢了位置的(G)替换为上来的(L)(更新右儿子)
更新(E)的信息(由下到上)
走向(E)的父亲(A),注意我们已经换到了根,所以父亲为(A)(通过虚边走向父亲)
对(A)也进行这样的操作,那么直到再像父亲走的时候走到了空节点,结束
总结,其实循环只有四步:
1.转到根
2.改变右儿子
3.更新信息
4.走向父亲
void access(int x)//访问
{
for(int y = 0; x ;x = t[y = x].f)
{
splay(x);
t[x].ch[1] = y;
up(x);
}
}
二、( ext{makeroot})(换根)
懂了第一个操作,这个操作就显得简单很多
连通(x)到根,把(x)转到根
其它点的深度都改变了,但是我们发现他们的深度刚好都翻转了过来
所以我们可以这样:
void pushr(int x)//翻转操作
{
swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r ^= 1;
}
void makeroot(int x)//换根
{
access(x);
splay(x);
pushr(x);
}
三、( ext{findroot})(找根)
就是找当前点所在的( ext{Splay})的根?
Pi!
是原树的根
首先把(x)到根连通,把(x)转到根,一直向左走,最小的即为根
int findroot(int x)//找根(原树中) ,就是最小的那个
{
access(x);
splay(x);
while(t[x].ch[0]) down(x),x = t[x].ch[0];
splay(x);
return x;
}
四、( ext{merge})(合并)
自己给这个操作取的名字
我们询问(x,y)的路径上的信息,就要把(x,y)合到一棵树里面
故取名(merge),由于(merge)是关键字,所以简写为(merg) (好丑)
我们将(x)置为树的根(( ext{makeroot})),通过( ext{access})操作连通(x,y),将(y)旋转到根,路径上的点就在(y)的子树中,我们可以通过访问(y)中的信息,获取路径上的信息
void merg(int x,int y)//提取路径,把x和y搞到一棵Splay里面,再乱搞
{
makeroot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
}
五、( ext{link})(加边)
判断是否已经连通
如果没连通,连虚边
判连通的两个方法:
1.普遍的
将(x)置为根,找(y)所在的树的根,如果不是(x),不连通,否则连通
2.特殊的:只有加边
并查集维护
void link(int x,int y)//连边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) != x) t[x].f = y;
}
六、( ext{cut})(删边)
首先判断是否连通
连通之后再判断是否有一条相连的边
我们可以通过这样的方法判断:
把(x)置为根
如果(y)的父亲是(x)并且(y)没有左子树(即(y)的祖先就(x)一个)
删掉:(y)的父亲置为(0),(x)的右儿子置为(0)
别忘了更新(x)的信息!!!
void cut(int x,int y)//删边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) == x && t[y].f == x && !t[y].ch[0])//保证它们相连
{
t[y].f = t[x].ch[1] = 0;
up(x);
}
}
练习
其实都是板题,就弹飞绵羊稍微有一点思维
代码
板题代码
//12252024832524
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 100005;
int n,m;
int v[MAXN];
int Read()
{
int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();
while(c > '9' || c < '0'){if(c == '-')f = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x*10) + (c^48);c = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
void Put1(int x)
{
if(x > 9) Put1(x/10);
putchar(x%10^48);
}
void Put(int x)
{
if(x < 0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
Put1(x);
}
template <typename T>T Max(T x,T y){return x > y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Min(T x,T y){return x < y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Abs(T x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;}
struct Splay//LinkCutTree
{
int tot;
int st[MAXN];//栈
struct node
{
int val,ch[2],f;
bool r;//翻转标记
}t[MAXN];
bool nroot(int x)//判断节点是否为一个Splay的根
{
return t[t[x].f].ch[0] == x || t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x;
//如果连的是轻边,他的父亲的儿子里就没有它
}
void pushr(int x)//翻转操作
{
swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r ^= 1;
}
void up(int x)
{
t[x].val = t[t[x].ch[0]].val ^ t[t[x].ch[1]].val ^ v[x];
}
void down(int x)
{
if(t[x].r)
{
if(t[x].ch[0]) pushr(t[x].ch[0]);
if(t[x].ch[1]) pushr(t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r = 0;
}
}
bool chk(int x)
{
return (t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x);
}
void rotate(int x)
{
int y = t[x].f;
int z = t[y].f;
int k = chk(x);
int w = t[x].ch[k^1];
t[y].ch[k] = w;
if(w) t[w].f = y;
if(nroot(y)) t[z].ch[chk(y)] = x;
t[x].f = z;
t[x].ch[k^1] = y;
t[y].f = x;
up(y);
up(x);
}
void splay(int x,int to = 0)
{
int y = x,z = 0;
st[++z] = y;
while(nroot(y)) st[++z] = y = t[y].f;
while(z) down(st[z--]);
while(nroot(x))
{
y = t[x].f;
if(nroot(y))
{
if(chk(x) != chk(y)) rotate(x);
else rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
up(x);
}
void access(int x)//访问
{
for(int y = 0; x ;x = t[y = x].f)
{
splay(x);
t[x].ch[1] = y;
