Minimum Sum
Time Limit: 16000/8000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 3611 Accepted Submission(s): 829
Problem Description
You are given N positive integers, denoted as x0, x1 ... xN-1. Then give you some intervals [l, r]. For each interval, you need to find a number x to make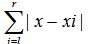 as
small as possible!
as
small as possible!
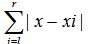 as
small as possible!
as
small as possible!
Input
The first line is an integer T (T <= 10), indicating the number of test cases. For each test case, an integer N (1 <= N <= 100,000) comes first. Then comes N positive integers x (1 <= x <= 1,000, 000,000) in the next line. Finally, comes an integer Q (1 <=
Q <= 100,000), indicting there are Q queries. Each query consists of two integers l, r (0 <= l <= r < N), meaning the interval you should deal with.
Output
For the k-th test case, first output “Case #k:” in a separate line. Then output Q lines, each line is the minimum value of 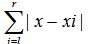 . Output a blank line after every
test case.
. Output a blank line after every
test case.
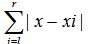 . Output a blank line after every
test case.
. Output a blank line after every
test case.
Sample Input
2
5
3 6 2 2 4
2
1 4
0 2
2
7 7
2
0 1
1 1
Sample Output
Case #1:
6
4
Case #2:
0
0
Author
standy
Source
题意:
给你一个区间,让你找出其中一个值,让所有值与它相减的绝对值的和最小。
思路:
于是成了找出其中的中间值减去最小,最开始简单粗暴地超时。然后发现求绝对值有点麻烦,于是在建树和查找的过程中找出比中间值小的数的和,然后分类计算吧。
感觉最开始没有考虑好方案,太随意了。
/*
hdu 3473
最开始直接算TL,然后发现由于是计算绝对值,在建树的时候需要记录比你查找的值小的和,
然后分开计算即可
*/
#include <functional>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cmath>
#include <Map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100010;
int tree[20][maxn];
int sorted[maxn];
int toleft[20][maxn];
ll sum[maxn];
ll lsum[20][maxn];
ll tsum;
void build(int l,int r,int dep) //模拟快排 并记录左树中比i小的个数
{
if(l == r)
return;
int mid = (l+r)>>1;
int same = mid-l+1;//可能有很多值与中间那个相等,但不一定被分到左边
for(int i = l;i <= r;i++)
{
if(tree[dep][i] < sorted[mid])
same--;
}
int lpos = l;
int rpos = mid+1;
for(int i = l;i <= r;i++)
{
if(tree[dep][i] < sorted[mid]){
tree[dep+1][lpos++] = tree[dep][i];
lsum[dep][i] = lsum[dep][i-1] + tree[dep][i];
}
else if(tree[dep][i] == sorted[mid] && same > 0)
{
tree[dep+1][lpos++] = tree[dep][i];
lsum[dep][i] = lsum[dep][i-1] + tree[dep][i];
same --;
}
else
{
tree[dep+1][rpos++] = tree[dep][i];
lsum[dep][i] = lsum[dep][i-1];
}
toleft[dep][i] = toleft[dep][l-1] + lpos -l;
}
build(l,mid,dep+1);
build(mid+1,r,dep+1);
}
int query(int L,int R,int l,int r,int dep,int k)
{
if(l == r)
return tree[dep][l];
int mid = (L+R)>>1;
int cnt = toleft[dep][r]-toleft[dep][l-1]; //所查找区间放在左树中的个数
if(cnt >= k)
{ //得到l左边放到左子树的个数,加上L即是开始位置
int lpos = L+toleft[dep][l-1]-toleft[dep][L-1];
int rpos = lpos+cnt-1;
return query(L,mid,lpos,rpos,dep+1,k);
}
else
{ //R-r可以得出后面空出了多少位置
int rpos = r+toleft[dep][R]-toleft[dep][r];
int lpos = rpos-(r-l-cnt);
tsum += lsum[dep][r] - lsum[dep][l-1];
return query(mid+1,R,lpos,rpos,dep+1,k-cnt);
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m,T;
int cas = 1;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i = 1;i <= n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&sorted[i]);
sum[i] = sum[i-1]+sorted[i];
tree[0][i] = sorted[i];
}
sort(sorted+1,sorted+n+1);
build(1,n,0);
scanf("%d",&m);
int l,r;
printf("Case #%d:
",cas++);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
l++;r++;tsum = 0;
ll k =(r-l)/2+1;
ll ans = 0;
ll aver = query(1,n,l,r,0,k);
ans = sum[r]-sum[l-1]-aver*(r-l+1-k)-tsum-aver;
ans += (k-1)*aver-tsum;
printf("%I64d
",ans);
}
puts("");
}
return 0;
}