In one well-known algorithm of finding the k-th order statistics we should divide all elements into groups of five consecutive elements and find the median of each five. A median is called the middle element of a sorted array (it's the third largest element for a group of five). To increase the algorithm's performance speed on a modern video card, you should be able to find a sum of medians in each five of the array.
A sum of medians of a sorted k-element set S = {a1, a2, ..., ak}, where a1 < a2 < a3 < ... < ak, will be understood by as
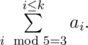
The 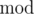 operator stands for taking the remainder, that is
operator stands for taking the remainder, that is 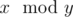 stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
stands for the remainder of dividing x by y.
To organize exercise testing quickly calculating the sum of medians for a changing set was needed.
The first line contains number n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of operations performed.
Then each of n lines contains the description of one of the three operations:
- add x — add the element x to the set;
- del x — delete the element x from the set;
- sum — find the sum of medians of the set.
For any add x operation it is true that the element x is not included in the set directly before the operation.
For any del x operation it is true that the element x is included in the set directly before the operation.
All the numbers in the input are positive integers, not exceeding 109.
For each operation sum print on the single line the sum of medians of the current set. If the set is empty, print 0.
Please, do not use the %lld specificator to read or write 64-bit integers in C++. It is preferred to use the cin, cout streams (also you may use the %I64d specificator).
6
add 4
add 5
add 1
add 2
add 3
sum
3
14
add 1
add 7
add 2
add 5
sum
add 6
add 8
add 9
add 3
add 4
add 10
sum
del 1
sum
11
13
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int MAX_N=1e5+5; #define X first #define Y second //BIT int bit[MAX_N], rb; int sum(int i){ int s=0; while(i){ s+=bit[i]; i-=i&-i; } return s; } void add(int i, int x){ while(i<=rb){ bit[i]+=x; i+=i&-i; } } typedef pair<int, int> P; P q[MAX_N]; int val[MAX_N]; char type[MAX_N][5]; int lisan(int N){ int v; for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ scanf("%s", type[i]); switch(*type[i]){ case 'a': case 'd': scanf("%d", &v); q[i]=P(v, i); break; case 's': q[i]=P(0, i); //TLE在这里 break; } } sort(q, q+N); int ord=0; for(int i=0; i<N; ord++){ val[ord]=q[i].X; do{ q[i].X=ord; i++; }while(i<N&&q[i].X==val[ord]); } return ord; } bool cmp(const P &a, const P &b){ return a.Y<b.Y; } //ST struct node{ int l, r, tag; ll sum[5]; int mid(){return (l+r)>>1;} }T[MAX_N<<2]; void shift(int id, int cnt){ cnt%=5; if(!cnt) return; ll tmp[5]; memcpy(tmp, T[id].sum, sizeof(tmp)); for(int i=0; i<5; i++){ int nt=(i+cnt+5)%5; T[id].sum[nt]=tmp[i]; } } void pushdown(int id){ node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<1], &rch=T[id<<1|1]; lch.tag+=now.tag, rch.tag+=now.tag; shift(id<<1, now.tag); shift(id<<1|1, now.tag); now.tag=0; //error prone } void unite(int id){ node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<1], &rch=T[id<<1|1]; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) now.sum[i]=lch.sum[i]+rch.sum[i]; } void build(int id, int l, int r){ node &now=T[id]; T[id].l=l, T[id].r=r, T[id].tag=0; memset(T[id].sum, 