up(x);
}
}
void makeroot(int x)//换根
{
access(x);
splay(x);
pushr(x);
}
int findroot(int x)//找根(原树中) ,就是最小的那个
{
access(x);
splay(x);
while(t[x].ch[0]) down(x),x = t[x].ch[0];
splay(x) ;
return x;
}
void merg(int x,int y)//提取路径,把x和y搞到一棵Splay里面,再乱搞
{
makeroot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
}
void link(int x,int y)//连边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) != x) t[x].f = y;
}
void cut(int x,int y)//删边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) == x && t[y].f == x && !t[y].ch[0])//保证它们相连
{
t[y].f = t[x].ch[1] = 0;
up(x);
}
}
}lct;
int main()
{
// freopen(".in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".out","w",stdout);
n = Read();
m = Read();
for(int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) v[i] = Read();
while(m --)
{
int opt = Read(),x = Read(),y = Read();
if(opt == 0) {lct.merg(x,y);Put(lct.t[y].val);putchar('
');}
else if(opt == 1) {lct.link(x,y);}
else if(opt == 2) {lct.cut(x,y);}
else if(opt == 3) {lct.splay(x,0);v[x] = y;}
else printf("fuck ccf
");
}
return 0;
}
OTOCI代码 (貌似不开O2过不了,令人窒息的常数)
//12252024832524
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 30005;
int n,m;
int v[MAXN];
int st[MAXN];//栈
int F[MAXN];
char opt[10];
inline int Read()
{
int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();
while(c > '9' || c < '0'){if(c == '-')f = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x*10) + (c^48);c = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
inline void Put1(int x)
{
if(x > 9) Put1(x/10);
putchar(x%10^48);
}
inline void Put(int x)
{
if(x < 0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
Put1(x);
}
template <typename T>T Max(T x,T y){return x > y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Min(T x,T y){return x < y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Abs(T x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;}
char gc()
{
char c = getchar();
while(c > 'z' || c < 'a') c = getchar();
return c;
}
int findSet(int x)
{
if(F[x] != x) F[x] = findSet(F[x]);
return F[x];
}
struct Splay//LinkCutTree
{
int tot;
struct node
{
int val,ch[2],f;
bool r;//翻转标记
}t[MAXN];
inline bool nroot(int x)//判断节点是否为一个Splay的根
{
return t[t[x].f].ch[0] == x || t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x;
//如果连的是轻边,他的父亲的儿子里就没有它
}
inline void pushr(int x)//翻转操作
{
swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r ^= 1;
}
inline void up(int x)
{
t[x].val = t[t[x].ch[0]].val + t[t[x].ch[1]].val + v[x];
}
inline void down(int x)
{
if(t[x].r)
{
if(t[x].ch[0]) pushr(t[x].ch[0]);
if(t[x].ch[1]) pushr(t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r = 0;
}
}
inline bool chk(int x)
{
return (t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x);
}
inline void rotate(int x)
{
int y = t[x].f;
int z = t[y].f;
int k = chk(x);
int w = t[x].ch[k^1];
t[y].ch[k] = w;
if(w) t[w].f = y;
if(nroot(y)) t[z].ch[chk(y)] = x;
t[x].f = z;
t[x].ch[k^1] = y;
t[y].f = x;
up(y);
up(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int to = 0)
{
int y = x,z = 0;
st[++z] = y;
while(nroot(y)) st[++z] = y = t[y].f;
while(z) down(st[z--]);
while(nroot(x))
{
y = t[x].f;
if(nroot(y))
{
if(chk(x) != chk(y)) rotate(x);
else rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
up(x);
}
inline void access(int x)//访问
{
for(int y = 0; x ;x = t[y = x].f)
{
splay(x);
t[x].ch[1] = y;
up(x);
}
}
inline void makeroot(int x)//换根
{
access(x);
splay(x);
pushr(x);
}
inline int findroot(int x)//找根(原树中) ,就是最小的那个
{
access(x);
splay(x);
while(t[x].ch[0]) down(x),x = t[x].ch[0];
splay(x) ;
return x;
}
inline int dis(int x,int y)//询问路径,把x和y搞到一棵Splay里面,再乱搞
