0.目录
1.顶层父类的创建
2.类族结构的进化
3.小结
参考前文传送门:
C++解析(29):类型识别
C++解析(31):自定义内存管理(完)
C++解析-外传篇(1):异常处理深度解析
C++解析-外传篇(2):函数的异常规格说明
C++解析-外传篇(3):动态内存申请的结果
1.顶层父类的创建
当代软件架构实践中的经验:
- 尽量使用单重继承的方式进行系统设计
- 尽量保持系统中只存在单一的继承树
- 尽量使用组合关系代替继承关系
不幸的事实:
- C++语言的灵活性使得代码中可以存在多个继承树
- C++编译器的差异使得同样的代码可能表现不同的行为
(编译器的差异:new操作如果失败会发生什么?)
创建 StLib::Object 类的意义:
- 遵循经典设计准则,所有数据结构都继承自Object类
- 定义动态内存申请的行为,提高代码的移植性
顶层父类的接口定义:

示例——顶层父类的创建:
创建Object.h
#ifndef OBJECT_H
#define OBJECT_H
namespace StLib
{
class Object
{
public:
void* operator new (size_t size) throw();
void operator delete (void* p);
void* operator new[] (size_t size) throw();
void operator delete[] (void* p);
virtual ~Object() = 0;
};
}
#endif // OBJECT_H
实现Object.cpp
#include "Object.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
void* Object::operator new (size_t size) throw()
{
cout << "Object::operator new: " << size << endl;
return malloc(size);
}
void Object::operator delete (void* p)
{
cout << "Object::operator delete: " << p << endl;
free(p);
}
void* Object::operator new[] (size_t size) throw()
{
return malloc(size);
}
void Object::operator delete[] (void* p)
{
free(p);
}
Object::~Object()
{
}
}
main.cpp测试
#include <iostream>
#include "Object.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace StLib;
class Test : public Object
{
public:
int i;
int j;
};
class Child : public Test
{
public:
int k;
};
int main()
{
Object* obj1 = new Test();
Object* obj2 = new Child();
cout << "obj1 = " << obj1 << endl;
cout << "obj2 = " << obj2 << endl;
// ... ...
delete obj1;
delete obj2;
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
Object::operator new: 16
Object::operator new: 24
obj1 = 0000025D8EA46F00
obj2 = 0000025D8EA42D50
Object::operator delete: 0000025D8EA46F00
Object::operator delete: 0000025D8EA42D50
2.类族结构的进化
遵循经典设计准则——StLib中的所有类位于单一的继承树:
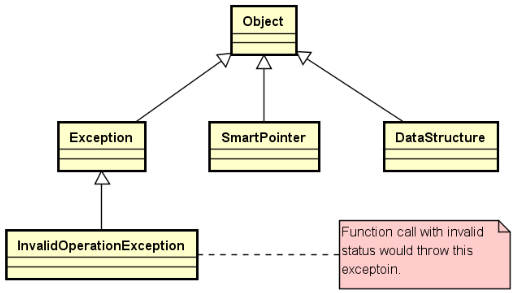
改进的关键点:
- Exception 类继承自 Object 类
- 堆空间中创建异常对象失败时,返回 NULL 指针
- 新增 InvalidOperationException 异常类
- 成员函数调用时,如果状态不正确则抛出异常
- SmartPointer 类继承自 Object 类
- 堆空间中创建智能指针对象失败时,返回 NULL 指针
最终Object类:
Object.h
#ifndef OBJECT_H
#define OBJECT_H
namespace StLib
{
class Object
{
public:
void* operator new (size_t size) throw();
void operator delete (void* p);
void* operator new[] (size_t size) throw();
void operator delete[] (void* p);
virtual ~Object() = 0;
};
}
#endif // OBJECT_H
Object.cpp
#include "Object.h"
#include <cstdlib>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
void* Object::operator new (size_t size) throw()
{
return malloc(size);
}
void Object::operator delete (void* p)
{
free(p);
}
void* Object::operator new[] (size_t size) throw()
{
return malloc(size);
}
void Object::operator delete[] (void* p)
{
free(p);
}
Object::~Object()
{
}
}
改进SmartPointer类:
SmartPointer.h
#ifndef SMARTPOINTER_H
#define SMARTPOINTER_H
#include "Object.h"
namespace StLib
{
template <typename T>
class SmartPointer : public Object
{
protected:
T* m_pointer;
public:
SmartPointer(T* p = NULL)
{
m_pointer = p;
}
SmartPointer(const SmartPointer<T>& obj)
{
m_pointer = obj.m_pointer;
const_cast<SmartPointer<T>&>(obj).m_pointer = NULL;
}
SmartPointer<T>& operator= (const SmartPointer<T>& obj)
{
if( this != &obj )
{
delete m_pointer;
m_pointer = obj.m_pointer;
const_cast<SmartPointer<T>&>(obj).m_pointer = NULL;
}
return *this;
}
T* operator-> ()
{
return m_pointer;
}
T& operator* ()
{
return *m_pointer;
}
bool isNull()
{
return (m_pointer == NULL);
}
T* get()
{
return m_pointer;
}
~SmartPointer()
{
delete m_pointer;
}
};
}
#endif // SMARTPOINTER_H
改进Exception类:
Exception.h
#ifndef EXCEPTION_H
#define EXCEPTION_H
#include "Object.h"
using namespace std;
namespace StLib
{
// 使用宏简化代码
#define THROW_EXCEPTION(e, m) (throw e(m, __FILE__, __LINE__))
class Exception : public Object
{
protected:
char* m_message;
char* m_location;
void init(const char* message, const char* file, int line);
public:
Exception(const char* message);
Exception(const char* file, int line);
Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line);
Exception(const Exception& e);
Exception& operator= (const Exception& e);
virtual const char* message() const;
virtual const char* location() const;
virtual ~Exception() = 0;
};
/*
* 计算异常
*/
class ArithmeticException : public Exception
{
public:
ArithmeticException() : Exception(0) { }
ArithmeticException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
ArithmeticException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