0, sizeof(T[id].sum)); if(l==r) return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; build(id<<1, l, mid); build(id<<1|1, mid+1, r); } void insert(int id, int pos, int ord, int v){ node &now=T[id]; if(now.l==now.r){ now.sum[ord%5]+=v; } else{ pushdown(id); if(pos<=now.mid()) insert(id<<1, pos, ord, v); else insert(id<<1|1, pos, ord, v); unite(id); } } void shift(int id, int lb, int cnt){ if(lb>rb) return; node &now=T[id]; if(now.l>=lb){ shift(id, cnt); now.tag+=cnt; } else{ pushdown(id); if(lb<=now.mid()) shift(id<<1, lb, cnt); shift(id<<1|1, lb, cnt); unite(id); } } int main(){ //freopen("in", "r", stdin); int N; scanf("%d", &N); rb=lisan(N); build(1, 1, rb); sort(q, q+N, cmp); for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ if(*type[i]=='a'){ int ord=sum(q[i].X)+1; add(q[i].X, 1); shift(1, q[i].X+1, 1); insert(1, q[i].X, ord, val[q[i].X]); } else if(*type[i]=='d'){ int ord=sum(q[i].X); add(q[i].X, -1); shift(1, q[i].X+1, -1); insert(1, q[i].X, ord, -val[q[i].X]); } else{ printf("%I64d ", T[1].sum[3]); } } return 0; }
其实我已经考虑到这种无sum询问的输入,但没注意到它会导致我的代码TLE
AC version
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; const int MAX_N=1e5+5; #define X first #define Y second //BIT int bit[MAX_N], rb; int sum(int i){ int s=0; while(i){ s+=bit[i]; i-=i&-i; } return s; } void add(int i, int x){ while(i<=rb){ bit[i]+=x; i+=i&-i; } } typedef pair<int, int> P; P q[MAX_N]; int val[MAX_N]; char type[MAX_N][5]; int lisan(int N){ int v; for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ scanf("%s", type[i]); switch(*type[i]){ case 'a': case 'd': scanf("%d", &v); q[i]=P(v, i); break; case 's': q[i]=P(INT_MAX, i); //注意这里的改动 break; } } sort(q, q+N); int ord=0; for(int i=0; i<N;){ ++ord; val[ord]=q[i].X; do{ q[i].X=ord; i++; }while(i<N&&q[i].X==val[ord]); } return ord; } bool cmp(const P &a, const P &b){ return a.Y<b.Y; } //ST struct node{ int l, r, tag; ll sum[5]; int mid(){return (l+r)>>1;} }T[MAX_N<<2]; void shift(int id, int cnt){ cnt%=5; if(!cnt) return; ll tmp[5]; memcpy(tmp, T[id].sum, sizeof(tmp)); for(int i=0; i<5; i++){ int nt=(i+cnt+5)%5; T[id].sum[nt]=tmp[i]; } } void pushdown(int id){ node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<1], &rch=T[id<<1|1]; lch.tag+=now.tag, rch.tag+=now.tag; shift(id<<1, now.tag); shift(id<<1|1, now.tag); now.tag=0; //error prone } void unite(int id){ node &now=T[id], &lch=T[id<<1], &rch=T[id<<1|1]; for(int i=0; i<5; i++) now.sum[i]=lch.sum[i]+rch.sum[i]; } void build(int id, int l, int r){ node &now=T[id]; T[id].l=l, T[id].r=r, T[id].tag=0; memset(T[id].sum, 0, sizeof(T[id].sum)); if(l==r) return; int mid=(l+r)>>1; build(id<<1, l, mid); build(id<<1|1, mid+1, r); } void insert(int id, int pos, int ord, int v){ node &now=T[id]; if(now.l==now.r){ now.sum[ord%5]+=v; } else{ pushdown(id); if(pos<=now.mid()) insert(id<<1, pos, ord, v); else insert(id<<1|1, pos, ord, v); unite(id); } } void shift(int id, int lb, int cnt){ if(lb>rb) return; node &now=T[id]; if(now.l>=lb){ shift(id, cnt); now.tag+=cnt; } else{ pushdown(id); if(lb<=now.mid()) shift(id<<1, lb, cnt); shift(id<<1|1, lb, cnt); unite(id); } } int main(){ //freopen("in", "r", stdin); int N; scanf("%d", &N); rb=lisan(N); build(1, 1, rb); sort(q, q+N, cmp); for(int i=0; i<N; i++){ if(*type[i]=='a'){ int ord=sum(q[i].X)+1; add(q[i].X, 1); shift(1, q[i].X+1, 1); insert(1, q[i].X, ord, val[q[i].X]); } else if(*type[i]=='d'){ int ord=sum(q[i].X); add(q[i].X, -1); shift(1, q[i].X+1, -1); insert(1, q[i].X, ord, -val[q[i].X]); } else{ printf("%I64d ", T[1].sum[3]); } } return 0; }