{
makeroot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
return t[y].val;
}
bool qconnect(int x,int y)
{
if(findSet(x) == findSet(y)) return 1;
return 0;
}
inline void link(int x,int y)//连边
{
makeroot(x);
if(!qconnect(x,y)) t[x].f = y,printf("yes
"),F[findSet(x)] = findSet(y);
else printf("no
");
}
inline void cut(int x,int y)//删边
{
makeroot(x);
if(qconnect(x,y) && t[y].f == x && !t[y].ch[0])//保证它们相连
{
t[y].f = t[x].ch[1] = 0;
up(x);
}
}
}lct;
int main()
{
// freopen(".in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".out","w",stdout);
n = Read();
for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++ i) v[i] = Read(),F[i] = i;
int x,y;
for(register int Q = Read(); Q ;-- Q)
{
char opt = gc();
x = Read();
y = Read();
if(opt == 'e') {if(!lct.qconnect(x,y)){printf("impossible
");continue;}Put(lct.dis(x,y));putchar('
');}
else if(opt == 'b') {lct.link(x,y);}
else if(opt == 'p') {lct.splay(x,0);v[x] = y;}
}
return 0;
}
弹飞绵羊代码
//12252024832524
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 200005;
int n,m;
int v[MAXN],tox[MAXN];
int st[MAXN];//栈
inline int Read()
{
int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();
while(c > '9' || c < '0'){if(c == '-')f = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x*10) + (c^48);c = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
inline void Put1(int x)
{
if(x > 9) Put1(x/10);
putchar(x%10^48);
}
inline void Put(int x)
{
if(x < 0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
Put1(x);
}
template <typename T>T Max(T x,T y){return x > y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Min(T x,T y){return x < y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Abs(T x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;}
char gc()
{
char c = getchar();
while(c > 'z' || c < 'a') c = getchar();
return c;
}
struct Splay//LinkCutTree
{
int tot;
struct node
{
int val,ch[2],f;
bool r;//翻转标记
}t[MAXN];
inline bool nroot(int x)//判断节点是否为一个Splay的根
{
return t[t[x].f].ch[0] == x || t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x;
//如果连的是轻边,他的父亲的儿子里就没有它
}
inline void pushr(int x)//翻转操作
{
swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r ^= 1;
}
inline void up(int x)
{
t[x].val = t[t[x].ch[0]].val + t[t[x].ch[1]].val + v[x];
}
inline void down(int x)
{
if(t[x].r)
{
if(t[x].ch[0]) pushr(t[x].ch[0]);
if(t[x].ch[1]) pushr(t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r = 0;
}
}
inline bool chk(int x)
{
return (t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x);
}
inline void rotate(int x)
{
int y = t[x].f;
int z = t[y].f;
int k = chk(x);
int w = t[x].ch[k^1];
t[y].ch[k] = w;
if(w) t[w].f = y;
if(nroot(y)) t[z].ch[chk(y)] = x;
t[x].f = z;
t[x].ch[k^1] = y;
t[y].f = x;
up(y);
up(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int to = 0)
{
int y = x,z = 0;
st[++z] = y;
while(nroot(y)) st[++z] = y = t[y].f;
while(z) down(st[z--]);
while(nroot(x))
{
y = t[x].f;
if(nroot(y))
{
if(chk(x) != chk(y)) rotate(x);
else rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
up(x);
}
inline void access(int x)//访问
{
for(int y = 0; x ;x = t[y = x].f)
{
splay(x);
t[x].ch[1] = y;
up(x);
}
}
inline void makeroot(int x)//换根
{
access(x);
splay(x);
pushr(x);
}
inline int findroot(int x)//找根(原树中) ,就是最小的那个
{
access(x);
splay(x);
while(t[x].ch[0]) down(x),x = t[x].ch[0];
splay(x) ;
return x;
}
inline int dis(int x,int y)//询问路径,把x和y搞到一棵Splay里面,再乱搞
{
makeroot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
return t[y].val;
}
void link(int x,int y)//连边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) != x) t[x].f = y;