ArithmeticException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
ArithmeticException(const ArithmeticException& e) : Exception(e) { }
ArithmeticException& operator= (const ArithmeticException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 空指针异常
*/
class NullPointerException : public Exception
{
public:
NullPointerException() : Exception(0) { }
NullPointerException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
NullPointerException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
NullPointerException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
NullPointerException(const NullPointerException& e) : Exception(e) { }
NullPointerException& operator= (const NullPointerException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 越界异常
*/
class IndexOutOfBoundsException : public Exception
{
public:
IndexOutOfBoundsException() : Exception(0) { }
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
IndexOutOfBoundsException(const NullPointerException& e) : Exception(e) { }
IndexOutOfBoundsException& operator= (const NullPointerException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 内存不足异常
*/
class NoEnoughMemoryException : public Exception
{
public:
NoEnoughMemoryException() : Exception(0) { }
NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
NoEnoughMemoryException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
NoEnoughMemoryException(const NoEnoughMemoryException& e) : Exception(e) { }
NoEnoughMemoryException& operator= (const NoEnoughMemoryException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 参数错误异常
*/
class InvalidParameterException : public Exception
{
public:
InvalidParameterException() : Exception(0) { }
InvalidParameterException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
InvalidParameterException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
InvalidParameterException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
InvalidParameterException(const InvalidParameterException& e) : Exception(e) { }
InvalidParameterException& operator= (const InvalidParameterException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
/*
* 非法操作异常
*/
class InvalidOperationException : public Exception
{
public:
InvalidOperationException() : Exception(0) { }
InvalidOperationException(const char* message) : Exception(message) { }
InvalidOperationException(const char* file, int line) : Exception(file, line) { }
InvalidOperationException(const char* message, const char* file, int line) : Exception(message, file, line) { }
InvalidOperationException(const InvalidOperationException& e) : Exception(e) { }
InvalidOperationException& operator= (const InvalidOperationException& e)
{
Exception::operator= (e);
return *this;
}
};
}
#endif // EXCEPTION_H
Exception.cpp
#include "Exception.h"
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
namespace StLib
{
void Exception::init(const char* message, const char* file, int line)
{
/* message指向的字符串有可能在栈上,有可能在堆空间,还有可能在全局数据区
* strdup()将字符串复制一份到堆空间中
* file:发生异常的文件名
* line:发生异常的行号
* m_location的长度加2,一个给":",一个给"�"
*/
m_message = strdup(message);
if( file != NULL )
{
char sl[16] = {0};
itoa(line, sl, 10);
m_location = static_cast<char*>(malloc(strlen(file) + strlen(sl) + 2));
if( m_location != NULL )
{
m_location = strcpy(m_location, file);
m_location = strcat(m_location, ":");
m_location = strcat(m_location, sl);
}
}
else
{
m_location = NULL;
}
}
Exception::Exception(const char *message)
{
init(message, NULL, 0);
}
Exception::Exception(const char* file, int line)
{
init(NULL, file, line);
}
Exception::Exception(const char* message, const char* file, int line)
{
init(message, file, line);
}
Exception::Exception(const Exception& e)
{
m_message = strdup(e.m_message);
m_location = strdup(e.m_location);
}
Exception &Exception::operator= (const Exception& e)
{
if( this != &e )
{
free(m_message);
free(m_location);
m_message = strdup(e.m_message);
m_location = strdup(e.m_location);
}
return *this;
}
const char* Exception::message() const
{
return m_message;
}
const char* Exception::location() const
{
return m_location;
}
Exception::~Exception()
{
free(m_message);
free(m_location);
}
}
StLib 的开发方式和注意事项:
- 迭代开发
- 每次完成一个小的目标,持续开发,最终打造可复用类库
- 单一继承树
- 所有类都继承自Object,规范堆对象创建时的行为
- 只抛异常,不处理异常
- 使用 THROW_ EXCEPTION 抛出异常,提高可移植性
- 弱耦合性
- 尽量不使用标准库中的类和函数,提高可移植性
3.小结
- Object类是StLib中数据结构类的顶层父类
- Object类用于统一动态内存申请的行为
- 在堆中创建Object子类的对象,失败时返回NULL值
- Object类为纯虚父类,所有子类都能进行动态类型识别
第一阶段学习总结:
- 数据结构与算法之间的关系
- 算法效率的度量方法
- StLib的基础设施构建
- 顶层父类
- 智能指针
- 异常类