}
inline void cut(int x,int y)//删边
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) == x && t[y].f == x && !t[y].ch[0])//保证它们相连
{
t[y].f = t[x].ch[1] = 0;
up(x);
}
}
}lct;
int main()
{
// freopen(".in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".out","w",stdout);
n = Read();
for(register int i = 1;i <= n;++ i)
{
v[i] = 1;
tox[i] = Read();
if(i + tox[i] > n)
tox[i] = n+1-i;
lct.link(i,i+tox[i]);
}
for(register int Q = Read(); Q ;-- Q)
{
int opt = Read();
if(opt == 1) Put(lct.dis(Read()+1,n+1)),putchar('
');
else if(opt == 2)
{
int x = Read()+1;
lct.cut(x,x+tox[x]);
tox[x] = Read();
if(x + tox[x] > n) tox[x] = n+1-x;
lct.link(x,x+tox[x]);
}
else printf("fuck ccf
");
}
return 0;
}
洞穴勘测
//12252024832524
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int MAXN = 10005;
int n,m;
int v[MAXN],tox[MAXN];
int st[MAXN];//栈
inline int Read()
{
int x = 0,f = 1;char c = getchar();
while(c > '9' || c < '0'){if(c == '-')f = -1;c = getchar();}
while(c >= '0' && c <= '9'){x = (x*10) + (c^48);c = getchar();}
return x * f;
}
inline void Put1(int x)
{
if(x > 9) Put1(x/10);
putchar(x%10^48);
}
inline void Put(int x)
{
if(x < 0) putchar('-'),x = -x;
Put1(x);
}
template <typename T>T Max(T x,T y){return x > y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Min(T x,T y){return x < y ? x : y;}
template <typename T>T Abs(T x){return x < 0 ? -x : x;}
char gc()
{
char c = getchar();
while(c > 'Z' || c < 'A') c = getchar();
return c;
}
struct Splay//LinkCutTree
{
int tot;
struct node
{
int val,ch[2],f;
bool r;//翻转标记
}t[MAXN];
inline bool nroot(int x)//判断节点是否为一个Splay的根
{
return t[t[x].f].ch[0] == x || t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x;
//如果连的是轻边,他的父亲的儿子里就没有它
}
inline void pushr(int x)//翻转操作
{
swap(t[x].ch[0],t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r ^= 1;
}
inline void up(int x)
{
t[x].val = t[t[x].ch[0]].val + t[t[x].ch[1]].val + v[x];
}
inline void down(int x)
{
if(t[x].r)
{
if(t[x].ch[0]) pushr(t[x].ch[0]);
if(t[x].ch[1]) pushr(t[x].ch[1]);
t[x].r = 0;
}
}
inline bool chk(int x)
{
return (t[t[x].f].ch[1] == x);
}
inline void rotate(int x)
{
int y = t[x].f;
int z = t[y].f;
int k = chk(x);
int w = t[x].ch[k^1];
t[y].ch[k] = w;
if(w) t[w].f = y;
if(nroot(y)) t[z].ch[chk(y)] = x;
t[x].f = z;
t[x].ch[k^1] = y;
t[y].f = x;
up(y);
up(x);
}
inline void splay(int x,int to = 0)
{
int y = x,z = 0;
st[++z] = y;
while(nroot(y)) st[++z] = y = t[y].f;
while(z) down(st[z--]);
while(nroot(x))
{
y = t[x].f;
if(nroot(y))
{
if(chk(x) != chk(y)) rotate(x);
else rotate(y);
}
rotate(x);
}
up(x);
}
inline void access(int x)//访问
{
for(int y = 0; x ;x = t[y = x].f)
{
splay(x);
t[x].ch[1] = y;
up(x);
}
}
inline void makeroot(int x)//换根
{
access(x);
splay(x);
pushr(x);
}
inline int findroot(int x)//找根(原树中) ,就是最小的那个
{
access(x);
splay(x);
while(t[x].ch[0]) down(x),x = t[x].ch[0];
splay(x) ;
return x;
}
inline int dis(int x,int y)//询问路径,把x和y搞到一棵Splay里面,再乱搞
{
makeroot(x);
access(y);
splay(y);
return t[y].val;
}
bool qconnect(int x,int y)
{
makeroot(x);
if(findroot(y) == x) return 1;
return 0;
}
void link(int x,int y)//连边
{
if(!qconnect(x,y)) t[x].f = y;
}
inline void cut(int x,int y)//删边
{
if(qconnect(x,y) && t[y].f == x && !t[y].ch[0])//保证它们相连
{
t[y].f = t[x].ch[1] = 0;
up(x);
}
}
}lct;
int main()
{
// freopen(".in","r",stdin);
// freopen(".out","w",stdout);
n = Read();
for(register int Q = Read(); Q ;-- Q)
{
char c = gc();
if(c == 'C') lct.link(Read(),Read());
else if(c == 'D') lct.cut(Read(),Read());
else
{
if(lct.qconnect(Read(),Read())) printf("Yes
");
else printf("No
");
}
}
return 0;
}